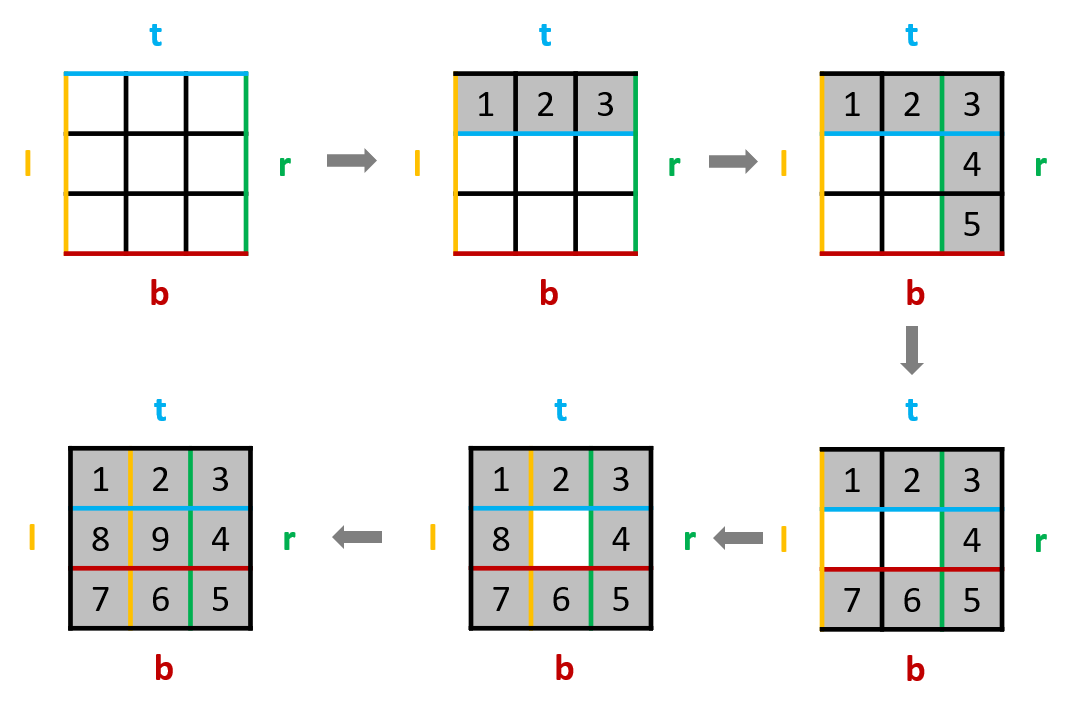
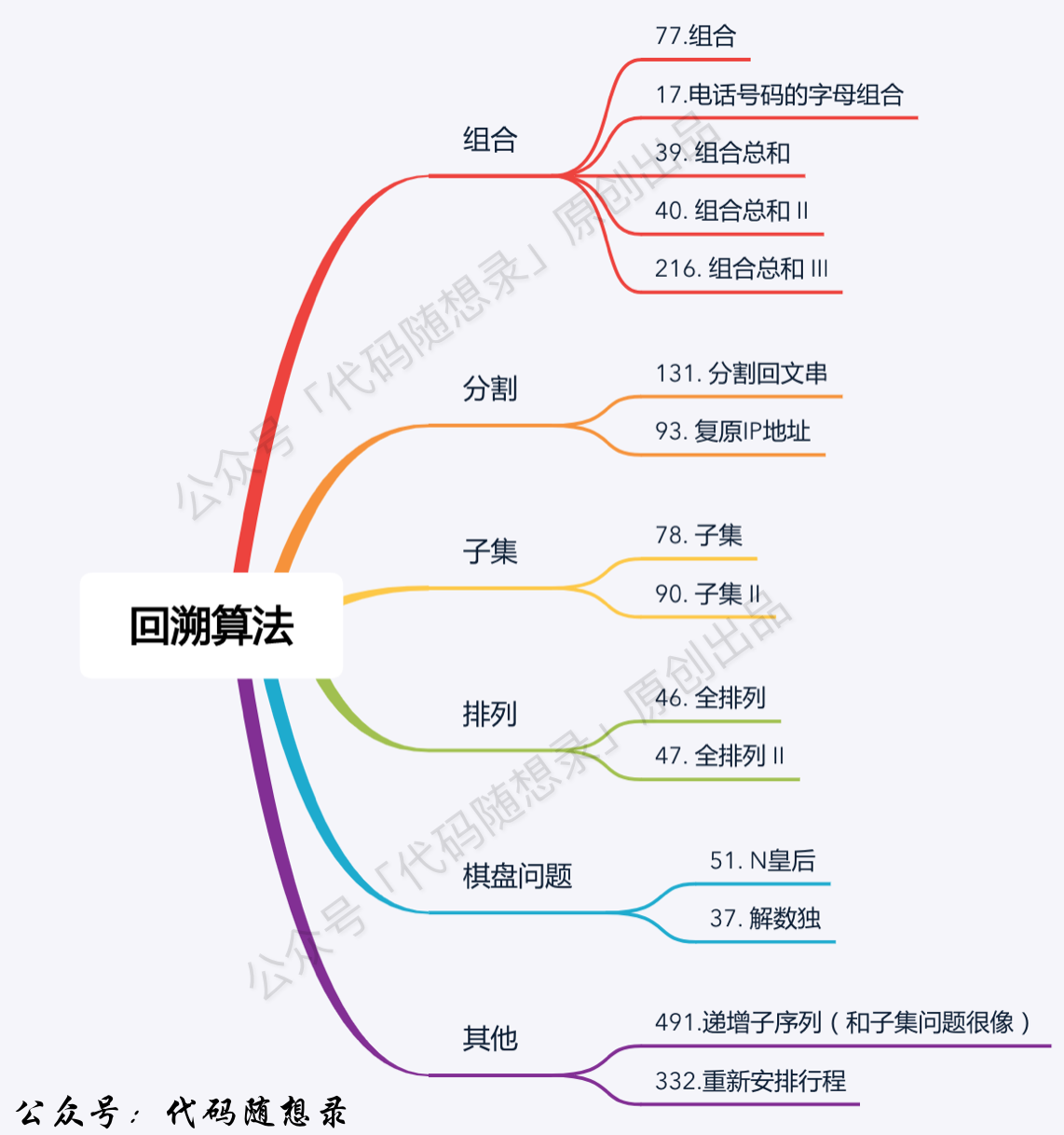
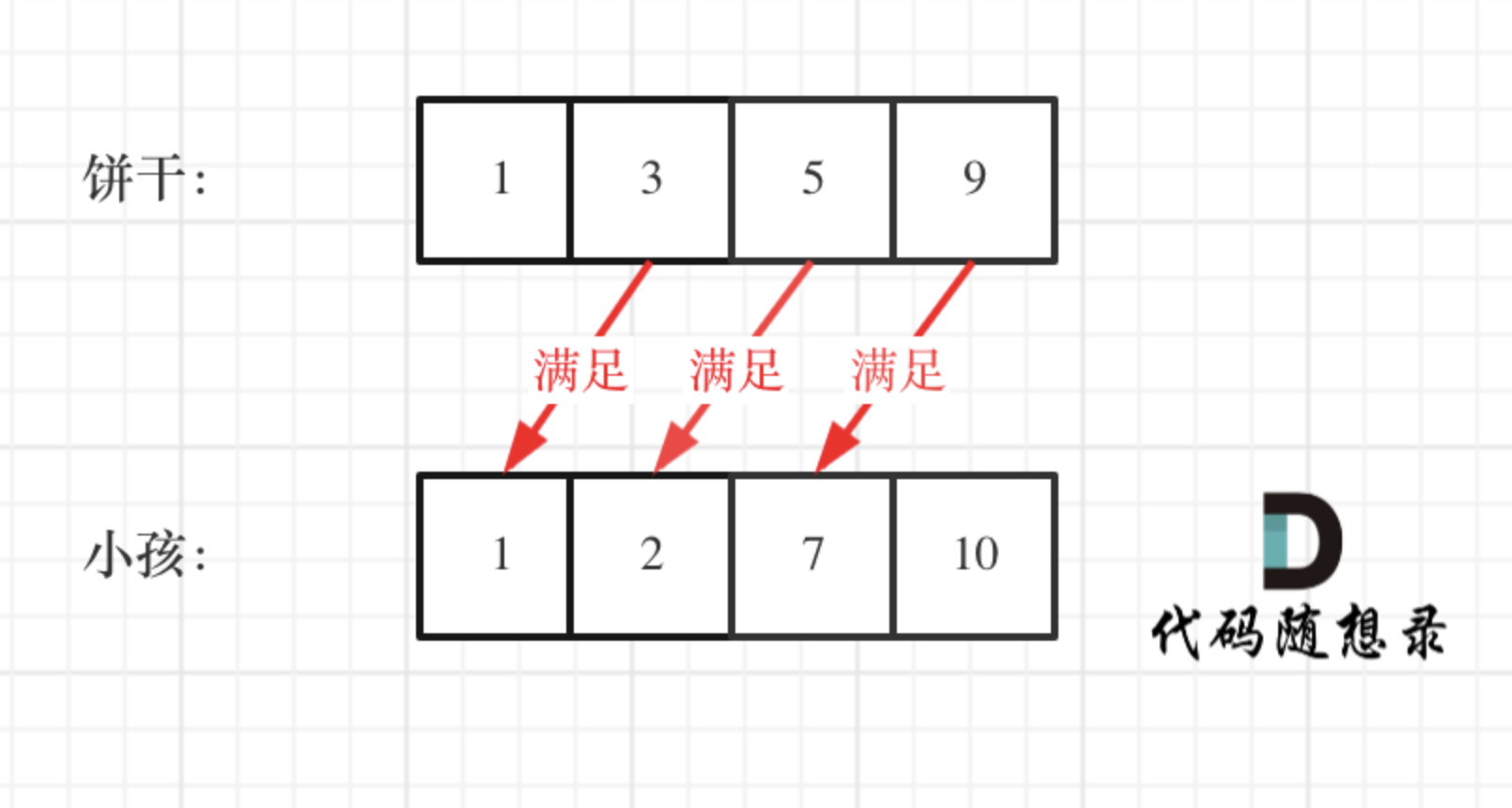
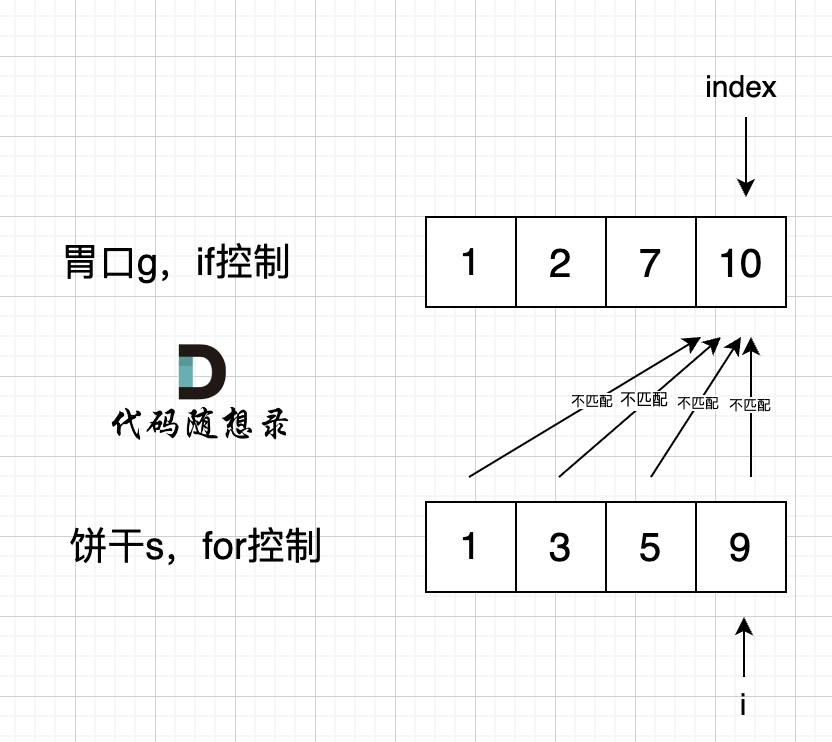
1. 数组 1.1 二分查找 通用模板 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution {public :int search (vector<int >& nums, int target) {int left = 0 ;int right = nums.size() - 1 ; while (left <= right) { int middle = left + ((right - left) / 2 );if (nums[middle] > target) {1 ; else if (nums[middle] < target) {1 ; else { return middle; return -1 ;
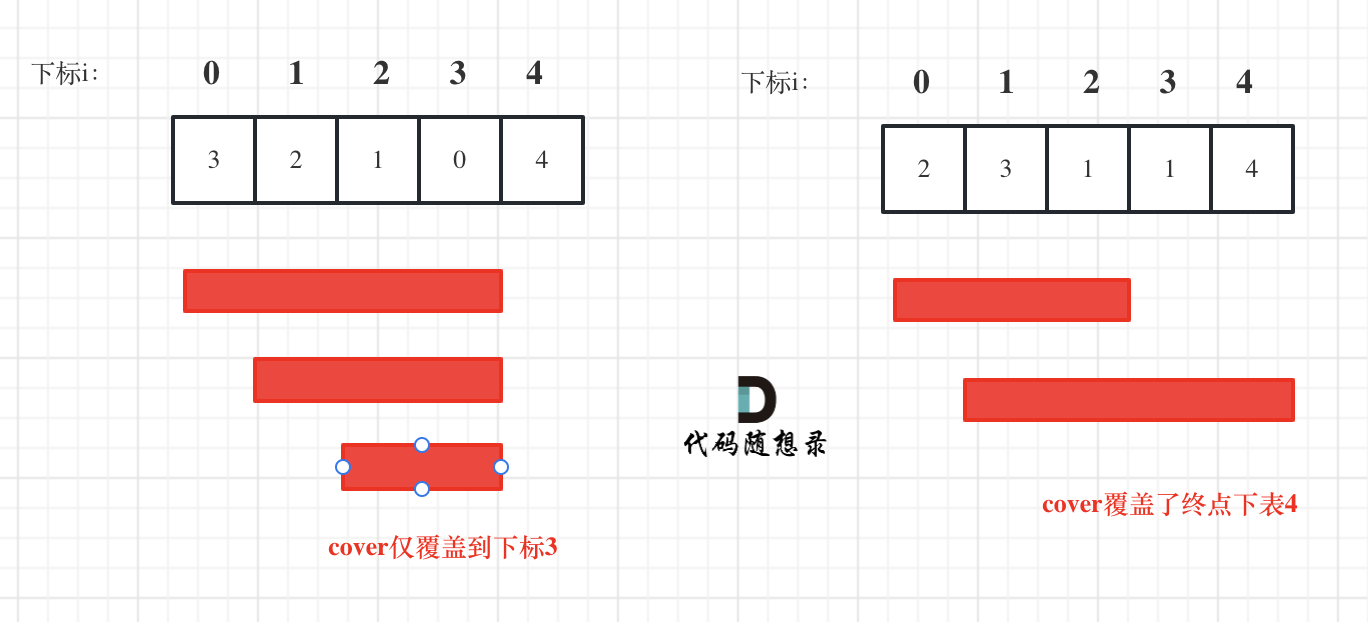
左右边界(lowerbound&upperbound) 当寻找左边界/右边界时,设置对应的标识(leftBorder = -1),寻找左边界时,条件为>=,右边界为<=,在对应条件的判断中更新边界标识符变量,同时更新l或者r寻找下一个位置是否满足边界条件。
lowerbound(x):大于等于x(≥x)的第一个数的下标位置
upperbound(x):大于x(>x)的第一个数的下标位置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public static int lowerBound (int [] arr, int target) {int left = 0 , right = arr.length;while (left < right) {int mid = left + (right - left) / 2 ;if (arr[mid] < target) {1 ;else {return left;public static int upperBound (int [] arr, int target) {int left = 0 , right = arr.length;while (left < right) {int mid = left + (right - left) / 2 ;if (arr[mid] <= target) {1 ;else {return left;
###开方数
同样是寻找<=某个值的最大值,即upperbound的计算。(可以寻找其他解法)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution {public int mySqrt (int x) {int l = 0 ; int r = x;int ans = -1 ;while (l <= r) {int mid = l + (r - l)/2 ;if ((long )mid * mid <= x) {1 ;else {1 ;return ans;
>=、>、<=、<判断模板
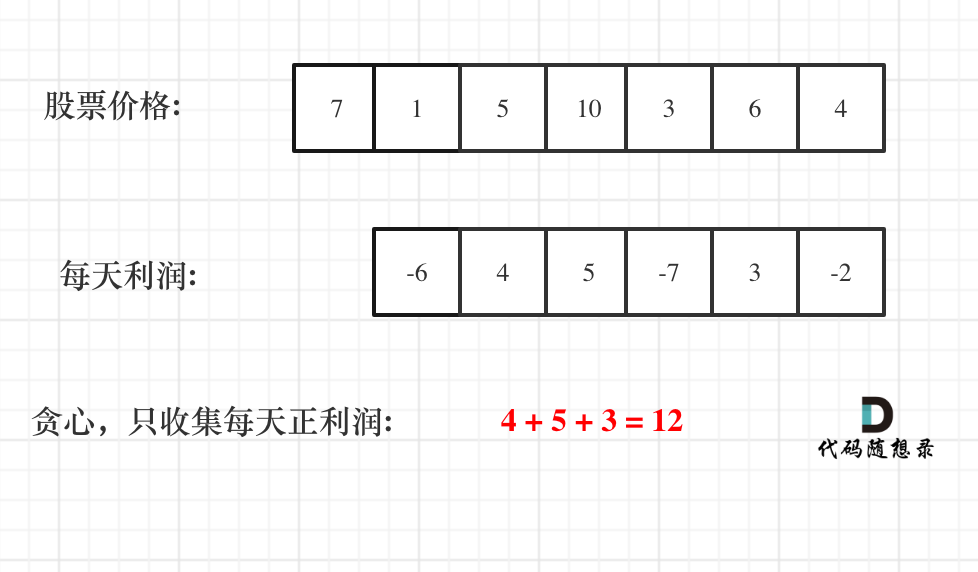
1.2 移除元素 1.3 有序数组的平方(双指针) 1.4 长度最小的子数组(滑动窗口) 滑动窗口
接下来就开始介绍数组操作中另一个重要的方法:滑动窗口。
所谓滑动窗口,就是不断的调节子序列的起始位置和终止位置,从而得出我们要想的结果。
在暴力解法中,是一个for循环滑动窗口的起始位置,一个for循环为滑动窗口的终止位置,用两个for循环 完成了一个不断搜索区间的过程。
那么滑动窗口如何用一个for循环来完成这个操作呢。
首先要思考 如果用一个for循环,那么应该表示 滑动窗口的起始位置,还是终止位置。
如果只用一个for循环来表示 滑动窗口的起始位置,那么如何遍历剩下的终止位置?
此时难免再次陷入 暴力解法的怪圈。
所以 只用一个for循环,那么这个循环的索引,一定是表示 滑动窗口的终止位置。
在本题中实现滑动窗口,主要确定如下三点:
窗口内是什么?
如何移动窗口的起始位置?
如何移动窗口的结束位置?
窗口就是 满足其和 ≥ s 的长度最小的 连续 子数组。
窗口的起始位置如何移动:如果当前窗口的值大于等于s了,窗口就要向前移动了(也就是该缩小了)。
窗口的结束位置如何移动:窗口的结束位置就是遍历数组的指针,也就是for循环里的索引。
滑动窗口的精妙之处在于根据当前子序列和大小的情况,不断调节子序列的起始位置。从而将O(n^2)暴力解法降为O(n)
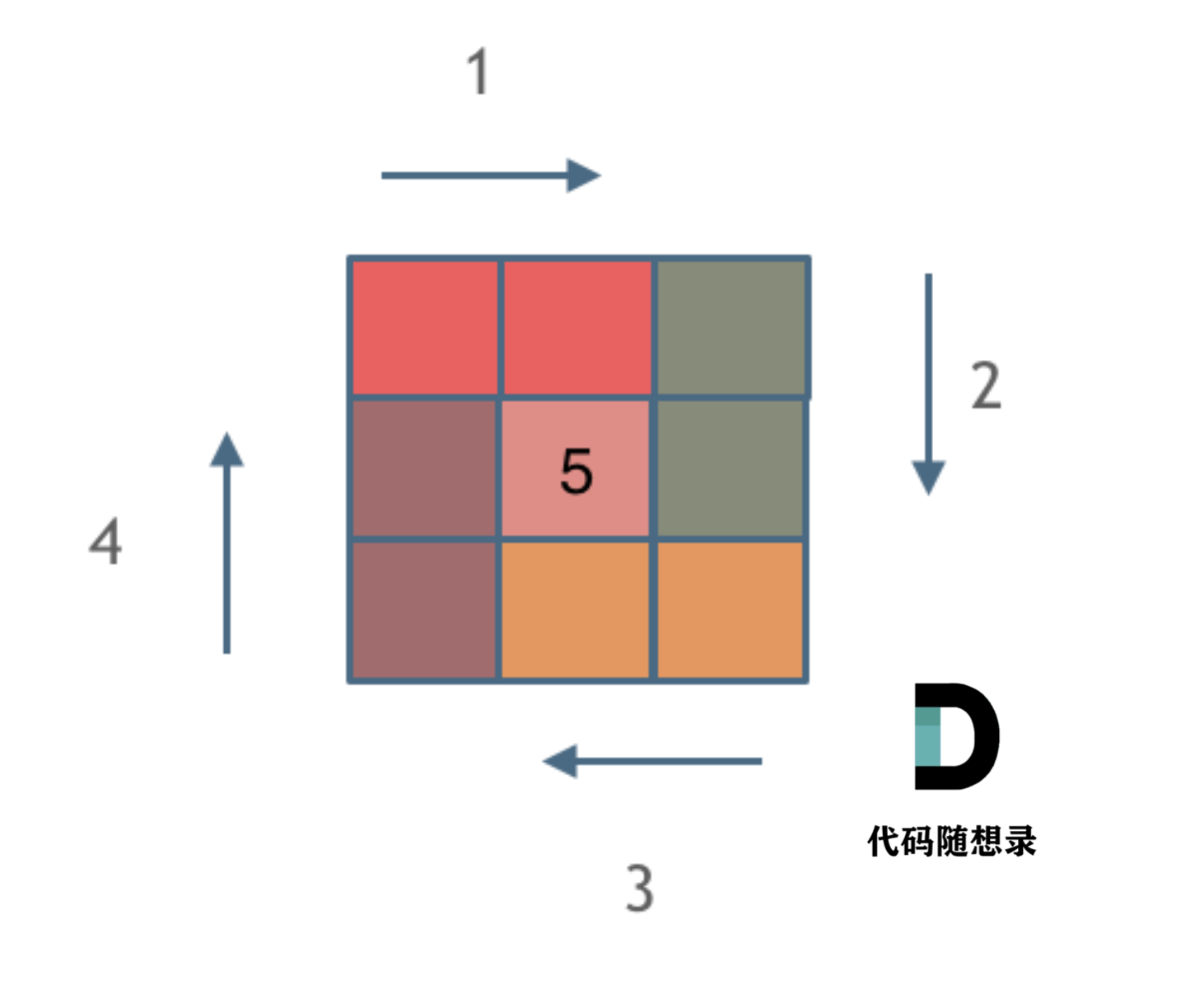
1.5 螺旋矩阵(模拟操作) 思路一:
初始化一个 n×n 大小的矩阵 mat,然后模拟整个向内环绕的填入过程:
定义当前左右上下边界 l,r,t,b,初始值 num = 1,迭代终止值 tar = n * n;
当 num <= tar 时,始终按照 从左到右 从上到下 从右到左 从下到上 填入顺序循环,每次填入后:
执行 num += 1:得到下一个需要填入的数字;
更新边界:例如从左到右填完后,上边界 t += 1,相当于上边界向内缩 1。
使用num <= tar而不是l < r || t < b作为迭代条件,是为了解决当n为奇数时,矩阵中心数字无法在迭代过程中被填充的问题。
最终返回 mat 即可。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 public int [][] generateMatrix(int n) {int left = 0 , right = n-1 , top = 0 , bottom = n-1 ;int count = 1 , target = n * n;int [][] res = new int [n][n];while (count <= target){for (int j = left; j <= right; j++) res[top][j] = count++;for (int i = top; i <=bottom; i++) res[i][right] = count++;for (int j = right; j >= left; j--) res[bottom][j] = count++;for (int i = bottom; i >= top; i--) res[i][left] = count++;return res;
思路二:
模拟顺时针画矩阵的过程:
填充上行从左到右
填充右列从上到下
填充下行从右到左
填充左列从下到上
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 class Solution {public int [][] generateMatrix(int n) {int [][] matrix= new int [n][n];int count = 1 ;int loop = n/2 ;int offset = 1 ;int x = 0 , y = 0 ;while (loop-- >= 0 ) {int i = x, j = y;for (;j < n - offset; j++) {for (;i < n - offset; i++) {for (;j > y; j--) {for (;i > x; i--) {if (n % 2 == 1 ) {2 ][n/2 ] = count;return matrix;
leetcode904——水果成篮(滑动窗口)
最小滑窗模板:给定数组 nums,定义滑窗的左右边界 i, j,求满足某个条件的滑窗的最小长度。
1 2 3 4 5 6 while j < len(nums):while 满足条件:while 内更新!)1 (最大程度的压缩i,使得滑窗尽可能的小)1
最大滑窗模板:给定数组 nums,定义滑窗的左右边界 i, j,求满足某个条件的滑窗的最大长度。
1 2 3 4 5 6 while j < len(nums):while 不满足条件:1 (最保守的压缩i,一旦满足条件了就退出压缩i的过程,使得滑窗尽可能的大)while 外更新!)1
是的,关键的区别在于,最大滑窗是在迭代右移右边界的过程中更新结果,而最小滑窗是在迭代右移左边界的过程中更新结果。因此虽然都是滑窗,但是两者的模板和对应的贪心思路并不一样,而真正理解后就可以在lc.76,lc.904,lc.3, lc.1004写出非常无脑的代码。
需要寻找一个窗口,该窗口中只包含两种数字,寻找长度最长的窗口。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 class Solution {public int totalFruit (int [] fruits) {int l = 0 ;int result = 0 ;new HashMap <>();for (int r = 0 ; r < fruits.length; r ++) {0 ) + 1 );while (fruitCount.size() > 2 ) {1 );if (fruitCount.get(fruits[l]) == 0 ) {1 );return result;class Solution1 {public int totalFruit (int [] fruits) {int left = 0 ,right = 0 ,ans = 0 ,a=0 ;int ln = fruits[left],rn = fruits[right];while (right < fruits.length){if (fruits[right] == rn || fruits[right] == ln){1 ;else {1 ;while (left >= 1 && fruits[left - 1 ] == ln) left--;1 ;return ans;
Leetcode76 最小覆盖子串 (滑动窗口) 方法一:减法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class Solution {public String minWindow (String s, String t) {new HashMap <>();char [] charT = t.toCharArray();for (char c: charT) {0 ) + 1 );int l = 0 ;int count = t.length();String result = "" ;for (int r = 0 ; r < s.length(); r ++) {if (charCount.containsKey(s.charAt(r))) {if (charCount.get(s.charAt(r)) > 0 ) {1 );while (count == 0 ) {if (result.length() > r - l + 1 || result.length() == 0 ) {1 );if (charCount.containsKey(s.charAt(l))) {if (charCount.get(s.charAt(l)) == 0 ) count ++;1 );return result;
方法二:窗口内字符个数与查找子串的字符个数比较(可优化) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 class Solution {public String minWindow (String s, String t) {char [] char_s = s.toCharArray();int length = s.length();int l = 0 ;int [] cntS = new int [128 ];int [] cntT = new int [128 ];int ansLeft = -1 , ansRight = length;for (char c: t.toCharArray()) {for (int r = 0 ; r < length; r++) {while (isCovered(cntS, cntT)) {if (r - l < ansRight - ansLeft) {return ansLeft < 0 ? "" : s.substring(ansLeft, ansRight + 1 );public boolean isCovered (int [] cntS, int [] cntT) {for (int i = 'A' ; i <= 'Z' ; i++) {if (cntS[i] < cntT[i]) {return false ;for (int i = 'a' ; i <= 'z' ; i++) {if (cntS[i] < cntT[i]) {return false ;return true ;
复杂度分析:
时间复杂度:O(∣Σ∣m+n),其中 m 为 s 的长度,n 为 t 的长度,∣Σ∣ 为字符集合的大小,本题字符均为英文字母,所以 ∣Σ∣=52。注意 left 只会增加不会减少,left 每增加一次,我们就花费 O(∣Σ∣) 的时间。因为 left 至多增加 m 次,所以二重循环的时间复杂度为 O(∣Σ∣m),再算上统计 t 字母出现次数的时间 O(n),总的时间复杂度为 O(∣Σ∣m+n)。
空间复杂度:O(∣Σ∣)。如果创建了大小为 128 的数组,则 ∣Σ∣=128。
方法三:优化版(感觉和方法一是一样的思想) 代码实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 class Solution {public String minWindow (String S, String t) {char [] s = S.toCharArray();int m = s.length;int ansLeft = -1 ;int ansRight = m;int [] cnt = new int [128 ];int less = 0 ;for (char c : t.toCharArray()) {if (cnt[c] == 0 ) {int left = 0 ;for (int right = 0 ; right < m; right++) { char c = s[right]; if (cnt[c] == 0 ) { while (less == 0 ) { if (right - left < ansRight - ansLeft) { char x = s[left]; if (cnt[x] == 0 ) {return ansLeft < 0 ? "" : S.substring(ansLeft, ansRight + 1 );
复杂度分析
1.6 前缀和 用处 计算区间和时十分有用
代码实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 import java.util.Scanner;public class Main {public static void main (String[] args) {Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in);int n = scanner.nextInt();int [] a = new int [n + 1 ];int [] b = new int [n + 1 ];for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i ++) {for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i ++) {1 ] + a[i];while (scanner.hasNextInt()) {int l = scanner.nextInt();int r = scanner.nextInt();1 ]);
复杂度分析 2. 链表 2.1 移除链表元素 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution {public ListNode removeElements (ListNode head, int val) {ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode (0 );ListNode cur = dummyNode;while (cur.next != null ) {if (cur.next.val == val) {else {return dummyNode.next;
注意 :如果cur.next.val == val时,不能直接将cur = cur.next,因为这样会跳过下一个元素的验证,还可能会直接跳到cur = null导致while判断条件出错(null没有.next属性)。
##2.2 翻转链表
思路一:双指针法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public ListNode reverseList (ListNode head) {ListNode pre = null ;ListNode cur = head;ListNode temp = null ;if (cur == null ) {return cur;while (cur != null ) {return pre;
思路二:递归(从前往后) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution {public ListNode reverseList (ListNode head) {return reverse(null , head);private ListNode reverse (ListNode prev, ListNode cur) {if (cur == null ) {return prev;ListNode temp = null ;return reverse(cur, temp);
思路三:递归(从后往前) 思路图:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution {reverseList (ListNode head) {if (head == null ) return null ;if (head.next == null ) return head;ListNode last = reverseList(head.next);null ;return last;
2.3 两两交换链表中的节点 思路一:迭代,直接顺着链表进行交换 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public ListNode swapPairs (ListNode head) {ListNode dummy = new ListNode (0 );ListNode cur = dummy;while (cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null ) {ListNode firstNode = cur.next;ListNode secondNode = cur.next.next;return dummy.next;
思路二:递归,不断更换头节点 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public ListNode swapPairs (ListNode head) {if (head == null || head.next == null ) return head;ListNode next = head.next;ListNode newNode = swapPairs(next.next);return next;
2.4 删除链表倒数第N个元素 思路:双指针 ,fast优先走n步,之后slow开始走,当fast走到链表尾此时找到需要删除的元素
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {new ListNode(0 );next = head;for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i ++) {next ;while (fast.next != null ) {next ;next ;if (slow.next != null ) {next = slow.next .next ;return dummy.next ;
2.5 寻找两个链表的交点 思路一:两链表对齐 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 public ListNode getIntersectionNode (ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {int lenA = 0 , lenB = 0 ;ListNode curA = headA, curB = headB;while (curA != null ) {while (curB != null ) {if (lenA < lenB) {int tmpLen = lenA;ListNode tmpNode = curA;int num = lenA - lenB;while (num != 0 ) {while (curA != null ) {if (curA == curB) {return curA;return null ;
思路二:合并链表实现同步移动 即如果两个链表相交,那么无论两个指针从哪个链表开始,它们最终都会在相交点相遇。
遍历完A后去B寻找,遍历完B后去A寻找,两者在到达相交点时经过的步数是相同的:
lenA + step_b(b从开头到相交点的步数)
lenB + step_a(a从开头到相交点的步数)
两者是相同的。(可画图验证)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public ListNode getIntersectionNode (ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {ListNode p1 = headA, p2 = headB;while (p1 != p2) {if (p1 == null ) p1 = headB;else p1 = p1.next;if (p2 == null ) p2 = headA;else p2 = p2.next;return p1;
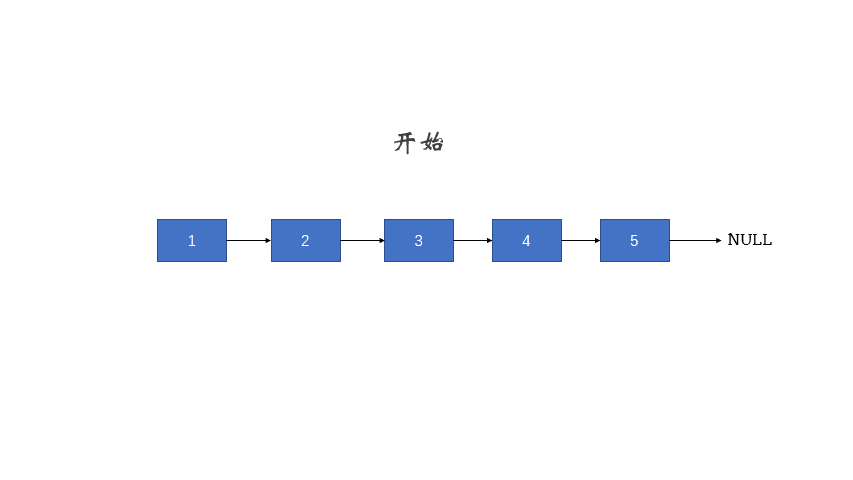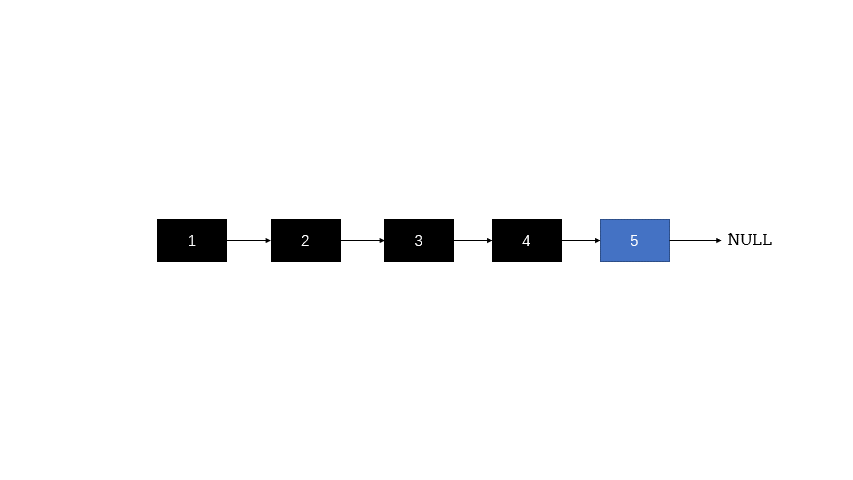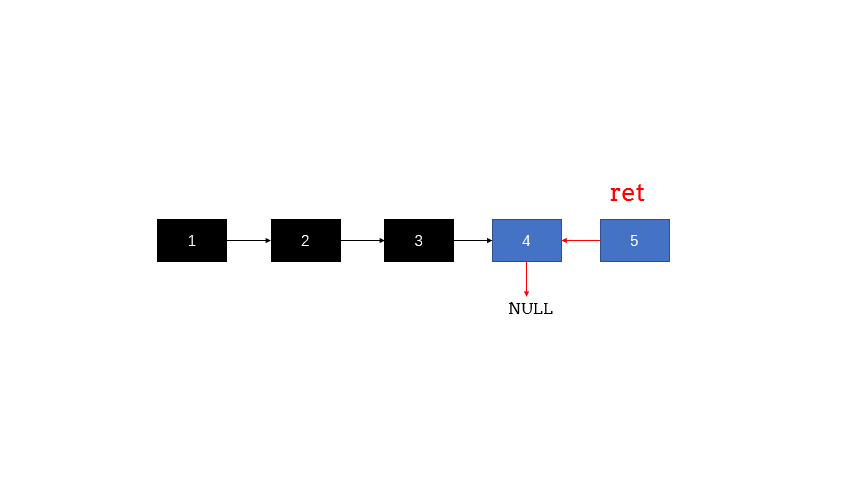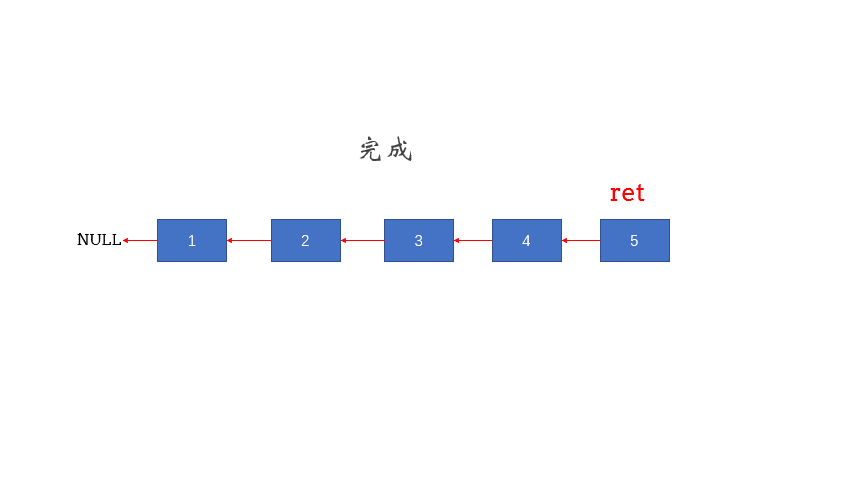
2.6 环形链表(判断链表是否有环,环的入口) 思路一:快慢指针 判断链表是否有环 快慢指针:可以使用快慢指针法,分别定义 fast 和 slow 指针,从头结点出发,fast指针每次移动两个节点,slow指针每次移动一个节点,如果 fast 和 slow指针在途中相遇 ,说明这个链表有环。
fast指针一定先进入环中,如果fast指针和slow指针相遇的话,一定是在环中相遇,这是毋庸置疑的。
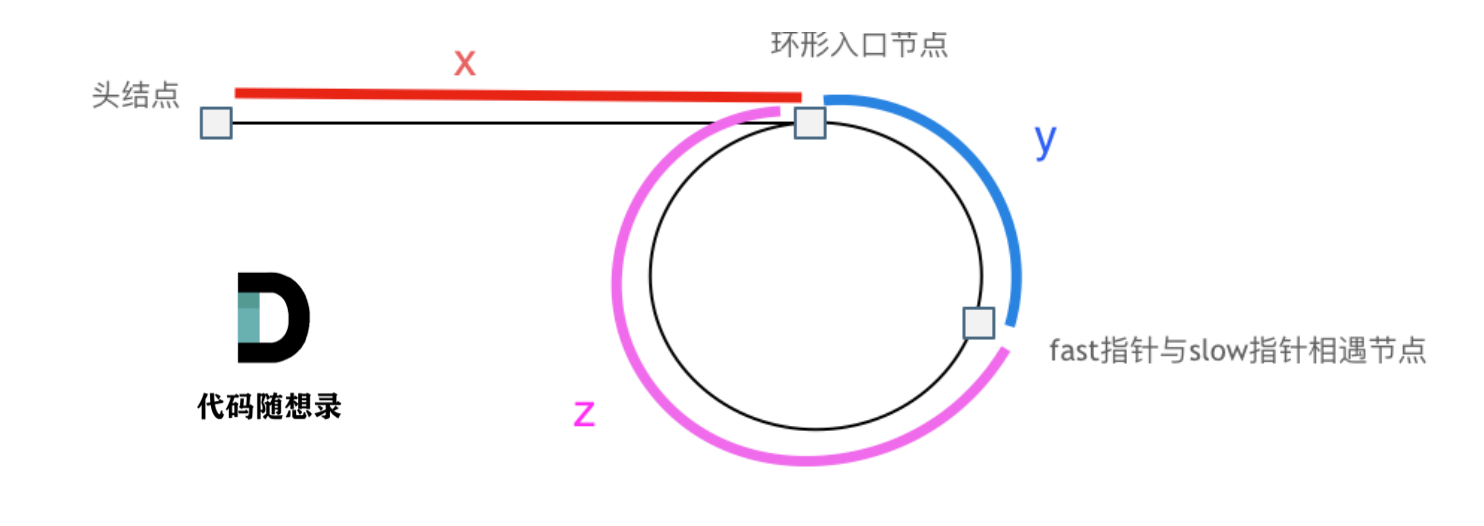
环的入口
通过数学推导可知:
若n = 1,则有x=z,这就意味着,从头结点出发一个指针,从相遇节点 也出发一个指针,这两个指针每次只走一个节点, 那么当这两个指针相遇的时候就是 环形入口的节点 。
也就是在相遇节点处,定义一个指针index1,在头结点处定一个指针index2。
让index1和index2同时移动,每次移动一个节点, 那么他们相遇的地方就是 环形入口的节点。
若n > 1,fast指针在环形转n圈之后才遇到 slow指针。
其实这种情况和n为1的时候效果是一样的,一样可以通过这个方法找到环形的入口节点,只不过,index1 指针在环里 多转了(n-1)圈,然后再遇到index2,相遇点依然是环形的入口节点。
代码实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public ListNode detectCycle (ListNode head) {ListNode slow = head;ListNode fast = head;while (fast != null && fast.next != null ) {if (slow == fast) {ListNode index1 = fast;ListNode index2 = head;while (index1 != index2) {return index1;return null ;
答疑 为什么第一次在环中相遇,slow的 步数 是 x+y 而不是 x + 若干环的长度 + y 呢?
关于找环的入口,为什么慢指针不会出现走好几圈才被快指针追上。可以先假设当慢指针第一次到环入口处的时候,和快指针的距离为m,此时快指针已经在环里面走了,而慢指针接下来也会在环里面走。再假设环长为s,所以快指针和慢指针的距离是(s-m),(注:都是按顺时针看距离),而快指针每次都会比慢指针多走一步,相当于每次都以一步的距离再缩进距离,所以当慢指针走(s-m)步的时候,快指针就能把距离缩为0了,也就是两点相遇了。而s-m是肯定小于s的,也就是小于一圈,所以慢指针肯定在没有走完一圈的时候就会被快指针追上。
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(N),其中 N 为链表中节点的数目。在最初判断快慢指针是否相遇时,slow 指针走过的距离不会超过链表的总长度;随后寻找入环点时,走过的距离也不会超过链表的总长度。因此,总的执行时间为 O(N)+O(N)=O(N)。
空间复杂度:O(1)。我们只使用了 slow,fast,ptr 三个指针。
思路二:哈希表 思路与算法 一个非常直观的思路是:我们遍历链表中的每个节点,并将它记录下来;一旦遇到了此前遍历过的节点,就可以判定链表中存在环。借助哈希表可以很方便地实现。
代码实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public ListNode detectCycle (ListNode head) {ListNode pos = head;new HashSet <ListNode>();while (pos != null ) {if (visited.contains(pos)) {return pos;else {return null ;
复杂度分析
快慢指针总结
fast先走,slow后走,两者移动步幅相同
fast和slow同时走,移动步幅不同,slow每次移动一步,fast每次移动2步
双指针法将时间复杂度:O(n^2)的解法优化为 O(n)的解法。也就是降一个数量级,题目如下:
链表相关双指针题目:
3. 哈希表 3.1 哈希表基础 哈希表,也称散列表。
哈希表是根据关键码的值而直接进行访问的数据结构。
一般哈希表都是用来快速判断一个元素是否出现集合里。
例如要查询一个名字是否在这所学校里。要枚举的话时间复杂度是O(n),但如果使用哈希表的话, 只需要O(1)就可以做到。
常见的三种哈希结构 当我们想使用哈希法来解决问题的时候,我们一般会选择如下三种数据结构。
数组(array)
set(集合)
map(映射)
哈希法也是牺牲了空间换取了时间 ,因为我们要使用额外的数组,set或者是map来存放数据,才能实现快速的查找。
如果在做面试题目的时候遇到需要判断一个元素是否出现过 的场景也应该第一时间想到哈希法
3.2 有效的字母异位词 代码实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public boolean isAnagram (String s, String t) {new HashMap <>();for (char a: s.toCharArray()) {0 ) + 1 );for (char b: t.toCharArray()) {if (cntS.getOrDefault(b, -1 ) == -1 ) {return false ;else {0 ) - 1 );for (char c:cntS.keySet()) {if (cntS.get(c) != 0 ) {return false ;return true ;
相关题目从此开始暂时搁置
3.3 两个数组的交集 思路一:使用hashmap 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public int [] intersection(int [] nums1, int [] nums2) {new HashSet <>();new HashSet <>();for (int i: nums1) {for (int i: nums2) {if (nums1_set.contains(i)) {return result_set.stream().mapToInt((x) -> x).toArray();
遇到哈希问题我直接都用set不就得了,用什么数组啊。
直接使用set 不仅占用空间 比数组大 ,而且速度 要比数组慢 ,set把数值映射到key上都要做hash计算的。
时间复杂度 O (m +n )
思路二:使用hash数组 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public int [] intersection(int [] nums1, int [] nums2) {int [] hash1 = new int [1002 ];int [] hash2 = new int [1002 ];for (int i : nums1)for (int i : nums2)new ArrayList <>();for (int i = 0 ; i < 1002 ; i++)if (hash1[i] > 0 && hash2[i] > 0 )int index = 0 ;int res[] = new int [resList.size()];for (int i : resList)return res;
3.4 快乐数 根据我们的探索,我们猜测会有以下三种可能。
最终会得到 1。
最终会进入循环。
值会越来越大,最后接近无穷大。
第三个情况比较难以检测和处理。我们怎么知道它会继续变大,而不是最终得到 1 呢?我们可以仔细想一想,每一位数的最大数字的下一位数是多少。
Digits
Largest
Next
1
9
81
2
99
162
3
999
243
4
9999
324
13
9999999999999
1053
对于 3 位数的数字,它不可能大于 243。这意味着它要么被困在 243 以下的循环内,要么跌到 1。4 位或 4 位以上的数字在每一步都会丢失一位,直到降到 3 位为止。所以我们知道,最坏的情况下,算法可能会在 243 以下的所有数字上循环,然后回到它已经到过的一个循环或者回到 1。但它不会无限期地进行下去,所以我们排除第三种选择。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public int getSum (int n) {int res = 0 ;while (n > 0 ) {10 ) * (n % 10 );10 ;return res;public boolean isHappy (int n) {new HashSet <>();while (n != 1 && !cnt.contains(n)) {return n == 1 ;
复杂度分析 确定这个问题的时间复杂度对于一个「简单」级别的问题来说是一个挑战。如果您对这些问题还不熟悉,可以尝试只计算 getNext(n) 函数的时间复杂度。
思路二:快慢指针 通过反复调用 getNext(n) 得到的链是一个隐式的链表。隐式意味着我们没有实际的链表节点和指针,但数据仍然形成链表结构。起始数字是链表的头 “节点”,链中的所有其他数字都是节点。next 指针是通过调用 getNext(n) 函数获得。
意识到我们实际有个链表,那么这个问题就可以转换为检测一个链表是否有环。因此我们在这里可以使用弗洛伊德循环查找算法。这个算法是两个奔跑选手,一个跑的快,一个跑得慢。在龟兔赛跑的寓言中,跑的慢的称为 “乌龟”,跑得快的称为 “兔子”。
不管乌龟和兔子在循环中从哪里开始,它们最终都会相遇。这是因为兔子每走一步就向乌龟靠近一个节点(在它们的移动方向上)。
算法
我们不是只跟踪链表中的一个值,而是跟踪两个值,称为快跑者和慢跑者。在算法的每一步中,慢速在链表中前进 1 个节点,快跑者前进 2 个节点(对 getNext(n) 函数的嵌套调用)。
如果 n 是一个快乐数,即没有循环,那么快跑者最终会比慢跑者先到达数字 1。
如果 n 不是一个快乐的数字,那么最终快跑者和慢跑者将在同一个数字上相遇。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution {public int getNext (int n) {int totalSum = 0 ;while (n > 0 ) {int d = n % 10 ;10 ;return totalSum;public boolean isHappy (int n) {int slowRunner = n;int fastRunner = getNext(n);while (fastRunner != 1 && slowRunner != fastRunner) {return fastRunner == 1 ;
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(logn)。该分析建立在对前一种方法的分析的基础上,但是这次我们需要跟踪两个指针而不是一个指针来分析,以及在它们相遇前需要绕着这个循环走多少次。
如果没有循环,那么快跑者将先到达 1,慢跑者将到达链表中的一半。我们知道最坏的情况下,成本是 O(2⋅logn)=O(logn)。
一旦两个指针都在循环中,在每个循环中,快跑者将离慢跑者更近一步。一旦快跑者落后慢跑者一步,他们就会在下一步相遇。假设循环中有 k 个数字。如果他们的起点是相隔 k−1 的位置(这是他们可以开始的最远的距离),那么快跑者需要 k−1 步才能到达慢跑者,这对于我们的目的来说也是不变的。因此,主操作仍然在计算起始 n 的下一个值,即 O(logn)。
空间复杂度:O(1),对于这种方法,我们不需要哈希集来检测循环。指针需要常数的额外空间。
3.5 两数之和 哈希表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public int [] twoSum(int [] nums, int target) {new HashMap <>();for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) {if (map.containsKey(target - nums[i])) {return new int []{map.get(target - nums[i]), i};throw new IllegalArgumentException ("No two sum solution" );
3.6 四数相加 思路一:分组+哈希表 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public int fourSumCount (int [] nums1, int [] nums2, int [] nums3, int [] nums4) {new HashMap <>();for (int a: nums1) {for (int b: nums2) {0 ) + 1 );int count = 0 ;for (int c: nums3) {for (int d: nums4) {0 );return count;
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(n^2)$。我们使用了两次二重循环,时间复杂度均为$O(n^2)$。在循环中对哈希映射进行的修改以及查询操作的期望时间复杂度均为 O(1),因此总时间复杂度为$O(n^2)$。
空间复杂度:$O(n^2)$,即为哈希映射需要使用的空间。在最坏的情况下,A[i]+B[j] 的值均不相同,因此值的个数为$n^2$,也就需要 $O(n^2)$的空间。
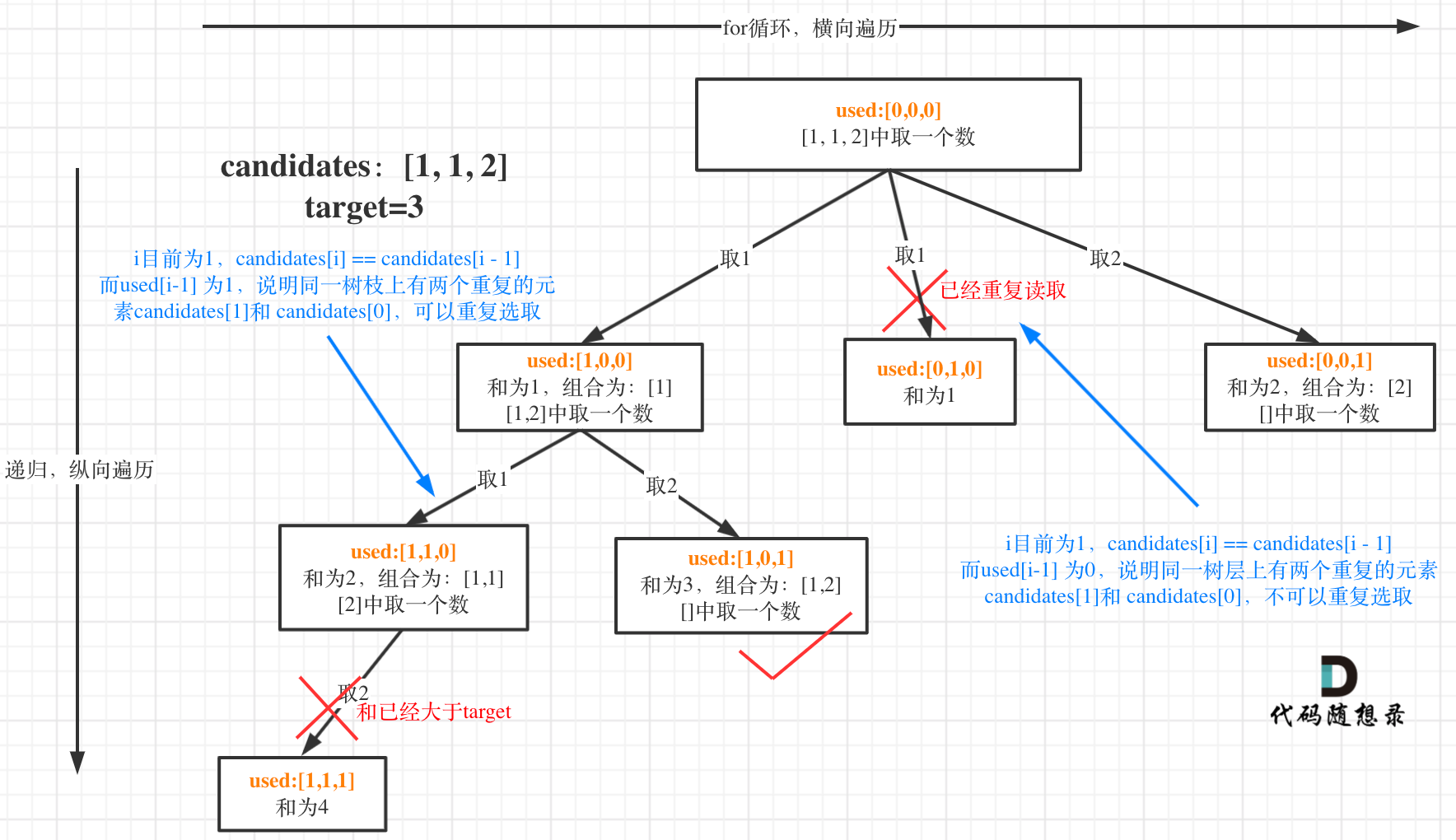
3.7 三数之和 思路一:双指针 代码实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 public List<List<Integer>> threeSum (int [] nums) {int length = nums.length;new ArrayList <>();for (int i = 0 ; i < length - 2 ; i++) {int first = nums[i];if (i > 0 && first == nums[i - 1 ]) {continue ;if (first + nums[i + 1 ] + nums[i + 2 ] > 0 ) break ;if (first + nums[length - 1 ] + nums[length - 2 ] < 0 ) continue ;int l = i + 1 ;int r = length - 1 ;while (l < r) {int s = nums[l] + nums[r] + first;if (s > 0 ) {else if (s < 0 ) {else {while (l < r && nums[l] == nums[l - 1 ]) l++;while (l < r && nums[r] == nums[r + 1 ]) r--;return res;
时空复杂度
时间复杂度: O(n^2)
空间复杂度: O(1)
思路二:哈希(看不懂,不推荐) 代码实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 vector<vector<int >> threeSum (vector<int >& nums) {int >> result;for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.size(); i++) {if (nums[i] > 0 ) {break ;if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1 ]) { continue ;int > set;for (int j = i + 1 ; j < nums.size(); j++) {if (j > i + 2 1 ]1 ] == nums[j-2 ]) { continue ;int c = 0 - (nums[i] + nums[j]);if (set.find(c) != set.end()) {else {return result;
时空复杂度
时间复杂度: O(n^2)
空间复杂度: O(n)
3.8 四数之和 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 public List<List<Integer>> fourSum (int [] nums, int target) {new ArrayList <>();int n = nums.length;for (int i = 0 ; i < n - 3 ; i ++) {if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1 ]) continue ;if (nums[i] > target && target >= 0 ) break ;for (int j = i + 1 ; j < n - 2 ; j ++) {if (j > i + 1 && nums[j] == nums[j - 1 ]) continue ;if (nums[i] + nums[j] > target && target >= 0 ) break ;int l = j + 1 ;int r = n - 1 ;while (l < r) {long s = (long ) nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[l] + nums[r];if (s > target) {else if (s < target) {else {while (l < r && nums[l] == nums[l - 1 ]) l++;while (l < r && nums[r] == nums[r + 1 ]) r--;return res;
4. 字符串 4.1 反转字符串 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public String reverseStr (String s, int k) {StringBuffer res = new StringBuffer ();int length = s.length();int start = 0 ;while (start < length) {StringBuffer temp = new StringBuffer ();int firstK = (start + k > length) ? length : start + k;int secondK = (start + (2 * k) > length) ? length : start + (2 * k);if (firstK < secondK) { 2 * k);return res.toString();
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 class Solution {public String reverseStr (String s, int k) {char [] ch = s.toCharArray();for (int i = 0 ; i < ch.length; i += 2 * k){int start = i;int end = Math.min(ch.length - 1 , start + k - 1 );while (start < end){return new String (ch);class Solution {public String reverseStr (String s, int k) {char [] ch = s.toCharArray();for (int i = 0 ;i < ch.length;i += 2 * k){int start = i;int end = Math.min(ch.length - 1 ,start + k - 1 );while (start < end){char temp = ch[start];return new String (ch);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution {public String reverseStr (String s, int k) {char [] ch = s.toCharArray();for (int i = 0 ; i< ch.length; i += 2 * k) {if (i + k <= ch.length) {1 );continue ;1 );return new String (ch);public void reverse (char [] ch, int i, int j) {for (; i < j; i++, j--) {char temp = ch[i];
4.2 替换数字 很多数组填充类的问题,其做法都是先预先给数组扩容带填充后的大小,然后在从后向前进行操作。
这么做有两个好处:
不用申请新数组。
从后向前填充元素,避免了从前向后填充元素时,每次添加元素都要将添加元素之后的所有元素向后移动的问题。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 import java.util.Scanner;public class Main {public static String replaceNumber (String s) {int count = 0 ; int sOldSize = s.length();for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); i++) {if (Character.isDigit(s.charAt(i))){char [] newS = new char [s.length() + count * 5 ];int sNewSize = newS.length;0 , newS, 0 , sOldSize);for (int i = sNewSize - 1 , j = sOldSize - 1 ; j < i; j--, i--) {if (!Character.isDigit(newS[j])) {else {'r' ;1 ] = 'e' ;2 ] = 'b' ;3 ] = 'm' ;4 ] = 'u' ;5 ] = 'n' ;5 ;return new String (newS);public static void main (String[] args) {Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in);String s = scanner.next();
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 import java.util.Scanner;public class Main {public static String replaceNumber (String s) {StringBuilder newS = new StringBuilder ();for (char a : s.toCharArray()) {if (Character.isDigit(a)) {"number" ); else {return newS.toString();public static void main (String[] args) {Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in);String s = scanner.next();
4.3 翻转字符串里的单词 思路
首先,去除多余的空格(参考双指针(快慢指针)的1.2 移除元素);接着,翻转整个字符串;最后,翻转每个单词。
代码实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 public String reverseWords (String s) {StringBuilder sb = removeExtreSpace(s);0 , sb.length() - 1 );int start = 0 ;for (int i = 0 ; i < sb.length(); i++) {if (sb.charAt(i) == ' ' ) {1 );1 ;1 );return sb.toString();public StringBuilder removeExtreSpace (String s) {int slow = 0 ;StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder ();for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); i++) {if (s.charAt(i) != ' ' ) {if (slow != 0 ) sb.append(' ' );while (i < s.length() && s.charAt(i) != ' ' ) {return sb;public void reverse (StringBuilder sb, int start, int end) {while (start < end) {char temp = sb.charAt(start);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 class Solution {public String reverseWords (String s) {StringBuilder sb = removeSpace(s);0 , sb.length() - 1 );return sb.toString();private StringBuilder removeSpace (String s) {int start = 0 ;int end = s.length() - 1 ;while (s.charAt(start) == ' ' ) start++;while (s.charAt(end) == ' ' ) end--;StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder ();while (start <= end) {char c = s.charAt(start);if (c != ' ' || sb.charAt(sb.length() - 1 ) != ' ' ) {return sb;public void reverseString (StringBuilder sb, int start, int end) {while (start < end) {char temp = sb.charAt(start);private void reverseEachWord (StringBuilder sb) {int start = 0 ;int end = 1 ;int n = sb.length();while (start < n) {while (end < n && sb.charAt(end) != ' ' ) {1 );1 ;1 ;class Solution {public String reverseWords (String s) {char [] chars = s.toCharArray();0 , chars.length - 1 );return new String (chars);public char [] removeExtraSpaces(char [] chars) {int slow = 0 ;for (int fast = 0 ; fast < chars.length; fast++) {if (chars[fast] != ' ' ) {if (slow != 0 )' ' ;while (fast < chars.length && chars[fast] != ' ' )char [] newChars = new char [slow];0 , newChars, 0 , slow); return newChars;public void reverse (char [] chars, int left, int right) {if (right >= chars.length) {"set a wrong right" );return ;while (left < right) {public void reverseEachWord (char [] chars) {int start = 0 ;for (int end = 0 ; end <= chars.length; end++) {if (end == chars.length || chars[end] == ' ' ) {1 );1 ;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution {public String reverseWords (String s) {char [] initialArr = s.toCharArray();char [] newArr = new char [initialArr.length+1 ];int newArrPos = 0 ;int i = initialArr.length-1 ;while (i>=0 ){while (i>=0 && initialArr[i] == ' ' ){i--;} int right = i;while (i>=0 && initialArr[i] != ' ' ){i--;} for (int j = i+1 ; j <= right; j++) {if (j == right){' ' ;if (newArrPos == 0 ){return "" ;else {return new String (newArr,0 ,newArrPos-1 );
复杂度
时间复杂度: O(n)
空间复杂度: O(1) 或 O(n),取决于语言中字符串是否可变
4.4 右旋转字符串 4.5 KMP字符串 题目描述
实现 strStr() 函数。
给定一个 haystack 字符串和一个 needle 字符串,在 haystack 字符串中找出 needle 字符串出现的第一个位置 (从0开始)。如果不存在,则返回 -1。
示例 1: 输入: haystack = “hello”, needle = “ll” 输出: 2
示例 2: 输入: haystack = “aaaaa”, needle = “bba” 输出: -1
说明: 当 needle 是空字符串时,我们应当返回什么值呢?这是一个在面试中很好的问题。 对于本题而言,当 needle 是空字符串时我们应当返回 0 。这与C语言的 strstr() 以及 Java的 indexOf() 定义相符。
思路
代码实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 class Solution {public int [] getNext(String s) {int [] next = new int [s.length()];int j = 0 ;0 ] = j;for (int i = 1 ; i < s.length(); i++) {while (j > 0 && s.charAt(j) != s.charAt(i)) {1 ];if (s.charAt(j) == s.charAt(i)) {return next;public int strStr (String haystack, String needle) {if (needle.length() == 0 ) {return 0 ;int [] next = getNext(needle);int j = 0 ;for (int i = 0 ; i < haystack.length(); i++) {while (j > 0 && needle.charAt(j) != haystack.charAt(i)) {1 ];if (haystack.charAt(i) == needle.charAt(j)) {if (j == needle.length()) {return i - j + 1 ;return -1 ;
4.6 最小循环节 题目描述
给定一个非空的字符串,判断它是否可以由它的一个子串重复多次构成。给定的字符串只含有小写英文字母,并且长度不超过10000。
示例 1:
输入: “abab”
输出: True
解释: 可由子字符串 “ab” 重复两次构成。
示例 2:
示例 3:
输入: “abcabcabcabc”
输出: True
解释: 可由子字符串 “abc” 重复四次构成。 (或者子字符串 “abcabc” 重复两次构成。
视频参考
AcWing 141. 周期(蓝桥杯集训·每日一题) - AcWing
代码实现
最小循环节判断准则:len-next[len]能够被len整除
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 class Solution {public boolean repeatedSubstringPattern (String s) {if (s.length() == 0 ) return false ;int [] next = new int [s.length()];int j = 0 ; 0 ] = j;int n = s.length();for (int i = 1 ; i < n; i++) {while (j > 0 && s.charAt(i) != s.charAt(j)) {1 ];if (s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j)) {if (next[n - 1 ] != 0 && n % (n - next[n - 1 ]) == 0 ) {return true ;return false ;class Solution {public boolean repeatedSubstringPattern (String s) {if (s.equals("" )) return false ;int len = s.length();" " + s;char [] chars = s.toCharArray();int [] next = new int [len + 1 ];for (int i = 2 , j = 0 ; i <= len; i++) {while (j > 0 && chars[i] != chars[j + 1 ]) j = next[j];if (chars[i] == chars[j + 1 ]) j++;if (next[len] > 0 && len % (len - next[len]) == 0 ) {return true ;return false ;
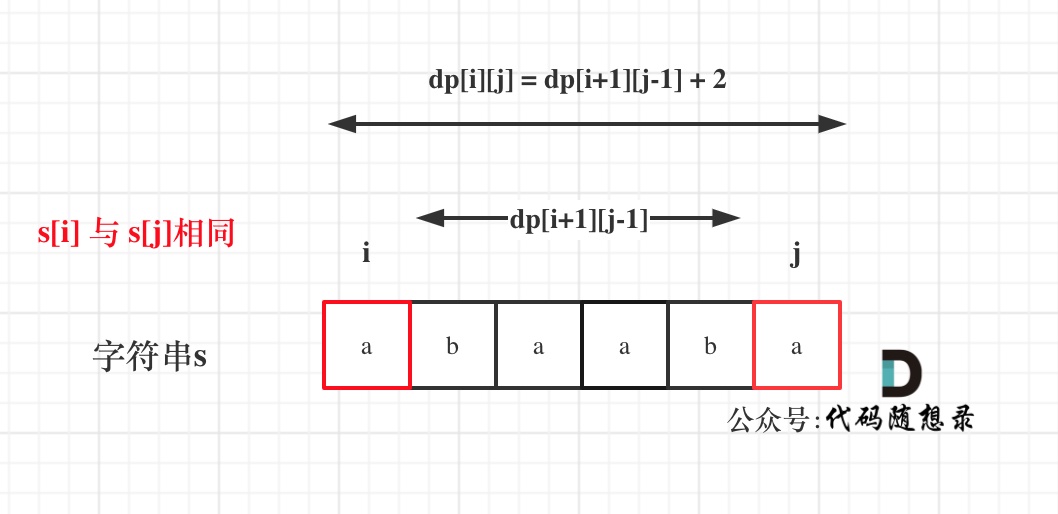
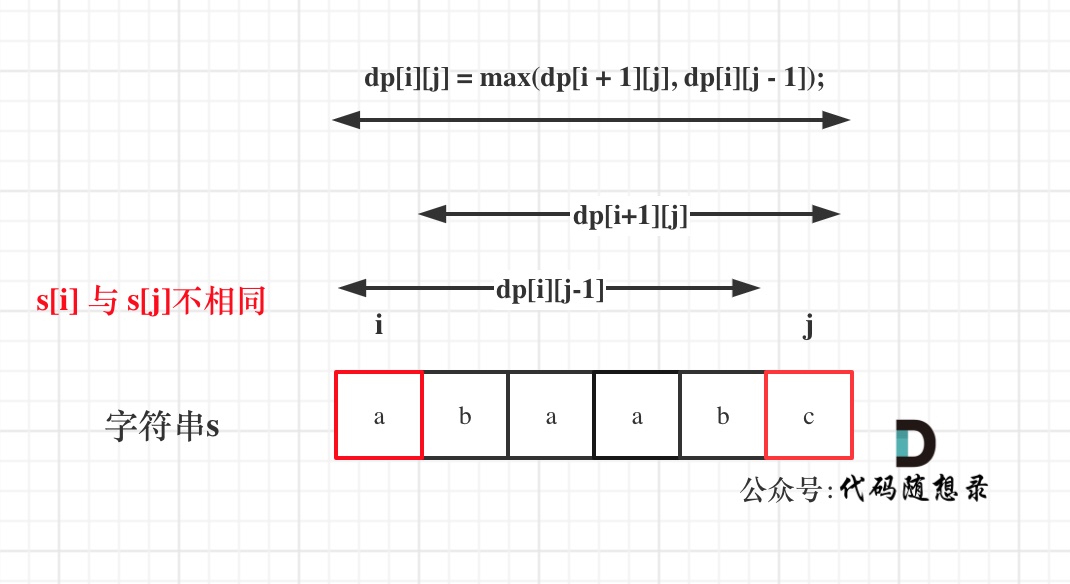
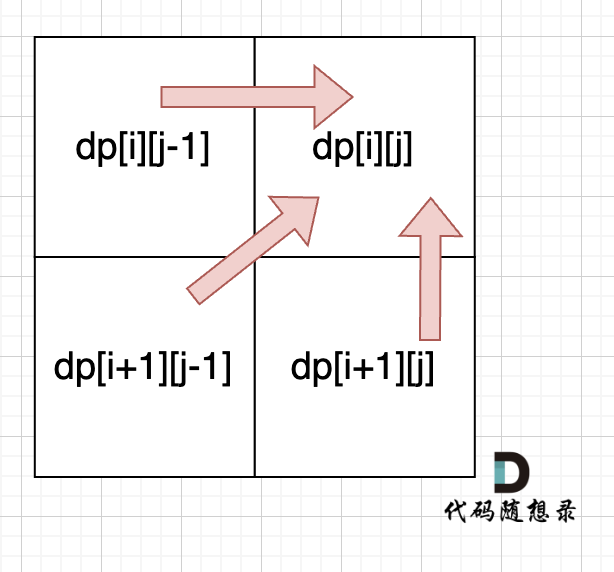
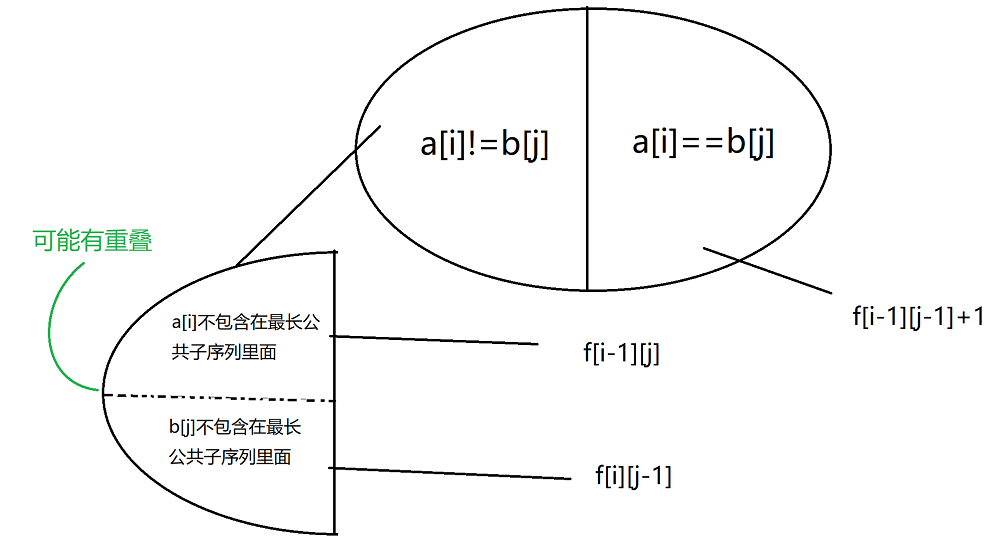
判断字符串s是否由重复子串组成,只要两个s拼接在一起,里面还出现一个s的话,就说明是由重复子串组成
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 class Solution {public :bool repeatedSubstringPattern (string s) erase (t.begin ()); t.erase (t.end () - 1 ); if (t.find (s) != std::string::npos) return true ; return false ;
6. 栈和队列 6.2 队列实现栈 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 class MyStack {public MyStack () {new LinkedList <>();public void push (int x) {public int pop () {int size = myQueue.size();while (size-- > 0 ) {return myQueue.poll(); public int top () {int size = myQueue.size();while (size-- > 0 ) {int res = myQueue.peek(); return res;public boolean empty () {return myQueue.isEmpty();
6.3 有效的括号 思路一
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution {public boolean isValid (String s) {new Stack <>();for (char a: s.toCharArray()) {if (a == '(' || a == '{' || a == '[' ) {else if (symbol.empty()) {return false ;else if (a == ')' ){if (symbol.peek() != '(' ) return false ;else if (a == '}' ){if (symbol.peek() != '{' ) return false ;else if (a == ']' ){if (symbol.peek() != '[' ) return false ;if (symbol.empty()) return true ;else return false ;
思路二:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution {public boolean isValid (String s) {new LinkedList <>();char ch;for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); i++) {if (ch == '(' ) {')' );else if (ch == '{' ) {'}' );else if (ch == '[' ) {']' );else if (deque.isEmpty() || deque.peek() != ch) {return false ;else {return deque.isEmpty();
6.4 删除字符串中的相邻相同元素 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution {public String removeDuplicates (String s) {new Stack <>();for (char a: s.toCharArray()) {if (!myStack.empty()) {if (myStack.peek() == a) {else {else {int size = myStack.size();if (size == 0 ) {return "" ;char [] res = new char [size];while (size > 0 ) {return new String (res);
6.5 后缀表达式求值(逆波兰表达式) 逆波兰表达式主要有以下两个优点:
去掉括号后表达式无歧义,上式即便写成 1 2 + 3 4 + * 也可以依据次序计算出正确结果。
适合用栈操作运算:遇到数字则入栈;遇到运算符则取出栈顶两个数字进行计算,并将结果压入栈中。
递归就是用栈来实现的。
所以栈与递归之间在某种程度上是可以转换的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution {public int evalRPN (String[] tokens) {new Stack <>();for (String token: tokens) {if ("+" .equals(token)) {int num2 = stack.pop();int num1 = stack.pop();else if ("-" .equals(token)) {int num2 = stack.pop();int num1 = stack.pop();else if ("*" .equals(token)) {int num2 = stack.pop();int num1 = stack.pop();else if ("/" .equals(token)) {int num2 = stack.pop();int num1 = stack.pop();else {return stack.pop();
Deque用法 支持在两端插入和移除元素的线性集合。 deque 这个名字是“Double-ended queues”的缩写。此接口定义访问双端元素的方法。提供了插入、删除和获取元素的方法。这些方法中的每一个都以两种形式存在:一种在操作失败时引发异常,另一种返回特殊值( null 或 false,具体取决于操作)。后一种形式的插入操作专门设计用于容量受限 Deque 的实现;在大多数实现中,插入操作不会失败。
1 public interface Deque <E> extends Queue <E>
1 2 3 4 5 * 第一个元素(头部) 最后一个元素(尾部)addFirst (e) offerFirst (e) addLast (e) offerLast (e)removeFirst () pollFirst () removeLast () pollLast ()getFirst () peekFirst () getLast () peekLast ()
1、此接口继承了Queue接口。当双端用作 FIFO(先进先出)行为队列时 Deque的部分方法与 Queue的等价:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 * Queue 方法 等效 Deque 的方法add (e) addLast (e)offer (e) offerLast (e)remove () removeFirst ()poll () pollFirst ()element () getFirst ()peek () peekFirst ()
2、Deque 也可以用作LIFO(后进先出)堆栈。应优先使用此接口而不是旧 Stack 类。当双端面用作堆栈时,元素将从双端的开头推送和弹出。
1 2 3 4 * 堆栈方法 等效 Deque 方法push (e) addFirst (e)pop () removeFirst ()peek () peekFirst ()
3、Deque方法详解
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 public interface Deque <E> extends Queue <E> {void addFirst (E e) ;void addLast (E e) ;boolean offerFirst (E e) ;boolean offerLast (E e) ;removeFirst () ;removeLast () ;pollFirst () ;pollLast () ;getFirst () ;getLast () ;peekFirst () ;peekLast () ;boolean removeFirstOccurrence (Object o) ;boolean removeLastOccurrence (Object o) ;
6.6 滑动窗口最大值(单调队列) 思路一:实现自己的单调队列
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 class MyQueue {new LinkedList <>();void poll (int val) {if (deque.peek() == val) {void add (int val) {while (!deque.isEmpty() && val > deque.getLast()) {int peek () {return deque.peek();class Solution {public int [] maxSlidingWindow(int [] nums, int k) {MyQueue myqueue = new MyQueue ();int [] res = new int [nums.length - k + 1 ];int index = 0 ;for (int i = 0 ; i < k; i++) {for (int i = k; i < nums.length; i++) {return res;
思路二:存储下标
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 class Solution {public int [] maxSlidingWindow(int [] nums, int k) {new ArrayDeque <>();int n = nums.length;int [] res = new int [n - k + 1 ];int idx = 0 ;for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) {while (!deque.isEmpty() && deque.peek() < i - k + 1 ){while (!deque.isEmpty() && nums[deque.peekLast()] < nums[i]) {if (i >= k - 1 ){return res;
6.7 前k个高频元素 思路
优先级队列priority_queue
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution {public int [] topKFrequent(int [] nums, int k) {new HashMap <>();int [] res = new int [k];int []> pq = new PriorityQueue <>((o1, o2) -> o1[1 ] - o2[1 ]);int len = nums.length;for (int i = 0 ; i < len; i ++) {0 ) + 1 );for (var x: map.entrySet()) {int [] tmp = new int [2 ];0 ] = x.getKey();1 ] = x.getValue();if (pq.size() > k) {for (int i = k - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) {0 ];return res;
拓展
大家对这个比较运算在建堆时是如何应用的,为什么左大于右就会建立小顶堆,反而建立大顶堆比较困惑。
确实 例如我们在写快排的cmp函数的时候,return left>right 就是从大到小,return left<right 就是从小到大。
优先级队列的定义正好反过来了,可能和优先级队列的源码实现有关(我没有仔细研究),我估计是底层实现上优先队列队首指向后面,队尾指向最前面的缘故!
##栈经典题目
###栈在系统中的应用
如果还记得编译原理的话,编译器在词法分析的过程中处理括号、花括号等这个符号的逻辑,就是使用了栈这种数据结构。
再举个例子,linux系统中,cd这个进入目录的命令我们应该再熟悉不过了。
这个命令最后进入a目录,系统是如何知道进入了a目录呢 ,这就是栈的应用。这在leetcode上也是一道题目,编号:71. 简化路径,大家有空可以做一下。
递归的实现是栈:每一次递归调用都会把函数的局部变量、参数值和返回地址等压入调用栈中 ,然后递归返回的时候,从栈顶弹出上一次递归的各项参数,所以这就是递归为什么可以返回上一层位置的原因。
所以栈在计算机领域中应用是非常广泛的。
有的同学经常会想学的这些数据结构有什么用,也开发不了什么软件,大多数同学说的软件应该都是可视化的软件例如APP、网站之类的,那都是非常上层的应用了,底层很多功能的实现都是基础的数据结构和算法。
所以数据结构与算法的应用往往隐藏在我们看不到的地方!
括号匹配问题 在栈与队列:系统中处处都是栈的应用 (opens new window) 中我们讲解了括号匹配问题。
括号匹配是使用栈解决的经典问题。
建议要写代码之前要分析好有哪几种不匹配的情况,如果不动手之前分析好,写出的代码也会有很多问题。
先来分析一下 这里有三种不匹配的情况,
第一种情况,字符串里左方向的括号多余了,所以不匹配。
第二种情况,括号没有多余,但是括号的类型没有匹配上。
第三种情况,字符串里右方向的括号多余了,所以不匹配。
这里还有一些技巧,在匹配左括号的时候,右括号先入栈,就只需要比较当前元素和栈顶相不相等就可以了,比左括号先入栈代码实现要简单的多了!
字符串去重问题 在栈与队列:匹配问题都是栈的强项 (opens new window) 中讲解了字符串去重问题。 1047. 删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项
思路就是可以把字符串顺序放到一个栈中,然后如果相同的话 栈就弹出,这样最后栈里剩下的元素都是相邻不相同的元素了。
逆波兰表达式问题 在栈与队列:有没有想过计算机是如何处理表达式的? (opens new window) 中讲解了求逆波兰表达式。
本题中每一个子表达式要得出一个结果,然后拿这个结果再进行运算,那么这岂不就是一个相邻字符串消除的过程,和栈与队列:匹配问题都是栈的强项 (opens new window) 中的对对碰游戏是不是就非常像了。
队列的经典题目 滑动窗口最大值问题 在栈与队列:滑动窗口里求最大值引出一个重要数据结构 (opens new window) 中讲解了一种数据结构:单调队列。
这道题目还是比较绕的,如果第一次遇到这种题目,需要反复琢磨琢磨
主要思想是队列没有必要维护窗口里的所有元素,只需要维护有可能成为窗口里最大值的元素就可以了,同时保证队列里的元素数值是由大到小的。
那么这个维护元素单调递减的队列就叫做单调队列,即单调递减或单调递增的队列。C++中没有直接支持单调队列,需要我们自己来一个单调队列
而且不要以为实现的单调队列就是 对窗口里面的数进行排序,如果排序的话,那和优先级队列又有什么区别了呢。
设计单调队列的时候,pop,和push操作要保持如下规则:
pop(value):如果窗口移除的元素value等于单调队列的出口元素,那么队列弹出元素,否则不用任何操作
push(value):如果push的元素value大于入口元素的数值,那么就将队列出口的元素弹出,直到push元素的数值小于等于队列入口元素的数值为止
保持如上规则,每次窗口移动的时候,只要问que.front()就可以返回当前窗口的最大值。
一些同学还会对单调队列都有一些困惑,首先要明确的是,题解中单调队列里的pop和push接口,仅适用于本题。
单调队列不是一成不变的,而是不同场景不同写法 ,总之要保证队列里单调递减或递增的原则,所以叫做单调队列。
不要以为本题中的单调队列实现就是固定的写法。
我们用deque作为单调队列的底层数据结构,C++中deque是stack和queue默认的底层实现容器(这个我们之前已经讲过),deque是可以两边扩展的,而且deque里元素并不是严格的连续分布的。
求前 K 个高频元素 在栈与队列:求前 K 个高频元素和队列有啥关系? (opens new window) 中讲解了求前 K 个高频元素。
通过求前 K 个高频元素,引出另一种队列就是优先级队列 。
什么是优先级队列呢?
其实就是一个披着队列外衣的堆 ,因为优先级队列对外接口只是从队头取元素,从队尾添加元素,再无其他取元素的方式,看起来就是一个队列。
而且优先级队列内部元素是自动依照元素的权值排列。那么它是如何有序排列的呢?
缺省情况下priority_queue利用max-heap(大顶堆)完成对元素的排序,这个大顶堆是以vector为表现形式的complete binary tree(完全二叉树)。
什么是堆呢?
堆是一棵完全二叉树,树中每个结点的值都不小于(或不大于)其左右孩子的值。 如果父亲结点是大于等于左右孩子就是大顶堆,小于等于左右孩子就是小顶堆。
所以大家经常说的大顶堆(堆头是最大元素),小顶堆(堆头是最小元素),如果懒得自己实现的话,就直接用priority_queue(优先级队列)就可以了,底层实现都是一样的,从小到大排就是小顶堆,从大到小排就是大顶堆。
本题就要使用优先级队列来对部分频率进行排序。 注意这里是对部分数据进行排序而不需要对所有数据排序!
所以排序的过程的时间复杂度是 $O(\log k)$ ,整个算法的时间复杂度是 $O(n\log k)$ 。
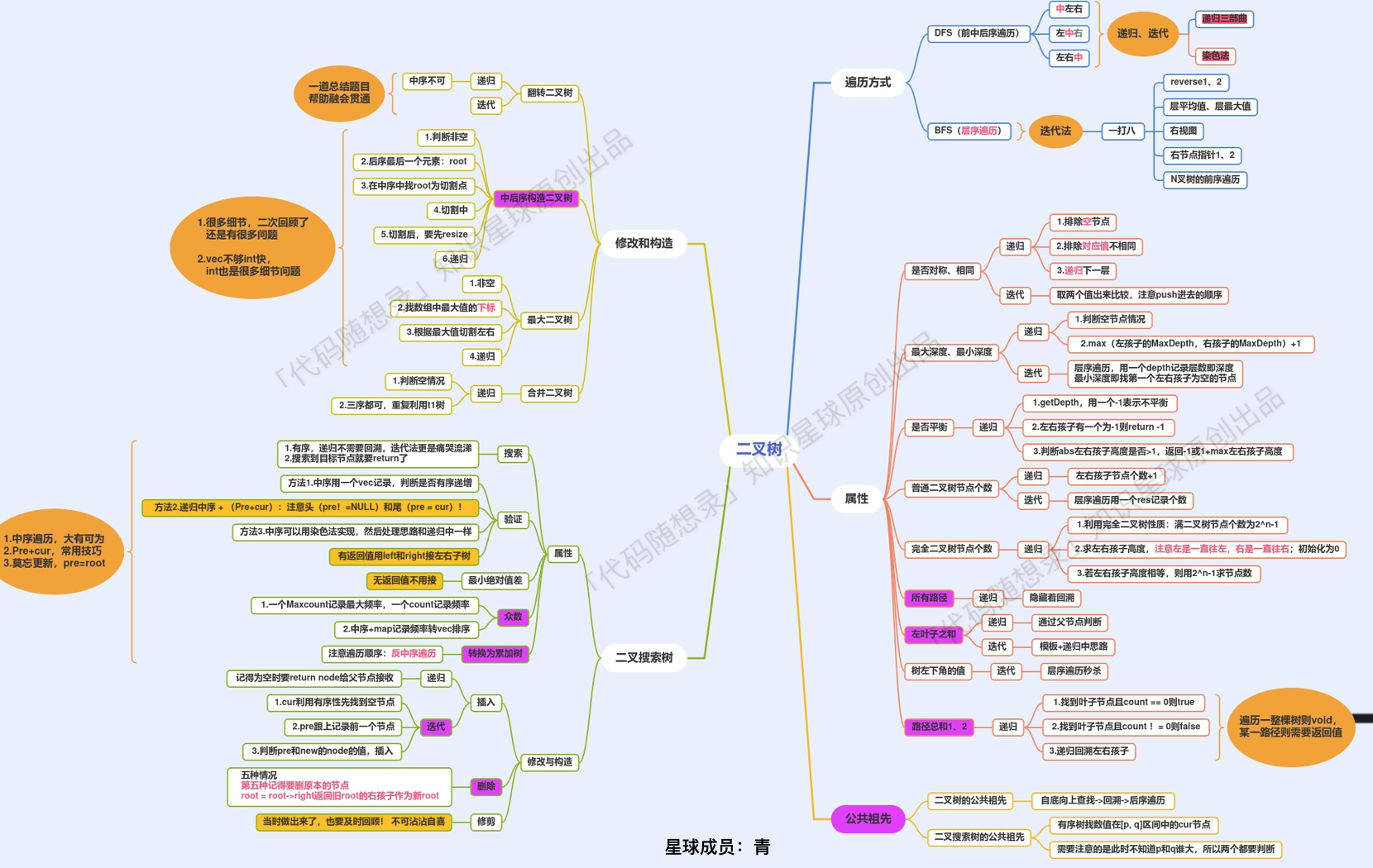
7. 二叉树 7.1 二叉树理论基础
7.2 二叉树的遍历 7.2.1 二叉树的递归遍历 7.2.2 二叉树的迭代遍历 1. 前序遍历&&后序遍历 前序遍历
前序遍历是中左右,每次先处理的是中间节点,那么先将根节点放入栈中,然后将右孩子加入栈,再加入左孩子。
为什么要先加入 右孩子,再加入左孩子呢? 因为这样出栈的时候才是中左右的顺序。
动画如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class Solution {public List<Integer> preorderTraversal (TreeNode root) {new ArrayList <>();new Stack <>();if (root == null ) return res;while (!st.isEmpty()) {TreeNode tmp = st.peek();if (tmp.right != null ) st.push(tmp.right);if (tmp.left != null ) st.push(tmp.left);return res;
后序遍历
将前序遍历翻转:
中左右->中右左(调换左右节点入栈顺序)->左右中(翻转最后的结果数组)
先序遍历是中左右,后序遍历是左右中,那么我们只需要调整一下先序遍历的代码顺序,就变成中右左的遍历顺序,然后在反转result数组,输出的结果顺序就是左右中了,如下图:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 class Solution {public List<Integer> postorderTraversal (TreeNode root) {new ArrayList <>();new Stack <>();if (root == null ) return res;while (!st.isEmpty()) {TreeNode tmp = st.pop();if (tmp.left != null ) st.push(tmp.left);if (tmp.right != null ) st.push(tmp.right);for (int i = 0 , j = res.size() - 1 ; i < j; i++, j--) {int tmp = res.get(i);return res;
2. 中序遍历 不同的根本原因:遍历的顺序与处理的顺序不同
与其他两种遍历方法相比,需要额外添加一个指针,指向遍历(访问)到的元素。栈用来存放遍历过的顺序。处理的时候按照遍历的逆向顺序进行处理。
为了解释清楚,我说明一下 刚刚在迭代的过程中,其实我们有两个操作:
处理:将元素放进result数组中 访问:遍历节点
分析一下为什么刚刚写的前序遍历的代码,不能和中序遍历通用呢,因为前序遍历的顺序是中左右,先访问的元素是中间节点,要处理的元素也是中间节点,所以刚刚才能写出相对简洁的代码,因为要访问的元素和要处理的元素顺序是一致的,都是中间节点。
那么再看看中序遍历,中序遍历是左中右,先访问的是二叉树顶部的节点,然后一层一层向下访问,直到到达树左面的最底部,再开始处理节点(也就是在把节点的数值放进result数组中),这就造成了处理顺序和访问顺序是不一致的。
那么在使用迭代法写中序遍历,就需要借用指针的遍历来帮助访问节点,栈则用来处理节点上的元素。
动画如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 class Solution {public List<Integer> inorderTraversal (TreeNode root) {new ArrayList <>();new Stack <>();if (root == null ) return res;TreeNode cur = root;while (cur != null || !st.isEmpty()) {if (cur != null ) {else {return res;
3. 统一迭代法 思路
在遍历二叉树时,我们先访问的是中间节点,而前序遍历刚好就是要先处理中间节点,访问和处理可以同时进行。后续遍历的代码和前序遍历一样,也是先访问中间节点并处理中间节点,只不过交换左右节点的入栈顺序并且最后翻转一下结果数组。
但是中序遍历要先处理的是左节点,但是访问时先访问的是中间节点,处理和访问不能同时进行。
迭代统一写法
用栈来保存访问过的节点,注意要保证出栈的顺序与遍历顺序一致。比如中序遍历是“左中右”,那么入栈的顺序应该为“右中左”,这样出栈时才是”左中右”。
我们要处理的节点都是中间节点,只不过三种遍历方式处理中间节点的顺序不一样。在中间节点入栈时我们要标记一下,用于判断该节点是中间节点。怎么标记呢?可以在中间节点入栈后再入栈一个空节点null。
首先判断根节点是否为空,不为空就入栈。
开始遍历时,让当前节点指向栈顶节点,分为2种情况:
栈顶节点不为空,那么我们要按顺序将该节点和它的左右节点入栈,这里就是三种遍历方式唯一不同的地方。
栈顶节点为空,说明遇到了可以处理的中间节点,将空节点弹出,然后弹出中间节点,并将它的值加入结果数组。
遍历结束的条件就是栈为空。
代码实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 class Solution {public List<Integer> inorderTraversal (TreeNode root) {new Stack <>();new ArrayList <>();if (root == null ) return res;while (!st.isEmpty()) {TreeNode cur = st.peek();if (cur != null ) {if (cur.right != null ) st.push(cur.right);null );if (cur.left != null ) st.push(cur.left);else { return res;var preorderTraversal = function(root) {let stack = []let ans = []if (root) stack.push(root)while (stack.length){let cur = stack[stack.length - 1 ]if (cur){ else { return ans
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 if (cur.right != null ) st.push(cur.right);if (cur.left != null ) st.push(cur.left);null );
1 2 3 4 5 6 if (cur.right != null ) st.push(cur.right);null );if (cur.left != null ) st.push(cur.left);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 null );if (cur.right != null ) st.push(cur.right);if (cur.left != null ) st.push(cur.left);
7.2.3 二叉树的层序遍历 思路
二叉树的层序遍历可以借助队列来实现。
按照实现方法的不同,可以分为递归和迭代两种方式。
方法一:迭代,借助队列实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder (TreeNode root) {new ArrayList <>();new LinkedList <>();if (root == null ) return res;while (!q.isEmpty()) {new ArrayList <>();int size = q.size();for (int i = 0 ; i < size; i++) {TreeNode tmp = q.poll();if (tmp.left != null ) q.offer(tmp.left);if (tmp.right != null ) q.offer(tmp.right);return res;
方法二:递归
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 public void checkFun (TreeNode node, List<List<Integer>> resList, Integer deep) {if (node == null ) return ;if (resList.size() == deep) {new ArrayList <Integer>();1 );1 );public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder (TreeNode root) {new ArrayList <List<Integer>>();0 );return resList;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;class TreeNode {int val;int val) {this .val = val;public class LevelOrderTraversal {public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder (TreeNode root) {new ArrayList <>();0 , result);return result;private void traverse (TreeNode node, int level, List<List<Integer>> result) {if (node == null ) {return ;if (result.size() <= level) {new ArrayList <>());1 , result);1 , result);public static void main (String[] args) {TreeNode root = new TreeNode (1 );new TreeNode (2 );new TreeNode (3 );new TreeNode (4 );new TreeNode (5 );new TreeNode (6 );new TreeNode (7 );LevelOrderTraversal traversal = new LevelOrderTraversal ();
说明
递归逻辑 :
传递当前节点和层级信息,递归遍历树。
如果当前层级的 List 尚未创建,则新建一个。
将节点值添加到相应层级列表中。
终止条件 :
如果节点为空(node == null),直接返回。
时间复杂度 :
每个节点被访问一次,因此时间复杂度为 $O(n)$,其中 n 是节点总数。
空间复杂度 :
递归栈的深度等于树的高度,最坏情况下空间复杂度为 $O(h)$,其中 h 是树的高度。
7.3 翻转二叉树 关键在于遍历顺序 ,前中后序应该选哪一种遍历顺序?
遍历的过程中去翻转每一个节点的左右孩子就可以达到整体翻转的效果。
注意只要把每一个节点的左右孩子翻转一下,就可以达到整体翻转的效果
这道题目使用前序遍历和后序遍历都可以,唯独中序遍历不方便 ,因为中序遍历会把某些节点的左右孩子翻转了两次!建议拿纸画一画,就理解了
那么层序遍历可以不可以呢?依然可以的!只要把每一个节点的左右孩子翻转一下的遍历方式都是可以的!
思路一:递归法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution {public void reverse (TreeNode node) {if (node == null ) return ;TreeNode tmp = new TreeNode ();public TreeNode invertTree (TreeNode root) {return root;
我们下文以前序遍历为例,通过动画来看一下翻转的过程:
我们来看一下递归三部曲:
确定递归函数的参数和返回值
参数就是要传入节点的指针,不需要其他参数了,通常此时定下来主要参数,如果在写递归的逻辑中发现还需要其他参数的时候,随时补充。
返回值的话其实也不需要,但是题目中给出的要返回root节点的指针,可以直接使用题目定义好的函数,所以就函数的返回类型为TreeNode*。
1 TreeNode* invertTree (TreeNode* root)
确定终止条件
当前节点为空的时候,就返回
1 if (root == NULL ) return root;
确定单层递归的逻辑
因为是先前序遍历,所以先进行交换左右孩子节点,然后反转左子树,反转右子树。
1 2 3 swap (root->left, root->right);invertTree (root->left);invertTree (root->right);
基于这递归三步法,代码基本写完,C++代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 class Solution {public :TreeNode* invertTree (TreeNode* root) {if (root == NULL ) return root;swap (root->left, root->right); invertTree (root->left); invertTree (root->right); return root;
思路二:迭代法
深度优先遍历(前序、后序遍历)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution {public void swap (TreeNode root) {TreeNode temp = root.left;public List<Integer> preorderTraversal (TreeNode root) {new ArrayList <>();new Stack <>();if (root == null ) return res;while (!st.isEmpty()) {TreeNode tmp = st.peek();if (tmp.right != null ) st.push(tmp.right);if (tmp.left != null ) st.push(tmp.left);return res;
广度优先遍历(层序遍历)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution {public TreeNode invertTree (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) {return null ;}new ArrayDeque <>();while (!deque.isEmpty()) {int size = deque.size();while (size-- > 0 ) {TreeNode node = deque.poll();if (node.left != null ) deque.offer(node.left);if (node.right != null ) deque.offer(node.right);return root;public void swap (TreeNode root) {TreeNode temp = root.left;
7.4 对称二叉树 首先想清楚,判断对称二叉树要比较的是哪两个节点,要比较的可不是左右节点!
对于二叉树是否对称,要比较的是根节点的左子树与右子树是不是相互翻转的,理解这一点就知道了其实我们要比较的是两个树(这两个树是根节点的左右子树) ,所以在递归遍历的过程中,也是要同时遍历两棵树。
思路一:迭代 我们可以实现这样一个递归函数,通过「同步移动」两个指针的方法来遍历这棵树,p 指针和 q 指针一开始都指向这棵树的根,随后 p 右移时,q 左移,p 左移时,q 右移。每次检查当前 p 和 q 节点的值是否相等,如果相等再判断左右子树是否对称。
代码随想录 (programmercarl.com)
https://leetcode.cn/problems/symmetric-tree/solutions/2361627/101-dui-cheng-er-cha-shu-fen-zhi-qing-xi-8oba
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 class Solution {public boolean compare (TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {if (left == null && right == null ) return true ;else if (left == null || right == null ) {return false ;else if (left.val != right.val){return false ;boolean out = compare(left.left, right.right);boolean in = compare(left.right, right.left);return out∈public boolean isSymmetric (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) return true ;return compare(root.left, root.right);class Solution {public boolean isSymmetric (TreeNode root) {return check(root.left, root.right);public boolean check (TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {if (p == null && q == null ) {return true ;if (p == null || q == null ) {return false ;return p.val == q.val && check(p.left, q.right) && check(p.right, q.left);
思路二:递归 这道题目我们也可以使用迭代法,但要注意,这里的迭代法可不是前中后序的迭代写法,因为本题的本质是判断两个树是否是相互翻转的,其实已经不是所谓二叉树遍历的前中后序的关系了。
这里我们可以使用队列来比较两个树(根节点的左右子树)是否相互翻转,(注意这不是层序遍历 )
还是模仿上述操作,首先比较当前左右节点,判断null->判断值是否相等->值相等则将需要比较的节点对加入队列(左节点左孩子,右节点右孩子),(左节点右孩子,右节点左孩子)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution {public boolean isSymmetric (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) return true ;new LinkedList <>();while (!que.isEmpty()) {TreeNode leftNode = que.poll();TreeNode rightNode = que.poll();if (leftNode == null && rightNode == null ) {continue ;if (leftNode == null || rightNode == null || (leftNode.val != rightNode.val)) {return false ;return true ;
7.5 二叉树的最大深度 思路一:迭代法(层序遍历) 在二叉树中,一层一层的来遍历二叉树,记录一下遍历的层数就是二叉树的深度
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution {public int maxDepth (TreeNode root) {int depth = 0 ;new LinkedList <>();if (root == null ) return depth;while (!que.isEmpty()) {int size = que.size();while (size-- > 0 ) {TreeNode node = que.poll();if (node.left != null ) que.offer(node.left);if (node.right != null ) que.offer(node.right);return depth;
思路二:递归法(后序遍历:高度;前序遍历:深度) 本题可以使用前序(中左右),也可以使用后序遍历(左右中),使用前序 求的就是深度 ,使用后序 求的是高度 。
二叉树节点的深度:指从根节点到该节点的最长简单路径边的条数或者节点数(取决于深度从0开始还是从1开始)
二叉树节点的高度:指从该节点到叶子节点的最长简单路径边的条数或者节点数(取决于高度从0开始还是从1开始)
而根节点的高度就是二叉树的最大深度 ,所以本题中我们通过后序 求的根节点高度来求的二叉树最大深度。
后序遍历(DFS) 如果我们知道了左子树和右子树的最大深度 l 和 r,那么该二叉树的最大深度即为$max(l,r)+1$。
而左子树和右子树的最大深度又可以以同样的方式进行计算。因此我们可以用「深度优先搜索」的方法来计算二叉树的最大深度。具体而言,在计算当前二叉树的最大深度时,可以先递归计算出其左子树和右子树的最大深度,然后在 $O(1) $时间内计算出当前二叉树的最大深度。递归在访问到空节点时退出。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 class Solution {public int maxDepth (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) return 0 ;int leftDepth = maxDepth(root.left);int rightDepth = maxDepth(root.right);return Math.max(leftDepth, rightDepth) + 1 ;
####前序遍历
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution {int maxnum = 0 ;public int maxDepth (TreeNode root) {0 );return maxnum;void ans (TreeNode tr,int tmp) {if (tr==null ) return ;
7.6 二叉树的最小深度 思路一:递归法 求二叉树的最小深度和求二叉树的最大深度的差别主要在于处理左右孩子不为空的逻辑。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 class Solution {public int minDepth (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) return 0 ;if (root.left == null && root.right != null ) return 1 + minDepth(root.right);else if (root.left != null && root.right == null ) return 1 + minDepth(root.left);return 1 + Math.min(minDepth(root.left), minDepth(root.right));
确定递归函数的参数和返回值
参数为要传入的二叉树根节点,返回的是int类型的深度。
代码如下:
1 int getDepth (TreeNode* node)
确定终止条件
终止条件也是遇到空节点返回0,表示当前节点的高度为0。
代码如下:
1 if (node == NULL ) return 0 ;
确定单层递归的逻辑
这块和求最大深度可就不一样了,一些同学可能会写如下代码:
1 2 3 4 int leftDepth = getDepth (node->left);int rightDepth = getDepth (node->right);int result = 1 + min (leftDepth, rightDepth);return result;
如果这么求的话,没有左孩子的分支会算为最短深度。
所以,如果左子树为空,右子树不为空,说明最小深度是 1 + 右子树的深度。
反之,右子树为空,左子树不为空,最小深度是 1 + 左子树的深度。 最后如果左右子树都不为空,返回左右子树深度最小值 + 1 。
代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 int leftDepth = getDepth (node->left); int rightDepth = getDepth (node->right); if (node->left == NULL && node->right != NULL ) { return 1 + rightDepth;if (node->left != NULL && node->right == NULL ) { return 1 + leftDepth;int result = 1 + min (leftDepth, rightDepth);return result;
遍历的顺序为后序(左右中),可以看出:求二叉树的最小深度和求二叉树的最大深度的差别主要在于处理左右孩子不为空的逻辑。
思路二:迭代法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution {public int minDepth (TreeNode root) {new LinkedList <>();int depth = 0 ;if (root == null ) return depth;while (!que.isEmpty()) {int size = que.size();while (size-- > 0 ) {TreeNode node = que.poll();if (node.left == null && node.right == null ) return depth;if (node.left != null ) que.offer(node.left);if (node.right != null ) que.offer(node.right);return depth;
7.7 完全二叉树的节点个数 普通二叉树 递归
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Solution {public int count (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) return 0 ;int leftCount = count(root.left);int rightCount = count(root.right);return leftCount + rightCount + 1 ;public int countNodes (TreeNode root) {return count(root);
迭代
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution {public int countNodes (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) return 0 ;new LinkedList <>();int result = 0 ;while (!queue.isEmpty()) {int size = queue.size();while (size -- > 0 ) {TreeNode cur = queue.poll();if (cur.left != null ) queue.offer(cur.left);if (cur.right != null ) queue.offer(cur.right);return result;
完全二叉树 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 class Solution {public int countNodes (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) return 0 ;TreeNode left = root.left;TreeNode right = root.right;int leftDepth = 0 , rightDepth = 0 ; while (left != null ) { while (right != null ) { if (leftDepth == rightDepth) {return (2 << leftDepth) - 1 ; return countNodes(root.left) + countNodes(root.right) + 1 ;class Solution {public int countNodes (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) return 0 ;TreeNode leftNode = root.left;TreeNode rightNode = root.right;int l = 0 , r = 0 ;while (leftNode != null ) {while (rightNode != null ) {if (l == r) {return (2 << l) - 1 ;return countNodes(root.left) + countNodes(root.right) + 1 ;
时间复杂度:O(log n × log n)
空间复杂度:O(log n)
7.8 平衡二叉树 给定一个二叉树,判断它是否是高度平衡的二叉树。
本题中,一棵高度平衡二叉树定义为:一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1。
递归 要求比较高度,必然是要后序遍历。
递归三步曲分析:
明确递归函数的参数和返回值
参数:当前传入节点。 返回值:以当前传入节点为根节点的树的高度。
那么如何标记左右子树是否差值大于1呢?
如果当前传入节点为根节点的二叉树已经不是二叉平衡树了,还返回高度的话就没有意义了。
所以如果已经不是二叉平衡树了,可以返回-1 来标记已经不符合平衡树的规则了。
1 2 int getHeight (TreeNode* node)
明确终止条件
递归的过程中依然是遇到空节点了为终止,返回0,表示当前节点为根节点的树高度为0
1 2 3 if (node == NULL ) {return 0 ;
明确单层递归的逻辑
如何判断以当前传入节点为根节点的二叉树是否是平衡二叉树呢?当然是其左子树高度和其右子树高度的差值。
分别求出其左右子树的高度,然后如果差值小于等于1,则返回当前二叉树的高度,否则返回-1,表示已经不是二叉平衡树了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 int leftHeight = getHeight (node->left); if (leftHeight == -1 ) return -1 ;int rightHeight = getHeight (node->right); if (rightHeight == -1 ) return -1 ;int result;if (abs (leftHeight - rightHeight) > 1 ) { -1 ;else {1 + max (leftHeight, rightHeight); return result;int leftHeight = getHeight (node->left);if (leftHeight == -1 ) return -1 ;int rightHeight = getHeight (node->right);if (rightHeight == -1 ) return -1 ;return abs (leftHeight - rightHeight) > 1 ? -1 : 1 + max (leftHeight, rightHeight);
代码实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution {public int getHeight (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) return 0 ;int leftHeight = getHeight(root.left);if (leftHeight == -1 ) return -1 ;int rightHeight = getHeight(root.right);if (rightHeight == -1 ) return -1 ;if (Math.abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) > 1 ) {return -1 ;return 1 + Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight);public boolean isBalanced (TreeNode root) {return getHeight(root) == -1 ? false : true ;
Leetcode思路
方法一:自顶向下的递归
定义函数 height,用于计算二叉树中的任意一个节点 p 的高度:
有了计算节点高度的函数,即可判断二叉树是否平衡。具体做法类似于二叉树的前序遍历,即对于当前遍历到的节点,首先计算左右子树的高度,如果左右子树的高度差是否不超过 1,再分别递归地遍历左右子节点,并判断左子树和右子树是否平衡。这是一个自顶向下的递归的过程。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution {public boolean isBalanced (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) {return true ;else {return Math.abs(height(root.left) - height(root.right)) <= 1 && isBalanced(root.left) && isBalanced(root.right);public int height (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) {return 0 ;else {return Math.max(height(root.left), height(root.right)) + 1 ;
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(n^2)$,其中 n 是二叉树中的节点个数。
最坏情况下,二叉树是满二叉树,需要遍历二叉树中的所有节点,时间复杂度是 O(n)。
对于节点 p,如果它的高度是 d,则 height(p) 最多会被调用 d 次(即遍历到它的每一个祖先节点时)。对于平均的情况,一棵树的高度 h 满足 O(h)=O(logn),因为 d≤h,所以总时间复杂度为 O(nlogn)。对于最坏的情况,二叉树形成链式结构,高度为 O(n),此时总时间复杂度为 O(n2)。
空间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 是二叉树中的节点个数。空间复杂度主要取决于递归调用的层数,递归调用的层数不会超过 n。
方法二:自底向上的递归
方法一由于是自顶向下递归,因此对于同一个节点,函数 height 会被重复调用,导致时间复杂度较高。如果使用自底向上的做法,则对于每个节点,函数 height 只会被调用一次。
自底向上递归的做法类似于后序遍历,对于当前遍历到的节点,先递归地判断其左右子树是否平衡,再判断以当前节点为根的子树是否平衡。如果一棵子树是平衡的,则返回其高度(高度一定是非负整数),否则返回 −1。如果存在一棵子树不平衡,则整个二叉树一定不平衡。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution {public boolean isBalanced (TreeNode root) {return height(root) >= 0 ;public int height (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) {return 0 ;int leftHeight = height(root.left);int rightHeight = height(root.right);if (leftHeight == -1 || rightHeight == -1 || Math.abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) > 1 ) {return -1 ;else {return Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1 ;
迭代 本题的迭代方式可以先定义一个函数,专门用来求高度。
这个函数通过栈模拟的后序遍历找每一个节点的高度(其实是通过求传入节点为根节点的最大深度来求的高度)
然后再用栈来模拟后序遍历,遍历每一个节点的时候,再去判断左右孩子的高度是否符合
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 class Solution {public boolean isBalanced (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) {return true ;new Stack <>();TreeNode pre = null ;while (root!= null || !stack.isEmpty()) {while (root != null ) {TreeNode inNode = stack.peek();if (inNode.right == null || inNode.right == pre) {if (Math.abs(getHeight(inNode.left) - getHeight(inNode.right)) > 1 ) {return false ;null ;else {return true ;public int getHeight (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) {return 0 ;new LinkedList <>();int depth = 0 ;while (!deque.isEmpty()) {int size = deque.size();for (int i = 0 ; i < size; i++) {TreeNode poll = deque.poll();if (poll.left != null ) {if (poll.right != null ) {return depth;class Solution {public boolean isBalanced (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) {return true ;new Stack <>();TreeNode pre = null ;while (root != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {while (root != null ) {TreeNode inNode = stack.peek();if (inNode.right == null || inNode.right == pre) {if (Math.abs(getHeight(inNode.left) - getHeight(inNode.right)) > 1 ) {return false ;null ;else {return true ;public int getHeight (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) {return 0 ;int leftHeight = root.left != null ? root.left.val : 0 ;int rightHeight = root.right != null ? root.right.val : 0 ;int height = Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1 ;return height;
通过本题可以了解求二叉树深度 和 二叉树高度的差异,求深度适合用前序遍历,而求高度适合用后序遍历。
本题迭代法其实有点复杂,大家可以有一个思路,也不一定说非要写出来。
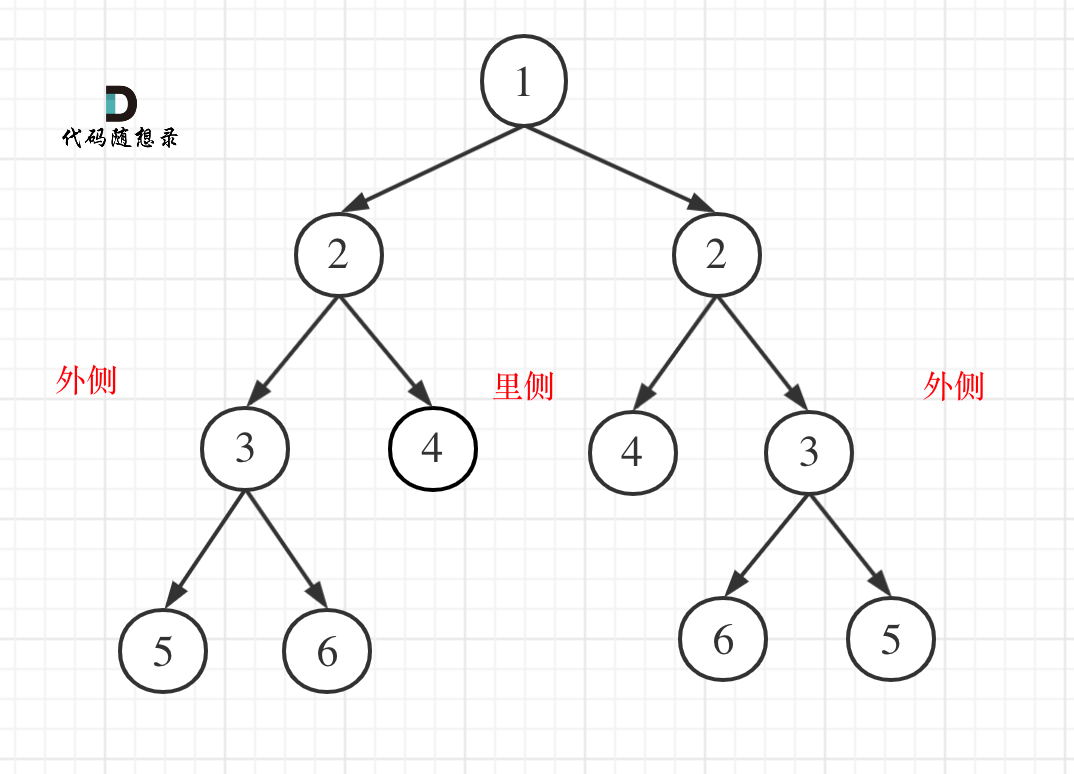
7.9 二叉树的所有路径 四种解法:https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-paths/solutions/400434/257-er-cha-shu-de-suo-you-lu-jing-tu-wen-jie-xi-by
思路 这道题目要求从根节点到叶子的路径,所以需要前序遍历 ,这样才方便让父节点指向孩子节点,找到对应的路径。
在这道题目中将第一次涉及到回溯 ,因为我们要把路径记录下来,需要回溯来回退一个路径再进入另一个路径。
解法一:递归
递归函数参数以及返回值
要传入根节点,记录每一条路径的path,和存放结果集的result,这里递归不需要返回值,代码如下:
1 void traversal (TreeNode* cur, vector<int >& path, vector<string>& result)
确定递归终止条件
在写递归的时候都习惯了这么写:
1 2 3 if (cur == NULL ) {
但是本题的终止条件这样写会很麻烦,因为本题要找到叶子节点,就开始结束的处理逻辑了(把路径放进result里)。
那么什么时候算是找到了叶子节点? 是当 cur不为空,其左右孩子都为空的时候,就找到叶子节点。
所以本题的终止条件是:
1 2 3 if (cur->left == NULL && cur->right == NULL ) {
为什么没有判断cur是否为空呢,因为下面的逻辑可以控制空节点不入循环。
再来看一下终止处理的逻辑。
那么为什么使用了vector 结构来记录路径呢? 因为在下面处理单层递归逻辑的时候,要做回溯,使用vector方便来做回溯。
可能有的同学问了,我看有些人的代码也没有回溯啊。
其实是有回溯的,只不过隐藏在函数调用时的参数赋值里 ,即String + ‘->’ 。
这里我们先使用vector结构的path容器来记录路径,那么终止处理逻辑如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 if (cur->left == NULL && cur->right == NULL ) { for (int i = 0 ; i < path.size () - 1 ; i++) { to_string (path[i]);"->" ;to_string (path[path.size () - 1 ]); push_back (sPath); return ;
确定单层递归逻辑
因为是前序遍历,需要先处理中间节点,中间节点就是我们要记录路径上的节点,先放进path中。
1 path.push_back(cur->val );
然后是递归和回溯的过程,上面说过没有判断cur是否为空,那么在这里递归的时候,如果为空就不进行下一层递归了。
所以递归前要加上判断语句,下面要递归的节点是否为空,如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 if (cur->left) {traversal (cur->left, path, result);if (cur->right) {traversal (cur->right, path, result);
此时还没完,递归完,要做回溯啊,因为path 不能一直加入节点,它还要删节点,然后才能加入新的节点。
那么回溯要怎么回溯呢,一些同学会这么写,如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 if (cur->left) {traversal (cur->left, path, result);if (cur->right) {traversal (cur->right, path, result);pop_back ();
这个回溯就有很大的问题,我们知道,回溯和递归是一一对应的,有一个递归,就要有一个回溯 ,这么写的话相当于把递归和回溯拆开了, 一个在花括号里,一个在花括号外。
所以回溯要和递归永远在一起,世界上最遥远的距离是你在花括号里,而我在花括号外!
那么代码应该这么写:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 if (cur->left) {traversal (cur->left, path, result);pop_back (); if (cur->right) {traversal (cur->right, path, result);pop_back ();
整体代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 class Solution {public List<String> binaryTreePaths (TreeNode root) {new ArrayList <>();if (root == null ) {return res;new ArrayList <>();return res;private void traversal (TreeNode root, List<Integer> paths, List<String> res) {if (root.left == null && root.right == null ) {StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder ();for (int i = 0 ; i < paths.size() - 1 ; i++) {"->" );1 ));return ;if (root.left != null ) { 1 );if (root.right != null ) { 1 );
简化版代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution {new ArrayList <>();public List<String> binaryTreePaths (TreeNode root) {"" );return result;public void deal (TreeNode node, String s) {if (node == null )return ;if (node.left == null && node.right == null ) {new StringBuilder (s).append(node.val).toString());return ;String tmp = new StringBuilder (s).append(node.val).append("->" ).toString();
我自己写的时候实现如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution {public void path (TreeNode cur, String path, List<String> res) {if (cur == null ) return ;if (cur.left == null && cur.right == null ) {else {"->" ;public List<String> binaryTreePaths (TreeNode root) {new ArrayList <>();"" , res);return res;
这是leetcode题解的写法,和上述差不多
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public List<String> binaryTreePaths (TreeNode root) {new ArrayList <>();"" , res);return res;private void dfs (TreeNode root, String path, List<String> res) {if (root == null )return ;if (root.left == null && root.right == null ) {return ;"->" , res);"->" , res);
解法二:迭代 栈实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 public List<String> binaryTreePaths (TreeNode root) {new ArrayList <>();if (root == null )return res;new Stack <>();"" );while (!stack.isEmpty()) {String path = (String) stack.pop();TreeNode node = (TreeNode) stack.pop();if (node.left == null && node.right == null ) {if (node.right != null ) {"->" + node.right.val);if (node.left != null ) {"->" + node.left.val);return res;
队列实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 public List<String> binaryTreePaths (TreeNode root) {new ArrayList <>();if (root == null )return res;new LinkedList <>();"" );while (!queue.isEmpty()) {TreeNode node = (TreeNode) queue.poll();String path = (String) queue.poll();if (node.left == null && node.right == null ) {if (node.right != null ) {"->" + node.right.val);if (node.left != null ) {"->" + node.left.val);return res;
7.10 左子叶之和 这道题目要求左叶子之和,其实是比较绕的,因为不能判断本节点是不是左叶子节点。
此时就要通过节点的父节点来判断其左孩子是不是左叶子了。
递归法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 class Solution {public int sumOfLeftLeaves (TreeNode root) {return root != null ? dfs(root) : 0 ;public int dfs (TreeNode node) {int ans = 0 ;if (node.left != null ) {if (node.right != null && !isLeafNode(node.right)) {return ans;public boolean isLeafNode (TreeNode node) {return node.left == null && node.right == null ;class Solution {public int sumLeftLeaf (TreeNode cur) {if (cur == null ) return 0 ;int left = sumLeftLeaf(cur.left);if (cur.left != null && cur.left.left == null && cur.left.right == null ) left = cur.left.val;int right = sumLeftLeaf(cur.right);return left + right;public int sumOfLeftLeaves (TreeNode root) {return sumLeftLeaf(root);
简化版:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Solution {public :int sumOfLeftLeaves (TreeNode* root) {if (root == NULL) return 0 ;int leftValue = 0 ;if (root->left != NULL && root->left->left == NULL && root->left->right == NULL) {return leftValue + sumOfLeftLeaves(root->left) + sumOfLeftLeaves(root->right);
迭代法 前中后序遍历均可,只需要判断当前节点左孩子是否是叶子节点即可。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 class Solution {public int sumOfLeftLeaves (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) return 0 ;int sum = 0 ;new Stack <>();while (!st.isEmpty()) {TreeNode node = st.pop();if (node.left != null && node.left.left == null && node.left.right == null ) sum += node.left.val;if (node.left != null ) st.push(node.left);if (node.right != null ) st.push(node.right);return sum;class Solution {public int sumOfLeftLeaves (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) {return 0 ;new LinkedList <TreeNode>();int ans = 0 ;while (!queue.isEmpty()) {TreeNode node = queue.poll();if (node.left != null ) {if (isLeafNode(node.left)) {else {if (node.right != null ) {if (!isLeafNode(node.right)) {return ans;public boolean isLeafNode (TreeNode node) {return node.left == null && node.right == null ;
7.11 找树左下角的值 迭代法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 class Solution {public :int findBottomLeftValue (TreeNode* root) {if (root != NULL) que.push(root);int result = 0 ;while (!que.empty()) {int size = que.size();for (int i = 0 ; i < size; i++) {if (i == 0 ) result = node->val; if (node->left) que.push(node->left);if (node->right) que.push(node->right);return result;class Solution {public int findBottomLeftValue (TreeNode root) {new LinkedList <>();new ArrayList <>();while (!que.isEmpty()) {int size = que.size();new ArrayList <>();while (size-- > 0 ) {TreeNode node = que.poll();if (node.left != null ) que.offer(node.left);if (node.right != null ) que.offer(node.right);return res.get(res.size() - 1 ).get(0 );
递归法 我们来分析一下题目:在树的最后一行 找到最左边的值 。
首先要是最后一行,然后是最左边的值。
如果使用递归法,如何判断是最后一行呢,其实就是深度最大的叶子节点一定是最后一行。
所以要找深度最大的叶子节点。
那么如何找最左边的呢?可以使用前序遍历(当然中序,后序都可以,因为本题没有 中间节点的处理逻辑,只要左优先就行),保证优先左边搜索,然后记录深度最大的叶子节点,此时就是树的最后一行最左边的值。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution {private int Deep = -1 ;private int value = 0 ;public int findBottomLeftValue (TreeNode root) {0 );return value;private void findLeftValue (TreeNode root,int deep) {if (root == null ) return ;if (root.left == null && root.right == null ) {if (deep > Deep) {if (root.left != null ) findLeftValue(root.left,deep + 1 );if (root.right != null ) findLeftValue(root.right,deep + 1 );
递归三部曲:
确定递归函数的参数和返回值
参数必须有要遍历的树的根节点,还有就是一个int型的变量用来记录最长深度。 这里就不需要返回值了,所以递归函数的返回类型为void。
本题还需要类里的两个全局变量,maxLen用来记录最大深度,result记录最大深度最左节点的数
1 2 3 int maxDepth = INT_MIN; int result; void traversal (TreeNode* root, int depth)
确定终止条件
当遇到叶子节点的时候,就需要统计一下最大的深度了,所以需要遇到叶子节点来更新最大深度。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL ) {if (depth > maxDepth) {return ;
确定单层递归的逻辑
在找最大深度的时候,递归的过程中依然要使用回溯,代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 if (root->left) { traversal (root->left, depth);if (root->right) { traversal (root->right, depth);return ;
7.12 路经总和 ※什么时候递归需要返回值?
如果需要搜索整棵二叉树且不用处理递归返回值,递归函数就不要返回值。(这种情况就是本文下半部分介绍的113.路径总和ii)
如果需要搜索整棵二叉树且需要处理递归返回值,递归函数就需要返回值。 (这种情况我们在236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先 (opens new window) 中介绍)
如果要搜索其中一条符合条件的路径,那么递归一定需要返回值,因为遇到符合条件的路径了就要及时返回。(本题的情况)
递归法 回溯 这里的回溯指 利用 DFS 找出从根节点到叶子节点的所有路径,只要有任意一条路径的 和 等于 sum,就返回 True。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 class Solution {public boolean res = false ;public void traversal (TreeNode root, int pathSum, int targetSum) {if (root.left == null && root.right == null ) {if (pathSum == targetSum) {true ;return ;if (root.left != null ) {if (root.right != null ) {public boolean hasPathSum (TreeNode root, int targetSum) {if (root == null ) return false ;return res;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;public class Solution {public boolean hasPathSum (TreeNode root, int sum) {if (root == null ) return false ;return dfs(root, sum, new ArrayList <>());private boolean dfs (TreeNode root, int target, List<Integer> path) {if (root == null ) return false ;if (target == 0 && root.left == null && root.right == null ) {return true ;boolean leftFlag = false , rightFlag = false ;if (root.left != null ) {new ArrayList <>(path));if (root.right != null ) {new ArrayList <>(path));1 ); return leftFlag || rightFlag;
leetcode&&代码随想录解法
确定递归函数的参数和返回类型
参数:需要二叉树的根节点,还需要一个计数器,这个计数器用来计算二叉树的一条边之和是否正好是目标和,计数器为int型。
返回值:boolean
确定终止条件
首先计数器如何统计这一条路径的和呢?
不要去累加然后判断是否等于目标和,那么代码比较麻烦,可以用递减 ,让计数器count初始为目标和,然后每次减去遍历路径节点上的数值 。
如果最后count == 0,同时到了叶子节点的话,说明找到了目标和。
如果遍历到了叶子节点,count不为0,就是没找到。
1 2 if (!cur->left && !cur->right && count == 0 ) return true ; if (!cur->left && !cur->right) return false ;
确定单层递归的逻辑
因为终止条件是判断叶子节点,所以递归的过程中就不要让空节点进入递归了。
递归函数是有返回值的,如果递归函数返回true,说明找到了合适的路径,应该立刻返回。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 if (cur->left) { if (traversal (cur->left, count - cur->left->val)) return true ; if (cur->right) { if (traversal (cur->right, count - cur->right->val)) return true ; return false ;
leetcode思路及算法
观察要求我们完成的函数,我们可以归纳出它的功能:询问是否存在从当前节点 root 到叶子节点的路径,满足其路径和为 sum。
假定从根节点到当前节点的值之和为 val,我们可以将这个大问题转化为一个小问题:是否存在从当前节点的子节点到叶子的路径,满足其路径和为 sum - val。
不难发现这满足递归的性质,若当前节点就是叶子节点,那么我们直接判断 sum 是否等于 val 即可(因为路径和已经确定,就是当前节点的值,我们只需要判断该路径和是否满足条件)。若当前节点不是叶子节点,我们只需要递归地询问它的子节点是否能满足条件即可。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 class solution {public boolean haspathsum (treenode root, int targetsum) {if (root == null ) {return false ;if (root.left == null && root.right == null ) {return targetsum == 0 ;if (root.left != null ) {boolean left = haspathsum(root.left, targetsum);if (left) { return true ;if (root.right != null ) {boolean right = haspathsum(root.right, targetsum);if (right) { return true ;return false ;class solution {public boolean haspathsum (treenode root, int targetsum) {if (root == null ) return false ; if (root.left == null && root.right == null ) return root.val == targetsum;return haspathsum(root.left, targetsum - root.val) || haspathsum(root.right, targetsum - root.val);
迭代法 广度优先搜索 首先我们可以想到使用广度优先搜索的方式,记录从根节点到当前节点的路径和,以防止重复计算。
这样我们使用两个队列,分别存储将要遍历的节点,以及根节点到这些节点的路径和即可。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution {public boolean hasPathSum (TreeNode root, int sum) {if (root == null ) {return false ;new LinkedList <TreeNode>();new LinkedList <Integer>();while (!queNode.isEmpty()) {TreeNode now = queNode.poll();int temp = queVal.poll();if (now.left == null && now.right == null ) {if (temp == sum) {return true ;continue ;if (now.left != null ) {if (now.right != null ) {return false ;
栈的迭代 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 class solution {public boolean haspathsum (treenode root, int targetsum) {if (root == null ) return false ;new stack <>();new stack <>();while (!stack1.isempty()) {int size = stack1.size();for (int i = 0 ; i < size; i++) {treenode node = stack1.pop();int sum = stack2.pop();if (node.left == null && node.right == null && sum == targetsum) {return true ;if (node.right != null ){if (node.left != null ) {return false ;
113. 路径总和ii 迭代——回溯法 加法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList <>();public void traversal (TreeNode root, List<Integer> path, int targetSum) {if (root.left == null && root.right == null ) {int sum = 0 ;for (int i: path) sum += i;if (sum == targetSum) res.add(path);return ;if (root.left != null ) {new ArrayList <>(path), targetSum);if (root.right != null ) {new ArrayList <>(path), targetSum);1 );public List<List<Integer>> pathSum (TreeNode root, int targetSum) {if (root == null ) return res;new ArrayList <>();return res;
减法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class solution {public List<List<Integer>> pathsum (TreeNode root, int targetsum) {new ArrayList <>();if (root == null ) return res; new LinkedList <>();return res;public void preorderdfs (TreeNode root, int targetsum, List<List<Integer>> res, List<Integer> path) {if (root.left == null && root.right == null ) {if (targetsum - root.val == 0 ) {new ArrayList <>(path));return ; if (root.left != null ) {1 ); if (root.right != null ) {1 );
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> pathSum (TreeNode root,int targetSum) {new LinkedList <>();new LinkedList <>();return result;private void travesal (TreeNode root, int count) {if (root == null ) return ;if (root.left == null && root.right == null && count == 0 ) {new LinkedList <>(path));
7.13 由中序和后序遍历序列构建二叉树 以下两种遍历顺序的组合可以构建二叉树:
前序和后序不能唯一确定一棵二叉树!,因为没有中序遍历无法确定左右部分,也就是无法分割。
实现思路
过程模拟,遵循循环不变量原则,在切分中序和后序数组的时候坚持左闭右开区间。
代码实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 class Solution {public TreeNode buildTree (int [] inorder, int [] postorder) {new HashMap <>();for (int i = 0 ; i < inorder.length; i++) { return findNode(inorder, 0 , inorder.length, postorder,0 , postorder.length); public TreeNode findNode (int [] inorder, int inBegin, int inEnd, int [] postorder, int postBegin, int postEnd) {if (inBegin >= inEnd || postBegin >= postEnd) { return null ;int rootIndex = map.get(postorder[postEnd - 1 ]); TreeNode root = new TreeNode (inorder[rootIndex]); int lenOfLeft = rootIndex - inBegin; 1 , inEnd,1 );return root;class Solution {public Map<Integer, Integer> map;public TreeNode buildTree (int [] inorder, int [] postorder) {new HashMap <>();int count = 0 ;for (int i: inorder) {return findNode(inorder, 0 , inorder.length, postorder, 0 , postorder.length);public TreeNode findNode (int [] inorder, int inBegin, int inEnd, int [] postorder, int postBegin, int postEnd) {if (inBegin >= inEnd || postBegin >= postEnd) return null ;int index = map.get(postorder[postEnd - 1 ]);TreeNode node = new TreeNode (inorder[index]);int len = index - inBegin;1 , inEnd, postorder, postBegin + len, postEnd - 1 );return node;
7.14 最大二叉树 根据题目描述,可知该问题本质是「区间求最值」 问题(RMQ)。
而求解 RMQ 有多种方式:递归分治 、有序集合/ST/线段树 和 单调栈 。
递归法 思路与算法
最简单的方法是直接按照题目描述进行模拟。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution {public TreeNode createNode (int [] nums, int left, int right) {if (right <= left) return null ;int index = 0 , max = -1 ;for (int i = left; i < right; i++) {if (nums[i] > max) {TreeNode node = new TreeNode (max);1 , right);return node;public TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree (int [] nums) {if (nums.length == 0 ) return null ;return createNode(nums, 0 , nums.length);
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(n^2)$,其中 n 是数组 nums 的长度。在最坏的情况下,数组严格递增或递减,需要递归 n 层,第 $i (0≤i<n)$ 层需要遍历 $n−i $个元素以找出最大值,总时间复杂度为 $O(n^2)$。
空间复杂度:$O(n)$,即为最坏情况下需要使用的栈空间。
单调栈 单调栈是找数组中比某个数大的最近的数
根据题目对树的构建的描述可知,nums 中的任二节点所在构建树的水平截面上的位置仅由下标大小决定。 “nums 中的任二节点所在构建树的水平截面上的位置仅由下标大小决定” 意味着,对于任意两个节点,它们在树中的相对位置(左右或上下)不会因为构建过程而发生改变,总是遵循它们在原始数组中的相对顺序。
不难想到可抽象为找最近元素问题,可使用单调栈求解。
具体的,我们可以从前往后处理所有的 nums[i],若存在栈顶元素并且栈顶元素的值比当前值要小,根据我们从前往后处理的逻辑,可确定栈顶元素可作为当前 nums[i] 对应节点的左节点,同时为了确保最终 nums[i] 的左节点为 [0,i−1] 范围的最大值,我们需要确保在构建 nums[i] 节点与其左节点的关系时,[0,i−1] 中的最大值最后出队,此时可知容器栈具有「单调递减」特性。基于此,我们可以分析出,当处理完 nums[i] 节点与其左节点关系后,可明确 nums[i] 可作为未出栈的栈顶元素的右节点。
我们通过递归操作的时候,会发现虽然每次都对数组进行了拆分操作,但是,对数组中的元素也会进行多次的重复遍历,那么有没有一种方式,可以仅通过对数组nums的一次遍历,就可以得出最终结果的呢? 其实有的,我们可以通过单调栈的方式进行操作。
采用单调栈的基本思路是这样的:
如果栈顶元素大于待插入的元素,那么直接入栈。
如果栈顶元素小于待插入的元素,那么栈顶元素出栈。
当然,在对比两个节点大小和出入栈的同时,依然还是会根据题意,进行二叉树的构造。即:
如果栈顶元素大于待插入的元素,则:栈顶元素.right = 待插入元素。
如果栈顶元素小于待插入的元素,则:待插入元素.left = 栈顶元素。
参考思路:https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-binary-tree/solutions/1762400/zhua-wa-mou-si-by-muse-77-myd7
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 class Solution {public TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree (int [] nums) {new ArrayDeque <>();for (int num: nums) {TreeNode cur = new TreeNode (num);while (!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peekLast().val < num) {if (!stack.isEmpty()) {return stack.peekFirst();class Solution { public :int >& nums) {int len = nums.size();if (len == 0 ){return nullptr;int > stk; for (int i = 0 ; i < len; i++){new TreeNode (nums[i]); while (!stk.empty() && nums[i] > nums[stk.back()]){ if (!stk.empty()){ return tree[stk[0 ]];
leetcode官解(看不懂) 思路参考网址:https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-binary-tree/solutions/1759348/zui-da-er-cha-shu-by-leetcode-solution-lbeo
找出每一个元素左侧和右侧第一个比它大的元素所在的位置 。这就是一个经典的单调栈问题了,可以参考 503. 下一个更大元素 II。如果左侧的元素较小,那么该元素就是左侧元素的右子节点;如果右侧的元素较小,那么该元素就是右侧元素的左子节点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 class Solution {public TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree (int [] nums) {int n = nums.length;new ArrayDeque <Integer>();int [] left = new int [n];int [] right = new int [n];1 );1 );new TreeNode [n];for (int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) {new TreeNode (nums[i]);while (!stack.isEmpty() && nums[i] > nums[stack.peek()]) {if (!stack.isEmpty()) {TreeNode root = null ;for (int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) {if (left[i] == -1 && right[i] == -1 ) {else if (right[i] == -1 || (left[i] != -1 && nums[left[i]] < nums[right[i]])) {else {return root;
7.15 合并二叉树 递归法 相信这道题目很多同学疑惑的点是如何同时遍历两个二叉树呢?
其实和遍历一个树逻辑是一样的,只不过传入两个树的节点,同时操作。
本题使用哪种遍历都是可以的!
确定递归函数的参数和返回值:
首先要合入两个二叉树,那么参数至少是要传入两个二叉树的根节点,返回值就是合并之后二叉树的根节点。
确定终止条件:
因为是传入了两个树,那么就有两个树遍历的节点t1 和 t2,如果t1 == NULL 了,两个树合并就应该是 t2 了(如果t2也为NULL也无所谓,合并之后就是NULL)。
反过来如果t2 == NULL,那么两个数合并就是t1(如果t1也为NULL也无所谓,合并之后就是NULL)。
确定单层递归的逻辑:
那么单层递归中,就要把两棵树的元素加到一起。
接下来t1 的左子树是:合并 t1左子树 t2左子树之后的左子树。
t1 的右子树:是 合并 t1右子树 t2右子树之后的右子树。
最终t1就是合并之后的根节点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution {public TreeNode mergeTrees (TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {if (root1 == null ) return root2;if (root2 == null ) return root1;TreeNode node = new TreeNode (root1.val + root2.val);return node;
迭代法 使用迭代法,如何同时处理两棵树呢?
思路我们在二叉树:我对称么? (opens new window) 中的迭代法已经讲过一次了,求二叉树对称的时候就是把两个树的节点同时加入队列进行比较。
本题我们也使用队列,模拟的层序遍历,代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 class Solution {public :TreeNode* mergeTrees (TreeNode* t1, TreeNode* t2) {if (t1 == NULL ) return t2;if (t2 == NULL ) return t1;push (t1);push (t2);while (!que.empty ()) {front (); que.pop ();front (); que.pop ();if (node1->left != NULL && node2->left != NULL ) {push (node1->left);push (node2->left);if (node1->right != NULL && node2->right != NULL ) {push (node1->right);push (node2->right);if (node1->left == NULL && node2->left != NULL ) {if (node1->right == NULL && node2->right != NULL ) {return t1;
总结 合并二叉树,也是二叉树操作的经典题目,如果没有接触过的话,其实并不简单,因为我们习惯了操作一个二叉树,一起操作两个二叉树,还会有点懵懵的。
这不是我们第一次操作两棵二叉树了,在二叉树:我对称么? (opens new window) 中也一起操作了两棵二叉树。
迭代法中,一般一起操作两个树都是使用队列模拟类似层序遍历,同时处理两个树的节点,这种方式最好理解,如果用模拟递归的思路的话,要复杂一些。
7.16 二叉搜索树的搜索 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 class Solution {public TreeNode searchBST (TreeNode root, int val) {if (root == null || root.val == val) {return root;TreeNode left = searchBST(root.left, val);if (left != null ) {return left;return searchBST(root.right, val);class Solution {public TreeNode searchBST (TreeNode root, int val) {if (root == null || root.val == val) {return root;if (val < root.val) {return searchBST(root.left, val);else {return searchBST(root.right, val);class Solution {public TreeNode searchBST (TreeNode root, int val) {if (root == null || root.val == val) {return root;new Stack <>();while (!stack.isEmpty()) {TreeNode pop = stack.pop();if (pop.val == val) {return pop;if (pop.right != null ) {if (pop.left != null ) {return null ;class Solution {public TreeNode searchBST (TreeNode root, int val) {while (root != null )if (val < root.val) root = root.left;else if (val > root.val) root = root.right;else return root;return null ;
7.17 验证二叉搜索树 要知道中序遍历下,输出的二叉搜索树节点的数值是有序序列。
有了这个特性,验证二叉搜索树,就相当于变成了判断一个序列是不是递增的了。
这道题目比较容易陷入两个陷阱:
不能单纯的比较左节点小于中间节点,右节点大于中间节点就完事了 。
样例中最小节点 可能是int的最小值,如果这样使用最小的int来比较也是不行的。可以直接取最左边的节点来比较(两种取法:一是取其值,二是直接比较treenode)
递归法 递归中序遍历将二叉搜索树转变成一个数组,然后判断该数组是否递增(二叉搜索树中不能出现重复元素)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution {public void traversal (TreeNode root, List<Integer> treenode) {if (root == null ) return ;if (root.left != null ) traversal(root.left, treenode);if (root.right != null ) traversal(root.right, treenode);public boolean isValidBST (TreeNode root) {new ArrayList <>();int pre = tree.get(0 );for (int i = 1 ; i < tree.size(); i++) {if (pre >= tree.get(i)) return false ;return true ;
直接比较元素可以不用获取数组再比较,直接在中序遍历过程中记录前一个节点进行比较。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution {TreeNode pre = null ; public boolean isValidBST (TreeNode root) {if (root == NULL) return true ;boolean left = isValidBST(root.left);if (pre != NULL && pre.val >= root.val) return false ;boolean right = isValidBST(root.right);return left && right;
迭代法 可以用迭代法模拟二叉树中序遍历。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution {public boolean isValidBST (TreeNode root) {new Stack <>();TreeNode cur = root;TreeNode pre = null ;while (!st.isEmpty() || cur != null ) {if (cur != null ) {else {if (pre != null && pre.val >= cur.val) return false ;return true ;
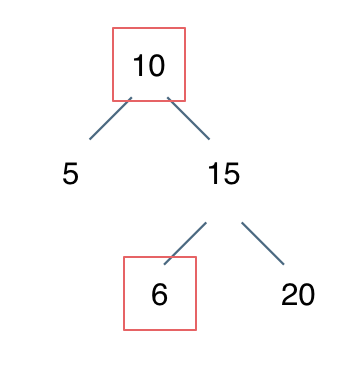
7.18 二叉搜索树的最小绝对差 遇到在二叉搜索树上求什么最值,求差值之类的,都要思考一下二叉搜索树可是有序的,要利用好这一特点。
同时要学会在递归遍历的过程中如何记录前后两个指针 。
我的解法 没有完全利用到二叉搜索树中序遍历有序的特性,此处考虑了前序遍历,每个节点与左右子树的差值规律如下:
当前节点与左子树的差值的最小值是与左子树的最右下角节点 做差(查找左子树的最大值)
当前节点与右子树的差值的最小值是与右子树的最左下角节点 做差(查找右子树的最大值)
利用此规律递归遍历整个树即可。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution {public int res = 100001 ;public void getMin (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) return ;if (root.left != null ) {TreeNode maxLeft = root.left;while (maxLeft.right != null ) maxLeft = maxLeft.right;if (root.val - maxLeft.val < res) res = root.val - maxLeft.val;if (root.right != null ) {TreeNode minRight = root.right;while (minRight.left != null ) minRight = minRight.left;if (minRight.val - root.val < res) res = minRight.val - root.val;public int getMinimumDifference (TreeNode root) {return res;
中序遍历递归 在中序遍历过程中记录前后两个节点,然后比较他们的差值是否为最小。相当于比较[1,2,3,6]中的(1,2)、(2,3)、(3,6)的差值。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution {int result = Integer.MAX_VALUE;public int getMinimumDifference (TreeNode root) {if (root==null )return 0 ;return result;public void traversal (TreeNode root) {if (root==null )return ;if (pre!=null ){
中序遍历迭代 过程同上,只不过使用迭代遍历
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution {public int getMinimumDifference (TreeNode root) {new Stack <>();TreeNode pre = null ;int result = Integer.MAX_VALUE;if (root != null )while (!stack.isEmpty()){TreeNode curr = stack.peek();if (curr != null ){if (curr.right != null )null );if (curr.left != null )else {TreeNode temp = stack.pop();if (pre != null )return result;
7.19 二叉搜索树的众数 思路
基于二叉搜索树中序遍历的性质:一棵二叉搜索树的中序遍历序列是一个非递减的有序序列。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution {new ArrayList <>();int val, count, maxCount;public void dfs (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) {return ;if (root.val == val) {else {1 ;if (count > maxCount) {else if (count == maxCount) {public int [] findMode(TreeNode root) {return res.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();
如果不是二叉搜索树,就把这个树都遍历了,用map统计频率,把频率排个序,最后取前面高频的元素的集合。
迭代法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 class Solution {public int [] findMode(TreeNode root) {TreeNode pre = null ;new Stack <>();new ArrayList <>();int maxCount = 0 ;int count = 0 ;TreeNode cur = root;while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {if (cur != null ) {else {if (pre == null || cur.val != pre.val) {1 ;else {if (count > maxCount) {else if (count == maxCount) {return result.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();
7.20 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先 https://leetcode.cn/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-tree/solutions/238552/er-cha-shu-de-zui-jin-gong-gong-zu-xian-by-leetc-2
解法一:递归 思路
后序遍历进行回溯,判断左右子树是否包含p或者q,进而判断最近公共祖先。
方法一:boolean判断
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution {private TreeNode ans;public Solution () {this .ans = null ;private boolean dfs (TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {if (root == null ) return false ;boolean lson = dfs(root.left, p, q);boolean rson = dfs(root.right, p, q);if ((lson && rson) || ((root.val == p.val || root.val == q.val) && (lson || rson))) {return lson || rson || (root.val == p.val || root.val == q.val);public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {this .dfs(root, p, q);return this .ans;
方法二:treenode判断
问 :为什么发现当前节点是 p 或者 q 就不再往下递归了?万一下面有 q 或者 p 呢?
答 :如果下面有 q 或者 p,那么当前节点就是最近公共祖先,直接返回当前节点。如果下面没有 q 和 p,那既然都没有要找的节点了,也不需要递归,直接返回当前节点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution {public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {if (root == null || root == p || root == q) {return root;TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);if (left != null && right != null ) { return root; return left != null ? left : right;
解法二:存储父节点 思路
我们可以用哈希表存储所有节点的父节点,然后我们就可以利用节点的父节点信息从 p 结点开始不断往上跳,并记录已经访问过的节点,再从 q 节点开始不断往上跳,如果碰到已经访问过的节点,那么这个节点就是我们要找的最近公共祖先。
算法
从根节点开始遍历整棵二叉树,用哈希表记录每个节点的父节点指针。
从 p 节点开始不断往它的祖先移动,并用数据结构记录已经访问过的祖先节点。
同样,我们再从 q 节点开始不断往它的祖先移动,如果有祖先已经被访问过,即意味着这是 p 和 q 的深度最深的公共祖先,即 LCA 节点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution {new HashMap <Integer, TreeNode>();new HashSet <Integer>();public void dfs (TreeNode root) {if (root.left != null ) {if (root.right != null ) {public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {while (p != null ) {while (q != null ) {if (visited.contains(q.val)) {return q;return null ;
7.21 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先 递归
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 class Solution {public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {if (root == null || root == p || root == q) return root;if ((p.val < root.val && q.val > root.val) || (p.val > root.val && q.val < root.val)) return root;else if (p.val < root.val && q.val < root.val) return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);else return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
迭代
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution {public :while (root) {if (root->val > p->val && root->val > q->val) {else if (root->val < p->val && root->val < q->val) {else return root;return NULL;
7.22 二叉搜索树的插入 迭代法 模拟插入过程即可。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution {public TreeNode insertIntoBST (TreeNode root, int val) {TreeNode node = new TreeNode (val);if (root == null ) return node;TreeNode cur = root;while (cur != null ) {if (cur.val < val) {if (cur.right == null ) {break ;else {else if (cur.val > val) {if (cur.left == null ) {break ;else {return root;
递归法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Solution {public :int val) {if (root == NULL) {new TreeNode (val);return node;if (root->val > val) root->left = insertIntoBST(root->left, val);if (root->val < val) root->right = insertIntoBST(root->right, val);return root;
7.23 删除二叉搜索树的节点 递归法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution {public TreeNode deleteNode (TreeNode root, int key) {if (root == null ) return root;if (root.val == key) {if (root.left == null ) {return root.right;else if (root.right == null ) {return root.left;else {TreeNode cur = root.right;while (cur.left != null ) {return root;if (root.val > key) root.left = deleteNode(root.left, key);if (root.val < key) root.right = deleteNode(root.right, key);return root;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution {public TreeNode deleteNode (TreeNode root, int key) {return root;private TreeNode delete (TreeNode root, int key) {if (root == null ) return null ;if (root.val > key) {else if (root.val < key) {else {if (root.left == null ) return root.right;if (root.right == null ) return root.left;TreeNode tmp = root.right;while (tmp.left != null ) {return root;
普通的二叉树删除节点
用交换值的操作来删除目标节点。
代码中目标节点(要删除的节点)被操作了两次:
第一次是和目标节点的右子树最左面节点交换。
第二次直接被NULL覆盖了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution {public :int key) {if (root == nullptr) return root;if (root->val == key) {if (root->right == nullptr) { return root->left;while (cur->left) {return root;
迭代法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 class Solution {public TreeNode deleteNode (TreeNode root, int key) {if (root == null ){return null ;TreeNode cur = root;TreeNode pre = null ;while (cur != null ){if (cur.val < key){else if (cur.val > key) {else {break ;if (pre == null ){return deleteOneNode(cur);if (pre.left !=null && pre.left.val == key){if (pre.right !=null && pre.right.val == key){return root;public TreeNode deleteOneNode (TreeNode node) {if (node == null ){return null ;if (node.right == null ){return node.left;TreeNode cur = node.right;while (cur.left !=null ){return node.right;class Solution {public TreeNode deleteNode (TreeNode root, int key) {if (root == null ) return null ;TreeNode cur = root;TreeNode parent = null ;while (cur != null ) {if (cur.val == key) {if (parent == null ) {if (cur.right == null ) root = cur.left;else if (cur.left == null ) root = cur.right;else {TreeNode tmp = cur.right;while (tmp.left != null ) {else if (parent.left != null && parent.left.val == key) {if (cur.right == null ) parent.left = cur.left;else if (cur.left == null ) parent.left = cur.right;else {TreeNode tmp = cur.right;while (tmp.left != null ) {else if (parent.right != null && parent.right.val == key){if (cur.right == null ) parent.right = cur.left;else if (cur.left == null ) parent.right = cur.right;else {TreeNode tmp = cur.right;while (tmp.left != null ) {break ;else if (cur.val > key) {else {return root;
7.24 修剪二叉搜索树 递归法 不需要遍历,直接利用二叉搜索树的性质即可。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution {public TreeNode trimBST (TreeNode root, int low, int high) {if (root == null ) return root;if (root.val < low) {return trimBST(root.right, low, high);else if (root.val > high) {return trimBST(root.left, low, high);else {return root;
时间复杂度:O (n )
空间复杂度:忽略递归带来的额外空间开销,复杂度为 O (1)
迭代法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 class Solution {public TreeNode trimBST (TreeNode root, int low, int high) {while (root != null && (root.val < low || root.val > high)) {if (root.val < low) {else {if (root == null ) {return null ;for (TreeNode node = root; node.left != null ; ) {if (node.left.val < low) {else {for (TreeNode node = root; node.right != null ; ) {if (node.right.val > high) {else {return root;class Solution {public TreeNode trimBST (TreeNode root, int low, int high) {if (root == null )return null ;while (root != null && (root.val < low || root.val > high)){if (root.val < low)else TreeNode curr = root;while (curr != null ){while (curr.left != null && curr.left.val < low){while (curr != null ){while (curr.right != null && curr.right.val > high){return root;
7.25 将有序数组转化为二叉搜索树 直观地看,我们可以选择中间数字作为二叉搜索树的根节点,这样分给左右子树的数字个数相同或只相差 1,可以使得树保持平衡。如果数组长度是奇数,则根节点的选择是唯一的,如果数组长度是偶数,则可以选择中间位置左边的数字作为根节点或者选择中间位置右边的数字作为根节点,选择不同的数字作为根节点则创建的平衡二叉搜索树也是不同的。
证明这棵树根结点为空或者左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1,证明过程如下:
1382. 将二叉搜索树变平衡 - 力扣(LeetCode)
方法一:中序遍历,总是选择中间位置左边的数字作为根节点 整数除法,总是会选择中间位置左边的元素为根节点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution {public TreeNode sort (int [] nums, int left, int right) {if (left >= right) return null ;int mid = (left + right) / 2 ;TreeNode root = new TreeNode (nums[mid]);1 , right);return root; public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST (int [] nums) {return sort(nums, 0 , nums.length);
7.26 将二叉搜索树转化为累加树 方法一:递归,反中序遍历 从树中可以看出累加的顺序是右中左,所以我们需要反中序遍历这个二叉树,然后顺序累加就可以了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution {int sum;public TreeNode convertBST (TreeNode root) {0 ;return root;public void convertBST1 (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) {return ;
方法二:迭代 迭代法其实就是中序模板题了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution {public TreeNode convertBST (TreeNode root) {int pre = 0 ;new Stack <>();if (root == null ) return null ;TreeNode cur = root;while (cur != null || !st.isEmpty()) {if (cur != null ) {else {return root;
二叉树总结
涉及到二叉树的构造,无论普通二叉树还是二叉搜索树一定前序,都是先构造中节点。
求普通二叉树的属性,一般是后序,一般要通过递归函数的返回值做计算。
求二叉搜索树的属性,一定是中序了,要不白瞎了有序性了。
注意在普通二叉树的属性中,我用的是一般为后序,例如单纯求深度就用前序,二叉树:找所有路径 (opens new window) 也用了前序,这是为了方便让父节点指向子节点。
代码随想录 (programmercarl.com)
8. 回溯算法
8.1 理论基础 回溯是递归的副产品,只要有递归就会有回溯。
所以以下讲解中,回溯函数也就是递归函数,指的都是一个函数 。
回溯法,一般可以解决如下几种问题:
组合问题:N个数里面按一定规则找出k个数的集合
切割问题:一个字符串按一定规则有几种切割方式
子集问题:一个N个数的集合里有多少符合条件的子集
排列问题:N个数按一定规则全排列,有几种排列方式
棋盘问题:N皇后,解数独等等
如何理解回溯法
回溯法解决的问题都可以抽象为树形结构 ,是的,我指的是所有回溯法的问题都可以抽象为树形结构!
因为回溯法解决的都是在集合中递归查找子集,集合的大小就构成了树的宽度,递归的深度就构成了树的深度 。
递归就要有终止条件,所以必然是一棵高度有限的树(N叉树)。
回溯法模板
回溯函数模板返回值以及参数
在回溯算法中,函数起名字为backtracking,起名随意。
回溯算法中函数返回值一般为void 。
再来看一下参数,因为回溯算法需要的参数可不像二叉树递归的时候那么容易一次性确定下来,所以一般是先写逻辑,然后需要什么参数,就填什么参数。
回溯函数终止条件
什么时候达到了终止条件,树中就可以看出,一般来说搜到叶子节点了,也就找到了满足条件的一条答案,把这个答案存放起来,并结束本层递归。
遍历过程
在上面我们提到了,回溯法一般是在集合中递归搜索,集合的大小构成了树的宽度,递归的深度构成的树的深度。
1 2 3 4 5 for (选择:本层集合中元素(树中节点孩子的数量就是集合的大小)) {backtracking (路径,选择列表);
大家可以从图中看出for循环可以理解是横向遍历,backtracking(递归)就是纵向遍历 ,这样就把这棵树全遍历完了,一般来说,搜索叶子节点就是找的其中一个结果了。
回溯算法模板框架如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 void backtracking (参数) if (终止条件) {return ;for (选择:本层集合中元素(树中节点孩子的数量就是集合的大小)) {backtracking (路径,选择列表);
回溯题型 https://leetcode.cn/problems/permutations/solutions/9914/hui-su-suan-fa-python-dai-ma-java-dai-ma-by-liweiw
回溯三问
8.2 组合问题
方法一:枚举下一个数选哪个 正序枚举 :
从前到后枚举,递归过程中传递起始元素。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution {new ArrayList <>();new ArrayList <>();public void backtracking (int n, int k, int startIndex) {if (path.size() == k) {new ArrayList <>(path));return ;for (int i = startIndex; i <= n; i++) {1 );1 );public List<List<Integer>> combine (int n, int k) {1 );return res;
剪枝优化:
当剩余的数的个数小于path中缺少的数的个数(k - path.size())时,不用继续遍历下去。
即把 i <= n 改成 i <= n - (k - path.size()) + 1 :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution {new ArrayList <>();new ArrayList <>();public void backtracking (int n, int k, int startIndex) {if (path.size() == k) {new ArrayList <>(path));return ;for (int i = startIndex; i <= n - (k - path.size()) + 1 ; i++) {1 );1 );public List<List<Integer>> combine (int n, int k) {1 );return res;
倒叙枚举:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution {private int k;private final List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList <>();private final List<Integer> path = new ArrayList <>();public List<List<Integer>> combine (int n, int k) {this .k = k;return ans;private void dfs (int i) {int d = k - path.size(); if (d == 0 ) { new ArrayList <>(path));return ;for (int j = i; j >= d; j--) {1 );1 );
方法二:选或不选(没看懂)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 import java.util.ArrayDeque;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Deque;import java.util.List;public class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> combine (int n, int k) {new ArrayList <>();if (k <= 0 || n < k) {return res;new ArrayDeque <>(k);1 , n, k, path, res);return res;private void dfs (int begin, int n, int k, Deque<Integer> path, List<List<Integer>> res) {if (k == 0 ) {new ArrayList <>(path));return ;if (begin > n - k + 1 ) {return ;1 , n, k, path, res);1 , n, k - 1 , path, res);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution {private int k;private final List<Integer> path = new ArrayList <>();private final List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList <>();public List<List<Integer>> combine (int n, int k) {this .k = k;return ans;private void dfs (int i) {int d = k - path.size(); if (d == 0 ) { new ArrayList <>(path));return ;if (i > d) {1 );1 );1 );
8.3 组合总和Ⅲ 方法一:枚举选哪个 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 class Solution {new ArrayList <>();new ArrayList <>();public void backtracking (int k, int n, int top, int index, int sum) {if (path.size() == k) {if (sum == n) res.add(new ArrayList <>(path));return ;if (sum > n) {return ;for (int i = index; i <= top - (k - path.size()) + 1 ; i++) {1 , sum + i);1 );public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum3 (int k, int n) {int sum1 = 0 ;int sum2 = 0 ;for (int i = 1 ; i <= k; i++) {for (int i = 9 ; i > 9 - k; i--) {if (sum1 > n || sum2 < n) return res;9 , 1 , 0 );return res;
倒叙方法
思路:在组合的基础上增加判断条件+剪枝。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum3 (int k, int n) {new ArrayList <>();new ArrayList <>(k);9 , n, k, ans, path);return ans;private void dfs (int i, int t, int k, List<List<Integer>> ans, List<Integer> path) {int d = k - path.size(); if (t < 0 || t > (i * 2 - d + 1 ) * d / 2 ) { return ;if (d == 0 ) { new ArrayList <>(path));return ;for (int j = i; j >= d; j--) {1 , t - j, k, ans, path);1 );
时间复杂度:分析回溯问题的时间复杂度,有一个通用公式:路径长度×搜索树的叶子数。对于本题,它等于 $O(k⋅C(9,k))$(去掉剪枝就是 77. 组合)。
空间复杂度:$O(k)$。返回值不计入。
方法二:选或不选 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class Solution {new ArrayList <>();new ArrayList <>();public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum3 (int k, int n) {9 );return res;private void backtracking (int k, int n, int maxNum) {if (k == 0 && n == 0 ) {new ArrayList <>(list));return ;if (maxNum == 0 1 ) / 2 1 + k) * k / 2 ) {return ;1 , n - maxNum, maxNum - 1 );1 );1 );
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum3 (int k, int n) {new ArrayList <>();new ArrayList <>(k);9 , n, k, ans, path);return ans;private void dfs (int i, int t, int k, List<List<Integer>> ans, List<Integer> path) {int d = k - path.size(); if (t < 0 || t > (i * 2 - d + 1 ) * d / 2 ) { return ;if (d == 0 ) { new ArrayList <>(path));return ;if (i > d) {1 , t, k, ans, path);1 , t - i, k, ans, path);1 );
8.4 电话号码的数字总和 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 class Solution {new ArrayList <>();public List<String> letterCombinations (String digits) {if (digits == null || digits.length() == 0 ) {return list;"" , "" , "abc" , "def" , "ghi" , "jkl" , "mno" , "pqrs" , "tuv" , "wxyz" };0 );return list;StringBuilder temp = new StringBuilder ();public void backTracking (String digits, String[] numString, int num) {if (num == digits.length()) {return ;String str = numString[digits.charAt(num) - '0' ];for (int i = 0 ; i < str.length(); i++) {1 );1 );class Solution {new HashMap <>();new ArrayList <>();new ArrayList <>();public void backtracking (String digits, int index) {if (path.size() == digits.length()) {String ans = "" ;for (String a: path) {return ;int digit = Character.getNumericValue(digits.charAt(index));String s = map.get(digit);for (char a: s.toCharArray()) {1 );1 );public List<String> letterCombinations (String digits) {2 , "abc" );3 , "def" );4 , "ghi" );5 , "jkl" );6 , "mno" );7 , "pqrs" );8 , "tuv" );9 , "wxyz" );if (digits.isEmpty()) {return res;0 );return res;class Solution {private static final String[] MAPPING = new String []{"" , "" , "abc" , "def" , "ghi" , "jkl" , "mno" , "pqrs" , "tuv" , "wxyz" };private final List<String> ans = new ArrayList <>();private char [] digits;private char [] path;public List<String> letterCombinations (String digits) {int n = digits.length();if (n == 0 ) {return List.of();this .digits = digits.toCharArray();new char [n]; 0 );return ans;private void dfs (int i) {if (i == digits.length) {new String (path));return ;for (char c : MAPPING[digits[i] - '0' ].toCharArray()) {1 );
17. 电话号码的字母组合 - 力扣(LeetCode)
8.5 组合总和 描述
给定一个无重复元素的数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。
candidates 中的数字可以无限制重复被选取。
说明:
所有数字(包括 target)都是正整数。
解集不能包含重复的组合。
示例 1:
输入:candidates = [2,3,6,7], target = 7,
所求解集为: [ [7], [2,2,3] ]
在求和问题中,排序之后加剪枝是常见的套路!
方法一:选或不选 终止情况 :
选中元素的和大于target(此处为left < 0)
选中元素的和等于target(left == 0)
数组已经遍历完成
思路 :
用 dfs (i ,left ) 来回溯,设当前枚举到 candidates [i ],剩余要选的元素之和为 left ,按照选或不选分类讨论:
不选:递归到 dfs (i +1,left )。
选:递归到 dfs (i ,left −candidates [i ])。注意 i 不变,表示在下次递归中可以继续选 candidates [i ]。
类似于完全背包。
如果递归中发现 left =0 则说明找到了一个合法组合,复制一份 path 加入答案。
递归边界:如果 i =n 或者 left <0 则返回。
递归边界:如果 i =n 或者 left <0 则返回。
递归入口:dfs (0,target )。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution {new ArrayList <>();new ArrayList <>();public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum (int [] candidates, int target) {0 , target, candidates);return ans;public void dfs (int index, int left, int [] candidates) {if (left == 0 ) {new ArrayList <>(path));return ;if (index == candidates.length || left < 0 ) {return ;1 , left, candidates);1 );
剪枝优化
把 candidates 从小到大排序,如果递归中发现 left <candidates [i ],由于后面的数字只会更大,所以无法把 left 减小到 0,可以直接返回。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution {new ArrayList <>();new ArrayList <>();public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum (int [] candidates, int target) {0 , target, candidates);return ans;public void dfs (int index, int left, int [] candidates) {if (left == 0 ) {new ArrayList <>(path));return ;if (index == candidates.length || left < candidate[index]) {return ;1 , left, candidates);1 );
方法二:枚举选哪一个 同样用 dfs (i ,left ) 来回溯,设当前枚举到 candidates [i ],剩余要选的元素之和为 left ,考虑枚举下个元素是谁:
在 [index ,length −1] 中枚举要填在 path 中的元素 candidates [i ],然后递归到 dfs (i ,left −candidates [i ])。
注意这里是递归到 i 不是 i +1,表示 candidates [i ] 可以重复选取
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution {new ArrayList <>();new ArrayList <>();public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum (int [] candidates, int target) {0 , target, candidates);return ans;public void dfs (int index, int left, int [] candidates) {if (left == 0 ) {new ArrayList <>(path));return ;for (int i = index; i < candidates.length && left >= candidates[i]; i++) {1 );
方法三:完全背包预处理+可行性剪枝 8.6 组合总和Ⅱ 将数组先排序的思路来自于这个问题:去掉一个数组中重复的元素。很容易想到的方案是:先对数组 升序 排序,重复的元素一定不是排好序以后相同的连续数组区域的第 1 个元素 。也就是说,剪枝发生在:同一层 数值相同的结点第 2、3 … 个结点 ,因为数值相同的第 1 个结点已经搜索出了包含了这个数值的全部结果 ,同一层的其它结点,候选数的个数更少,搜索出的结果一定不会比第 1 个结点更多,并且是第 1 个结点的子集 。
方法一:选或不选 为了使得解集不包含重复的组合。有以下 2 种方案:
使用 哈希表 天然的去重功能,但是编码相对复杂;
这里我们使用和第 39 题和第 15 题(三数之和)类似的思路:不重复就需要按 顺序 搜索, 在搜索的过程中检测分支是否会出现重复结果 。注意:这里的顺序不仅仅指数组 candidates 有序,还指按照一定顺序搜索结果。
1. 在不选的前面跳过至下一不同元素 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution {private List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList <>();private List<Integer> path = new ArrayList <>();public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2 (int [] candidates, int target) {0 , target, candidates);return ans;public void dfs (int index, int target, int [] candidates) {if (target == 0 ) {new ArrayList <>(path));return ;if (index == candidates.length || target < candidates[index]) {return ;1 , target - candidates[index], candidates);1 );while (index + 1 < candidates.length && candidates[index] == candidates[index + 1 ]) {1 , target, candidates);
2. 使用map记录相同元素的出现个数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 class Solution {int []> freq = new ArrayList <int []>();new ArrayList <List<Integer>>();new ArrayList <Integer>();public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2 (int [] candidates, int target) {for (int num : candidates) {int size = freq.size();if (freq.isEmpty() || num != freq.get(size - 1 )[0 ]) {new int []{num, 1 });else {1 )[1 ];0 , target);return ans;public void dfs (int pos, int rest) {if (rest == 0 ) {new ArrayList <Integer>(sequence));return ;if (pos == freq.size() || rest < freq.get(pos)[0 ]) {return ;1 , rest);int most = Math.min(rest / freq.get(pos)[0 ], freq.get(pos)[1 ]);for (int i = 1 ; i <= most; ++i) {0 ]);1 , rest - i * freq.get(pos)[0 ]);for (int i = 1 ; i <= most; ++i) {1 );
方法二:枚举选哪一个 1. 使用startIndex去重 需要去除递归树同一层中重复的元素。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 class Solution {new ArrayList <>();new LinkedList <>();int sum = 0 ;public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2 ( int [] candidates, int target ) {0 );return res;private void backTracking ( int [] candidates, int target, int start ) {if ( sum == target ) {new ArrayList <>( path ) );return ;for ( int i = start; i < candidates.length && sum + candidates[i] <= target; i++ ) {if ( i > start && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1 ] ) {continue ;1 );int temp = path.getLast();
2. 使用boolean数组标记元素 添加used数组标识前方相同元素是否被使用过。
在candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1]相同的情况下:
used[i - 1] == true,说明同一树枝candidates[i - 1]使用过
used[i - 1] == false,说明同一树层candidates[i - 1]使用过
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 class Solution {new LinkedList <>();new ArrayList <>();boolean [] used;int sum = 0 ;public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2 (int [] candidates, int target) {new boolean [candidates.length];false );0 );return ans;private void backTracking (int [] candidates, int target, int startIndex) {if (sum == target) {new ArrayList (path));for (int i = startIndex; i < candidates.length; i++) {if (sum + candidates[i] > target) {break ;if (i > 0 && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1 ] && !used[i - 1 ]) {continue ;true ;1 );false ;
8.7 分割回文串 思路
本题这涉及到两个关键问题:
切割问题,有不同的切割方式
判断回文
切割问题:切割一个a之后,在bcdef中再去切割第二段,切割b之后在cdef中再切割第三段……
切割问题,也可以抽象为一棵树形结构,如图:
递归用来纵向遍历,for循环用来横向遍历,切割线(就是图中的红线)切割到字符串的结尾位置,说明找到了一个切割方法。
方法一:选或不选 假设每对相邻字符之间有个逗号,那么就看每个逗号是选还是不选。
也可以理解成:是否要把 s [i ] 当成分割出的子串的最后一个字符。注意 s [n −1] 一定是最后一个字符,一定要选
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 class Solution {private final List<List<String>> ans = new ArrayList <>();private final List<String> path = new ArrayList <>();private String s;public List<List<String>> partition (String s) {this .s = s;0 , 0 );return ans;private void dfs (int i, int start) {if (i == s.length()) {new ArrayList <>(path)); return ;if (i < s.length() - 1 ) {1 , start);if (isPalindrome(start, i)) {1 ));1 , i + 1 ); 1 ); private boolean isPalindrome (int left, int right) {while (left < right) {if (s.charAt(left++) != s.charAt(right--)) {return false ;return true ;
看不懂
方法二:枚举下一个分隔符的位置 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 class Solution {private final List<List<String>> ans = new ArrayList <>();private final List<String> path = new ArrayList <>();private String s;public List<List<String>> partition (String s) {this .s = s;0 );return ans;private void dfs (int i) {if (i == s.length()) {new ArrayList <>(path)); return ;for (int j = i; j < s.length(); j++) { if (isPalindrome(i, j)) {1 ));1 );1 ); private boolean isPalindrome (int left, int right) {while (left < right) {if (s.charAt(left++) != s.charAt(right--)) {return false ;return true ;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 class Solution {new ArrayList <>();new ArrayList <>();public List<List<String>> partition (String s) {0 , new StringBuilder ());return res;private void backtracking (String s, int start, StringBuilder sb) {if (start == s.length()){new ArrayList <>(cur));return ;for (int i = start; i < s.length(); i++){if (check(sb)){1 , new StringBuilder ());1 );private boolean check (StringBuilder sb) {for (int i = 0 ; i < sb.length()/ 2 ; i++){if (sb.charAt(i) != sb.charAt(sb.length() - 1 - i)){return false ;}return true ;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution {new ArrayList <>();new ArrayList <>();private boolean isPalindrome (String s) {for (int l = 0 , r = s.length() - 1 ; l < r; l++, r--) {if (s.charAt(l) != s.charAt(r)) {return false ;return true ;public void dfs (int index, String s) {if (index == s.length()) {new ArrayList <>(path));for (int i = index; i < s.length(); i++) {if (isPalindrome(s.substring(index, i + 1 ))) {1 ));1 , s);1 );public List<List<String>> partition (String s) {0 , s);return ans;
动态规划优化回文串判断
待写
8.8 复原IP地址
约束条件限制了当前的选项,这道题的约束条件是:
一个片段的长度是 1~3
片段的值范围是 0~255
不能是 “0x”、”0xx” 形式(测试用例告诉我们的)
用这些约束进行充分地剪枝,去掉一些选择,避免搜索「不会产生正确答案」的分支。
更加清晰的方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 class Solution {new ArrayList <>();public List<String> restoreIpAddresses (String s) {0 , new ArrayList <>());return result;private void backTracking (String s, int index, List<String> path) {if (path.size() == 4 && index == s.length()) {"." , path));return ;for (int i = index; i < s.length() && i < index + 3 ; i++) {if (path.size() + (s.length() - index) < 4 || path.size() == 4 && index != s.length() || (4 - path.size()) * 3 < (s.length() - index)) {break ;if (i == index && s.charAt(i) == '0' ) {1 , path);1 );break ;String node = s.substring(index, i + 1 );if (isValid(node)) {1 , path);1 );public boolean isValid (String node) {int num = Integer.parseInt(node);if ("0" .equals(node) || (node.charAt(0 ) != '0' && num >= 0 && num <= 255 )) {return true ;return false ;
和上面类似的解法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 public class Solution {public List<String> restoreIpAddresses (String s) {this .s = s;new ArrayList <>();new ArrayList <>(), 0 );return res;private void dfs (List<String> res, List<String> subRes, int start) {if (subRes.size() == 4 && start == s.length()) {"." , subRes));return ;if (subRes.size() == 4 && start < s.length()) {return ;for (int len = 1 ; len <= 3 ; len++) {if (start + len - 1 >= s.length()) return ;if (len != 1 && s.charAt(start) == '0' ) return ;String str = s.substring(start, start + len);if (len == 3 && Integer.parseInt(str) > 255 ) return ;1 );
代码随想录解法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 class Solution {new ArrayList <>();public List<String> restoreIpAddresses (String s) {if (s.length() > 12 ) return result; 0 , 0 );return result;private void backTrack (String s, int startIndex, int pointNum) {if (pointNum == 3 ) {if (isValid(s,startIndex,s.length()-1 )) {return ;for (int i = startIndex; i < s.length(); i++) {if (isValid(s, startIndex, i)) {0 , i + 1 ) + "." + s.substring(i + 1 ); 2 , pointNum);0 , i + 1 ) + s.substring(i + 2 );else {break ;private Boolean isValid (String s, int start, int end) {if (start > end) {return false ;if (s.charAt(start) == '0' && start != end) { return false ;int num = 0 ;for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) {if (s.charAt(i) > '9' || s.charAt(i) < '0' ) { return false ;10 + (s.charAt(i) - '0' );if (num > 255 ) { return false ;return true ;class Solution {new ArrayList <>();public List<String> restoreIpAddresses (String s) {if (s.length() < 4 || s.length() > 12 ) return ans;StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder (s);0 , 0 );return ans;public void dfs (StringBuilder s, int index, int pointnum) {if (pointnum == 3 ) {if (isValid(s, index, s.length() - 1 )) {return ;for (int i = index; i < s.length() && i < index + 3 ; i++) {if (isValid(s, index, i)) {1 , "." );2 , pointnum + 1 );1 );else {break ;public boolean isValid (StringBuilder s, int start, int end) {if (start > end) return false ;if (s.charAt(start) == '0' && start != end) {return false ;if (Integer.parseInt(s.substring(start, end + 1 )) > 255 ) {return false ;return true ;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 class Solution {new ArrayList <String>();StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder ();public List<String> restoreIpAddresses (String s) {0 , 0 );return result;public void restoreIpAddressesHandler (String s, int start, int number) {if (start == s.length() && number == 4 ) {return ;if (start == s.length() || number == 4 ) {return ;for (int i = start; i < s.length() && i - start < 3 && Integer.parseInt(s.substring(start, i + 1 )) >= 0 1 )) <= 255 ; i++) {if (i + 1 - start > 1 && s.charAt(start) - '0' == 0 ) {break ;1 ));if (number < 3 ) {"." );1 , number);2 );
8.9 子集问题 求取子集问题,不需要任何剪枝!因为子集就是要遍历整棵树 。
子集是收集树形结构中树的所有节点的结果。
而组合问题、分割问题是收集树形结构中叶子节点的结果
方法一:选或不选 对于输入的 nums ,考虑每个 nums [i ] 是选还是不选,由此组合出 2n 个不同的子集。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution {new ArrayList <>();new ArrayList <>();public List<List<Integer>> subsets (int [] nums) {0 , nums);return ans;public void dfs (int index, int [] nums) {if (index == nums.length) {new ArrayList <>(subset));return ;1 , nums);1 , nums);1 );
方法二:枚举下一个选择的位置 注意:不需要在回溯中判断 i =n 的边界情况,因为此时不会进入循环,if i == n: return 这句话写不写都一样。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution {new ArrayList <>();new ArrayList <>();public List<List<Integer>> subsets (int [] nums) {0 , nums);return ans;public void dfs (int index, int [] nums) {new ArrayList <>(subset));if (index >= nums.length) {return ;for (int i = index; i < nums.length; i++) {1 , nums);1 );
方法三:二进制枚举 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> subsets (int [] nums) {int n = nums.length;new ArrayList <>(1 << n);for (int i = 0 ; i < (1 << n); i++) { new ArrayList <>();for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j++) {if ((i >> j & 1 ) == 1 ) { return ans;
8.10 子集Ⅱ 使用used数组
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 class Solution {new ArrayList <>();new LinkedList <>();boolean [] used;public List<List<Integer>> subsetsWithDup (int [] nums) {if (nums.length == 0 ){return result;new boolean [nums.length];0 );return result;private void subsetsWithDupHelper (int [] nums, int startIndex) {new ArrayList <>(path));if (startIndex >= nums.length){return ;for (int i = startIndex; i < nums.length; i++){if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1 ] && !used[i - 1 ]){continue ;true ;1 );false ;
不使用used数组,直接跳过
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution {new ArrayList <>();new ArrayList <>();int [] nums;public List<List<Integer>> subsetsWithDup (int [] nums) {this .nums = nums;0 );return ans;public void dfs (int index) {new ArrayList <>(subset));for (int i = index; i < nums.length; i++) {if (i > index && nums[i] == nums[i - 1 ]) {continue ;1 );1 );
8.11 递增子序列 方法一:枚举下一个选择的位置 使用used标记访问过的位置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution {new ArrayList <>();new ArrayList <>();int [] nums;public List<List<Integer>> findSubsequences (int [] nums) {this .nums = nums;0 );return ans;public void dfs (int index) {if (path.size() >= 2 ) {new ArrayList <>(path));int [] used = new int [201 ];for (int i = index; i < nums.length; i++) {if ((!path.isEmpty() && path.get(path.size() - 1 ) > nums[i]) || (used[nums[i] + 100 ] == 1 )) continue ;100 ] = 1 ;1 );1 );
使用set记录访问过的元素
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution {new ArrayList <>();new ArrayList <>();public List<List<Integer>> findSubsequences (int [] nums) {0 );return result;private void backTracking (int [] nums, int startIndex) {if (path.size() >= 2 )new ArrayList <>(path)); new HashSet <>();for (int i = startIndex; i < nums.length; i++){if (!path.isEmpty() && path.get(path.size() -1 ) > nums[i] || hs.contains(nums[i]))continue ;1 );1 );
方法二:选或不选 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution {new ArrayList <>();new ArrayList <>();int [] nums;public List<List<Integer>> findSubsequences (int [] nums) {this .nums = nums;0 , -101 );return ans;public void dfs (int index, int last) {if (index == nums.length) {if (path.size() >= 2 ) {new ArrayList <>(path));return ;if (nums[index] >= last) {1 , nums[index]);1 );if (last != nums[index]) {1 , last);
去重逻辑(枚举下一个选择的元素) 当题目中出现不能有重复的结果集,或者说出现了的重复元素会导致结果集出现重复的答案,此时就要考虑进行去重操作,去重大致分为两种。
第一种:题目所给的元素可以进行排序之后进行去重,而且最后的结果是题目所要的结果,这种题目我们需要设置一个跟题目中所给数组大小一样,且数组中的元素都为0的bool类型的数组,我们通常给这种数组起名位used,去重逻辑一般为:
1 if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1 ] && used[i - 1 ] == 0 ) continue ;
因为我们刚开始已经对数组进行排完序了,所以如果有相同的元素的话,我们前一个元素已经把所有可能的情况处理完成了,我们后面的该元素就不用再进行处理了,我们就要跳过这种情况,这叫做树层去重。
对应的题目为90.子集Ⅱ以及组合总和Ⅱ。
第二种:题目中数组的顺序不可以进行改变,此时我们需要使用哈希表进行去重操作,即unordered_set,将每一个元素加入到哈希表中,之后如果再遇到该元素就不进行处理,去重逻辑一般为:
1 2 3 4 unordered_set<int > used;if ((!path.empty() && nums[i] < path.back()) || used.find(nums[i]) != used.end()) {continue ;
对应的相关题目为该题491.递增的子序列
去重逻辑(选或不选)
第一种:数组元素可以排序,使用while跳过或者使用map记录相同元素的出现个数。见组合总和Ⅱ 。
第二种:数组元素顺序不可变,利用last元素。
8.12 全排列 排列问题 需要一个used数组,标记已经选择的元素。
每层都是从0开始搜索而不是startIndex
需要used数组记录path里都放了哪些元素了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution {new ArrayList <>();new ArrayList <>();public List<List<Integer>> permute (int [] nums) {boolean [] used = new boolean [nums.length];return ans;public void dfs (boolean [] used, int [] nums) {if (path.size() == nums.length) {new ArrayList <>(path));for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) {if (!used[i]) {true ;false ;1 );
判断path中有无当前元素
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution {new ArrayList <>();new LinkedList <>();public List<List<Integer>> permute (int [] nums) {if (nums.length == 0 ) return result;return result;public void backtrack (int [] nums, LinkedList<Integer> path) {if (path.size() == nums.length) {new ArrayList <>(path));for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) {if (path.contains(nums[i])) {continue ;
8.13 全排列Ⅱ 去重一定要对元素进行排序,这样我们才方便通过相邻的节点来判断是否重复使用了 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution {new ArrayList <>();new ArrayList <>();int [] nums;public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique (int [] nums) {this .nums = nums;boolean [] used = new boolean [nums.length];return ans;public void dfs (boolean [] used) {if (path.size() == nums.length) {new ArrayList <>(path));return ;for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) {if (used[i] || (i > 0 && !used[i - 1 ] && nums[i] == nums[i - 1 ])) continue ;true ;1 );false ;
1 时间复杂度: 最差情况所有元素都是唯一的。复杂度和全排列1 都是 O (n! * n) 对于 n 个元素一共有 n! 中排列方案。而对于每一个答案,我们需要 O (n) 去复制最终放到 result 数组
**如果改成 used[i - 1] == true, 也是正确的!**,去重代码如下:
1 2 3 if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1 ] && used[i - 1 ] == true ) {continue ;
这里去重不是树层去重,而是树枝去重,只有倒叙的排列才能通过。
例如[1,1‘,2],1,1’时无法通过,因为1已经在上一层用过;而1’,1可以通过,因为是倒叙,此时used为[false,true],第一个1之前不可能重复,因此必定有一个留存。
性能分析 之前并没有分析各个问题的时间复杂度和空间复杂度,这次来说一说。
这块网上的资料鱼龙混杂,一些所谓的经典面试书籍根本不讲回溯算法,算法书籍对这块也避而不谈,感觉就像是算法里模糊的边界。
所以这块就说一说我个人理解,对内容持开放态度,集思广益,欢迎大家来讨论!
子集问题分析:
时间复杂度:$O(n × 2^n)$,因为每一个元素的状态无外乎取与不取,所以时间复杂度为$O(2^n)$,构造每一组子集都需要填进数组,又有需要$O(n)$,最终时间复杂度:$O(n × 2^n)$。
空间复杂度:$O(n)$,递归深度为n,所以系统栈所用空间为$O(n)$,每一层递归所用的空间都是常数级别,注意代码里的result和path都是全局变量,就算是放在参数里,传的也是引用,并不会新申请内存空间,最终空间复杂度为$O(n)$。
排列问题分析:
时间复杂度:$O(n!)$,这个可以从排列的树形图中很明显发现,每一层节点为n,第二层每一个分支都延伸了n-1个分支,再往下又是n-2个分支,所以一直到叶子节点一共就是 n * n-1 * n-2 * ….. 1 = n!。每个叶子节点都会有一个构造全排列填进数组的操作(对应的代码:result.push_back(path)),该操作的复杂度为$O(n)$。所以,最终时间复杂度为:n * n!,简化为$O(n!)$。
空间复杂度:$O(n)$,和子集问题同理。
组合问题分析:
时间复杂度:$O(n × 2^n)$,组合问题其实就是一种子集的问题,所以组合问题最坏的情况,也不会超过子集问题的时间复杂度。
空间复杂度:$O(n)$,和子集问题同理。
一般说道回溯算法的复杂度,都说是指数级别的时间复杂度,这也算是一个概括吧
8.14 回溯算法去重问题的另一种写法 略,即使用set时不能将其设为全局变量,否则是对整棵树进行去重而不是树层去重。
8.15 重新安排行程 解法一:dfs+优先队列(堆),倒序存储答案 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution {new HashMap <String, PriorityQueue<String>>();new LinkedList <String>();public List<String> findItinerary (List<List<String>> tickets) {for (List<String> ticket : tickets) {String src = ticket.get(0 ), dst = ticket.get(1 );if (!map.containsKey(src)) {new PriorityQueue <String>());"JFK" );return itinerary;public void dfs (String curr) {while (map.containsKey(curr) && map.get(curr).size() > 0 ) {String tmp = map.get(curr).poll();
解法二:
使用unordered_map<string, map<string, int>> targets:unordered_map<出发机场, map<到达机场, 航班次数>> targets
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 class Solution {private Deque<String> res;private Map<String, Map<String, Integer>> map;private boolean backTracking (int ticketNum) {if (res.size() == ticketNum + 1 ){return true ;String last = res.getLast();if (map.containsKey(last)){for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> target : map.get(last).entrySet()){int count = target.getValue();if (count > 0 ){1 );if (backTracking(ticketNum)) return true ;return false ;public List<String> findItinerary (List<List<String>> tickets) {new HashMap <String, Map<String, Integer>>();new LinkedList <>();for (List<String> t : tickets){if (map.containsKey(t.get(0 ))){0 ));1 ), temp.getOrDefault(t.get(1 ), 0 ) + 1 );else {new TreeMap <>();1 ), 1 );0 ), temp);"JFK" );return new ArrayList <>(res);
使用unordered_map<string, multiset> targets:unordered_map<出发机场, 到达机场的集合> targets
此方法需要去重防止超时
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 class Solution {public List<String> findItinerary (List<List<String>> tickets) {new ArrayList <>();if (tickets == null || tickets.isEmpty()) {return res;new HashMap <>();for (List<String> ticket : tickets) {0 ), new ArrayList <>());0 )).add(ticket.get(1 ));for (List<String> neis : map.values()) {String start = "JFK" ;int totalLen = tickets.size() + 1 ;if (dfs(map, start, res, totalLen)) {return res;return res;private boolean dfs (Map<String,List<String>> map, String start, List<String> res, int totalLen) {if (res.size() == totalLen) return true ;if (!map.containsKey(start)) return false ;for (int i = 0 ; i < neis.size(); i++) {String nei = neis.get(i);if (i > 0 && nei.equals(neis.get(i - 1 ))) continue ;if (dfs(map, nei, res, totalLen)) {return true ;1 );return false ;
解法三:使用bool数组标记,回溯枚举下一个元素 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 class Solution {public boolean [] used;public List<String> path = new ArrayList <>();public List<String> findItinerary (List<List<String>> tickets) {1 ).compareTo(b.get(1 )));new boolean [tickets.size()];"JFK" );"JFK" , tickets);return path;public boolean dfs (String from, List<List<String>> tickets) {if (path.size() == tickets.size() + 1 ) {return true ;for (int i = 0 ; i < tickets.size(); i++) {if (i > 0 && tickets.get(i).equals(tickets.get(i - 1 )) && !used[i - 1 ]) continue ;if (tickets.get(i).get(0 ).equals(from) && !used[i]) {true ;1 ));if (dfs(tickets.get(i).get(1 ), tickets)) {return true ;false ;1 );return false ;
8.16 N皇后 问 :本题和 46. 全排列 的关系是什么?
答 :由于每行恰好放一个皇后,记录每行的皇后放在哪一列,可以得到一个 [0,n −1] 的排列 queens 。示例 1 的两个图,分别对应排列 [1,3,0,2] 和 [2,0,3,1]。所以我们本质上是在枚举列号的全排列 。
问 :如何 O(1) 判断两个皇后互相攻击?
答 :由于我们保证了每行每列恰好放一个皇后,所以只需检查斜方向。对于 ↗ 方向的格子,行号加列号是不变的。对于 ↖ 方向的格子,行号减列号是不变的。如果两个皇后,行号加列号相同,或者行号减列号相同,那么这两个皇后互相攻击。
问 :如何 O(1) 判断当前位置被之前放置的某个皇后攻击到?
答 :额外用两个数组 diag 1 和 diag 2 分别标记之前放置的皇后的行号加列号,以及行号减列号。如果当前位置的行号加列号在 diag 1 中(标记为 true),或者当前位置的行号减列号在 diag 2 中(标记为 true),么当前位置被之前放置的皇后攻击到,不能放皇后。
方法一: 结束后统一创建路径 ※
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 class Solution {new ArrayList <>();int [] col;public List<List<String>> solveNQueens (int n) {new int [n];1 );0 , n);return ans;public boolean valid (int r, int c) {for (int i = 0 ; i < r; i ++) {if (col[i] == c || i + col[i] == r + c || i - col[i] == r - c) return false ;return true ;public void dfs (int r, int n) {if (r == n) {new ArrayList <>();for (int c: col) {String tmp = "." .repeat(c) + "Q" + "." .repeat(n - c - 1 );for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) {if (valid(r, i)) {1 , n);
在判断时创建路径
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 class Solution {new ArrayList <>();new ArrayList <>();int [] chessboard; public List<List<String>> solveNQueens (int n) {new int [n];1 );0 , n);return res;public void backTrack (int row, int n) {if (row == n) {new ArrayList <String>(path));return ;for (int i=0 ; i<n; i++){if (!isValid(row, i)) continue ;new StringBuilder ();for (int j=0 ; j<n; j++){if (j!=i) str.append('.' );else str.append('Q' );1 , n);1 );1 ;private boolean isValid (int row, int col) {for (int i = 0 ; i < row; i++) {if (chessboard[i] == col) {return false ;if (chessboard[i] + i == row + col) {return false ;if (chessboard[i] - i == col - row) {return false ;return true ;
优化 空间换时间,使用boolean数组表示已经占用的直(斜)线
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 class Solution {public List<List<String>> solveNQueens (int n) {new ArrayList <>();int [] queens = new int [n]; boolean [] col = new boolean [n]; boolean [] diag1 = new boolean [n * 2 - 1 ]; boolean [] diag2 = new boolean [n * 2 - 1 ]; 0 , queens, col, diag1, diag2, ans);return ans;private void dfs (int r, int [] queens, boolean [] col, boolean [] diag1, boolean [] diag2, List<List<String>> ans) {int n = col.length;if (r == n) {new ArrayList <>(n); for (int c : queens) {char [] row = new char [n];'.' );'Q' ;new String (row));return ;for (int c = 0 ; c < n; c++) {int rc = r - c + n - 1 ; if (!col[c] && !diag1[r + c] && !diag2[rc]) { true ; 1 , queens, col, diag1, diag2, ans);false ;
方法二: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 class Solution {new ArrayList <>();public List<List<String>> solveNQueens (int n) {char [][] chessboard = new char [n][n];for (char [] c : chessboard) {'.' );0 , chessboard);return res;public void backTrack (int n, int row, char [][] chessboard) {if (row == n) {return ;for (int col = 0 ;col < n; ++col) {if (isValid (row, col, n, chessboard)) {'Q' ;1 , chessboard);'.' ;public List Array2List (char [][] chessboard) {new ArrayList <>();for (char [] c : chessboard) {return list;public boolean isValid (int row, int col, int n, char [][] chessboard) {for (int i=0 ; i<row; ++i) { if (chessboard[i][col] == 'Q' ) {return false ;for (int i=row-1 , j=col-1 ; i>=0 && j>=0 ; i--, j--) {if (chessboard[i][j] == 'Q' ) {return false ;for (int i=row-1 , j=col+1 ; i>=0 && j<=n-1 ; i--, j++) {if (chessboard[i][j] == 'Q' ) {return false ;return true ;
8.17 解数独 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 class Solution {public void solveSudoku (char [][] board) {public boolean dfs (char [][] board) {for (int i = 0 ; i < 9 ; i ++) {for (int j = 0 ; j < 9 ; j++) {if (board[i][j] != '.' ) continue ;for (char k = '1' ; k <= '9' ; k++) {if (valid(i, j, k, board)) {if (dfs(board)) return true ;'.' ;return false ;return true ;public boolean valid (int row, int col, char val, char [][] board) {for (int i = 0 ; i < 9 ; i++) {if (board[row][i] == val) {return false ;for (int i = 0 ; i < 9 ; i++) {if (board[i][col] == val) {return false ;int startRow = (row/3 ) * 3 ;int startCol = (col/3 ) * 3 ;for (int i = startRow; i < startRow + 3 ; i++) {for (int j = startCol; j < startCol + 3 ; j++) {if (board[i][j] == val) {return false ;return true ;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 class Solution {public void solveSudoku (char [][] board) {0 , 0 );public boolean solveSudoku (char [][] board, int lastI, int lastJ) {if (lastJ==9 ){0 ;if (lastI==9 )return true ;for (int i=lastI;i<9 ;i++,lastJ=0 ){for (int j=lastJ;j<9 ;j++){if (board[i][j]=='.' ){for (char k='1' ;k<='9' ;k++){if (isValid(board, i, j, k)){if (solveSudoku(board, i, j+1 )){return true ;'.' ;return false ;return true ;public boolean isValid (char [][] board, int i, int j, char c) {int blockRow = i/3 *3 ;int blockCol = j/3 *3 ;for (int k=0 ;k<9 ;k++){if (board[i][k]==c||board[k][j]==c)return false ;if (board[blockRow+k/3 ][blockCol+k%3 ]==c)return false ;return true ;
解法2:bit位运算(没看懂) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 class Solution {private int [] line = new int [9 ];private int [] column = new int [9 ];private int [][] block = new int [3 ][3 ];private boolean valid = false ;private List<int []> spaces = new ArrayList <int []>();public void solveSudoku (char [][] board) {for (int i = 0 ; i < 9 ; ++i) {for (int j = 0 ; j < 9 ; ++j) {if (board[i][j] == '.' ) {new int []{i, j});else {int digit = board[i][j] - '0' - 1 ;0 );public void dfs (char [][] board, int pos) {if (pos == spaces.size()) {true ;return ;int [] space = spaces.get(pos);int i = space[0 ], j = space[1 ];int mask = ~(line[i] | column[j] | block[i / 3 ][j / 3 ]) & 0x1ff ;for (; mask != 0 && !valid; mask &= (mask - 1 )) {int digitMask = mask & (-mask);int digit = Integer.bitCount(digitMask - 1 );char ) (digit + '0' + 1 );1 );public void flip (int i, int j, int digit) {1 << digit);1 << digit);3 ][j / 3 ] ^= (1 << digit);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 class Solution {private boolean [][] line = new boolean [9 ][9 ];private boolean [][] column = new boolean [9 ][9 ];private boolean [][][] block = new boolean [3 ][3 ][9 ];private boolean valid = false ;private List<int []> spaces = new ArrayList <int []>();public void solveSudoku (char [][] board) {for (int i = 0 ; i < 9 ; ++i) {for (int j = 0 ; j < 9 ; ++j) {if (board[i][j] == '.' ) {new int []{i, j});else {int digit = board[i][j] - '0' - 1 ;3 ][j / 3 ][digit] = true ;0 );public void dfs (char [][] board, int pos) {if (pos == spaces.size()) {true ;return ;int [] space = spaces.get(pos);int i = space[0 ], j = space[1 ];for (int digit = 0 ; digit < 9 && !valid; ++digit) {if (!line[i][digit] && !column[j][digit] && !block[i / 3 ][j / 3 ][digit]) {3 ][j / 3 ][digit] = true ;char ) (digit + '0' + 1 );1 );3 ][j / 3 ][digit] = false ;
9. 贪心算法 9.1 理论基础 贪心的本质是选择每一阶段的局部最优,从而达到全局最优 。
贪心的套路(什么时候用贪心) 说实话贪心算法并没有固定的套路 。
靠自己手动模拟,如果模拟可行,就可以试一试贪心策略,如果不可行,可能需要动态规划。
最好用的策略就是举反例,如果想不到反例,那么就试一试贪心吧 。
贪心一般解题步骤 贪心算法一般分为如下四步:
将问题分解为若干个子问题
找出适合的贪心策略
求解每一个子问题的最优解
将局部最优解堆叠成全局最优解
这个四步其实过于理论化了,我们平时在做贪心类的题目 很难去按照这四步去思考,真是有点“鸡肋”。
做题的时候,只要想清楚 局部最优 是什么,如果推导出全局最优,其实就够了。
贪心没有套路,说白了就是常识性推导加上举反例 。
9.2 分发饼干 这里的局部最优就是大饼干喂给胃口大的,充分利用饼干尺寸喂饱一个,全局最优就是喂饱尽可能多的小孩 。
可以尝试使用贪心策略,先将饼干数组和小孩数组排序。
然后从后向前遍历小孩数组,用大饼干优先满足胃口大的,并统计满足小孩数量。
思路一:优先考虑胃口,先喂饱大胃口 从代码中可以看出我用了一个 index 来控制饼干数组的遍历,遍历饼干并没有再起一个 for 循环,而是采用自减的方式,这也是常用的技巧。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution int findContentChildren(int [] g, int [] s) {int ans = 0 ;int index = s.length - 1 ;for (int i = g.length - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) {if (index >= 0 && s[index ] >= g[i]) {index --;return ans;
时间复杂度:O(nlogn)
空间复杂度:O(1)
注意事项 注意版本一的代码中,可以看出来,是先遍历的胃口,在遍历的饼干,那么可不可以 先遍历 饼干,在遍历胃口呢?
其实是不可以的。
外面的 for 是里的下标 i 是固定移动的,而 if 里面的下标 index 是符合条件才移动的。
如果 for 控制的是饼干, if 控制胃口,就是出现如下情况 :
思路二:优先考虑饼干,小饼干先喂饱小胃口 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class Solution {public int findContentChildren (int [] g, int [] s) {int start = 0 ;int count = 0 ;for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length && start < g.length; i++) {if (s[i] >= g[start]) {return count;class Solution {public :int findContentChildren (int [] g, int [] s) {int index = 0 ;for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length; i++) { if (index < g.length && g[index] <= s[i]){ return index;
9.3 摆动序列 解法一:贪心 只需要统计波峰和波谷的个数之和即可。
让序列有尽可能多的局部峰值。
局部最优:删除单调坡度上的节点(不包括单调坡度两端的节点),那么这个坡度就可以有两个局部峰值。
整体最优:整个序列有最多的局部峰值,从而达到最长摆动序列。
这就是贪心所贪的地方,让峰值尽可能的保持峰值,然后删除单一坡度上的节点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 class Solution {public int wiggleMaxLength (int [] nums) {int up = 1 ;int down = 1 ;if (nums.length == 0 || nums.length == 1 ) return nums.length;if (nums.length == 2 ) {if (nums[0 ] != nums[1 ]) return 2 ;else return 1 ;int pre = nums[0 ];for (int i = 1 ; i < nums.length; i++) {if (nums[i] > pre) {1 ;if (nums[i] < pre) {1 ;return Math.max(up, down);public int wiggleMaxLength (int [] nums) {int down = 1 , up = 1 ;for (int i = 1 ; i < nums.length; i++) {if (nums[i] > nums[i - 1 ])1 ;else if (nums[i] < nums[i - 1 ])1 ;return nums.length == 0 ? 0 : Math.max(down, up);
解法二:动态规划 考虑用动态规划的思想来解决这个问题。
很容易可以发现,对于我们当前考虑的这个数,要么是作为山峰(即 nums[i] > nums[i-1]),要么是作为山谷(即 nums[i] < nums[i - 1])。
设 dp 状态dp[i][0],表示考虑前 i 个数,第 i 个数作为山峰的摆动子序列的最长长度
设 dp 状态dp[i][1],表示考虑前 i 个数,第 i 个数作为山谷的摆动子序列的最长长度
则转移方程为:
dp[i][0] = max(dp[i][0], dp[j][1] + 1),其中0 < j < i且nums[j] < nums[i],表示将 nums[i]接到前面某个山谷后面,作为山峰。dp[i][1] = max(dp[i][1], dp[j][0] + 1),其中0 < j < i且nums[j] > nums[i],表示将 nums[i]接到前面某个山峰后面,作为山谷。
初始状态:
由于一个数可以接到前面的某个数后面,也可以以自身为子序列的起点,所以初始状态为:dp[0][0] = dp[0][1] = 1。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution {public int wiggleMaxLength (int [] nums) {int dp[][] = new int [nums.length][2 ];0 ][0 ] = dp[0 ][1 ] = 1 ;for (int i = 1 ; i < nums.length; i++){0 ] = dp[i][1 ] = 1 ;for (int j = 0 ; j < i; j++){if (nums[j] > nums[i]){1 ] = Math.max(dp[i][1 ], dp[j][0 ] + 1 );if (nums[j] < nums[i]){0 ] = Math.max(dp[i][0 ], dp[j][1 ] + 1 );return Math.max(dp[nums.length - 1 ][0 ], dp[nums.length - 1 ][1 ]);
9.4 最大子数组和 子数组是数组中的一个连续部分。
不能让“连续和”为负数的时候加上下一个元素,而不是 不让“连续和”加上一个负数 。
局部最优 :当前“连续和”为负数 的时候立刻放弃,从下一个元素 重新计算“连续和”,因为负数加上下一个元素 “连续和”只会越来越小。
全局最优 :选取最大“连续和”
从代码角度上来讲:遍历 nums,从头开始用 count 累积,如果 count 一旦加上 nums[i]变为负数,那么就应该从 nums[i+1]开始从 0 累积 count 了,因为已经变为负数的 count,只会拖累总和。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution {public int maxSubArray (int [] nums) {int ans = nums[0 ];int count = 0 ;for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) {if (count > ans) ans = count;if (count < 0 ) {0 ;return ans;
9.5 买卖股票的最佳时机Ⅱ 如果想到其实最终利润是可以分解的,那么本题就很容易了!
如何分解呢?
假如第 0 天买入,第 3 天卖出,那么利润为:prices[3] - prices[0]。
相当于(prices[3] - prices[2]) + (prices[2] - prices[1]) + (prices[1] - prices[0])。
把利润分解为每天为单位的维度,而不是从 0 天到第 3 天整体去考虑!
那么根据 prices 可以得到每天的利润序列:(prices[i] - prices[i - 1])…..(prices[1] - prices[0])。
如图:
一些同学陷入:第一天怎么就没有利润呢,第一天到底算不算的困惑中。
第一天当然没有利润,至少要第二天才会有利润,所以利润的序列比股票序列少一天!
从图中可以发现,其实我们需要收集每天的正利润就可以,收集正利润的区间,就是股票买卖的区间,而我们只需要关注最终利润,不需要记录区间 。
那么只收集正利润就是贪心所贪的地方!
局部最优:收集每天的正利润,全局最优:求得最大利润 。
需要说明的是,贪心算法只能用于计算最大利润,计算的过程并不是实际的交易过程 。
考虑题目中的例子 [1,2,3,4,5],数组的长度 n =5,由于对所有的 1≤i <*n* 都有 *a*[*i*]>a [i −1],因此答案为
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 class Solution {public int maxProfit (int [] prices) {int result = 0 ;for (int i = 1 ; i < prices.length; i++) {1 ], 0 );return result;
9.6 跳跃游戏 其实跳几步无所谓,关键在于可跳的覆盖范围 !
不一定非要明确一次究竟跳几步,每次取最大的跳跃步数,这个就是可以跳跃的覆盖范围。
每次取值更新其能到达的最大覆盖范围,循环上限为最大覆盖范围。
每次移动取最大跳跃步数(得到最大的覆盖范围),每移动一个单位,就更新最大覆盖范围。
贪心算法局部最优解:每次取最大跳跃步数(取最大覆盖范围),整体最优解:最后得到整体最大覆盖范围,看是否能到终点 。
i 每次移动只能在 cover 的范围内移动,每移动一个元素,cover 得到该元素数值(新的覆盖范围)的补充,让 i 继续移动下去。
而 cover 每次只取 max(该元素数值补充后的范围, cover 本身范围)。
如果 cover 大于等于了终点下标,直接 return true 就可以了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Solution {public boolean canJump (int [] nums) {int cover = 0 ;if (nums.length == 1 ) return true ;for (int i = 0 ; i <= cover; i++) {if (cover >= nums.length - 1 ) return true ;return false ;
9.7 跳跃游戏Ⅱ 方法一:正向查找 如果我们「贪心」地进行正向查找,每次找到可到达的最远位置,就可以在线性时间内得到最少的跳跃次数。
在具体的实现中,我们维护当前能够到达的最大下标位置,记为边界。我们从左到右遍历数组,到达边界时,更新边界并将跳跃次数增加 1。
在遍历数组时,我们不访问最后一个元素,这是因为在访问最后一个元素之前,我们的边界一定大于等于最后一个位置,否则就无法跳到最后一个位置了。如果访问最后一个元素,在边界正好为最后一个位置的情况下,我们会增加一次「不必要的跳跃次数」,因此我们不必访问最后一个元素。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 class Solution {public int jump (int [] nums) {int step = 0 ;int curDistance = 0 ;int nextDistance = 0 ;for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length - 1 ; i++) {if (i == curDistance) {return step;class Solution {public int jump (int [] nums) {if (nums == null || nums.length == 0 || nums.length == 1 ) {return 0 ;int count=0 ;int curDistance = 0 ;int maxDistance = 0 ;for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) {if (maxDistance>=nums.length-1 ){break ;if (i==curDistance){return count;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution :jump (self, nums: List[int ]) -> int :0 0 # 已建造的桥的右端点0 # 下一座桥的右端点的最大值for i in range (len(nums) - 1 ):if i == cur_right: # 到达已建造的桥的右端点1 return ansclass Solution {public int jump (int [] nums) {int result = 0 ;int end = 0 ;int temp = 0 ;for (int i = 0 ; i <= end && end < nums.length - 1 ; ++i) {if (i == end) {return result;
方法二:反向查找 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution {public int jump (int [] nums) {int position = nums.length - 1 ;int steps = 0 ;while (position > 0 ) {for (int i = 0 ; i < position; i++) {if (i + nums[i] >= position) {break ;return steps;
9.8 K次取反后最大化的数组和 方法一:分情况讨论 按照「负数从小到大的顺序进行取反」。
对取反次数 k 和 负数个数 cnt 进行分情况讨论:
k <=cnt :按照负数从小到大的顺序进行取反即可;k >cn t :按照负数从小到大的顺序进行取反后,根据「是否存在 0 值」和「剩余取反次数的奇偶性」进行分情况讨论:
存在 0 值 或 剩余取反次数为偶数:直接返回当前取反数组的总和( 0 值可抵消任意次数的取反操作,将偶数次的取反操作应用在同一数值上,结果不变);
不存在 0 值且剩余取反次数为奇数:此时从当前数值中取一个绝对值最小值(使用 id x 记录该值下标)进行取反,得到最终的取反数组。
最后对取反数组进行求和操作即可。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 class Solution {public int largestSumAfterKNegations (int [] nums, int k) {int n = nums.length, idx = 0 ;new PriorityQueue <>((a,b)->nums[a]-nums[b]);boolean zero = false ;for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) {if (nums[i] < 0 ) q.add(i);if (nums[i] == 0 ) zero = true ;if (Math.abs(nums[i]) < Math.abs(nums[idx])) idx = i;if (k <= q.size()) {while (k-- > 0 ) nums[q.peek()] = -nums[q.poll()];else {while (!q.isEmpty() && k-- > 0 ) nums[q.peek()] = -nums[q.poll()];if (!zero && k % 2 != 0 ) nums[idx] = -nums[idx];int ans = 0 ;for (int i : nums) ans += i;return ans;class Solution {public int largestSumAfterKNegations (int [] nums, int k) {int ans = 0 ;int count = 0 ;for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length && nums[i] < 0 ; i++) {if (count >= k) {for (int i = 0 ; i < k; i++) {1 ;for (int num: nums) {else if (count < k) {for (int i = 0 ; i < count; i++) {1 ;if (k % 2 != 0 ) {if (count == nums.length || nums[count] != 0 ) {0 ] *= -1 ;for (int num: nums) {return ans;class Solution {public int largestSumAfterKNegations (int [] nums, int k) {if (nums.length == 1 ) return nums[0 ];for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length && k > 0 ; i++) { if (nums[i] < 0 ) {if (k % 2 == 1 ) { 0 ] = -nums[0 ];int sum = 0 ;for (int num : nums) { return sum;
方法二:排序后按照统一规则处理 那么本题的解题步骤为:
第一步:将数组按照绝对值大小从大到小排序,注意要按照绝对值的大小
第二步:从前向后遍历,遇到负数将其变为正数,同时K–
第三步:如果K还大于0,那么反复转变数值最小的元素,将K用完
第四步:求和
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution {public int largestSumAfterKNegations (int [] nums, int K) {int len = nums.length; for (int i = 0 ; i < len; i++) {if (nums[i] < 0 && K > 0 ) {if (K % 2 == 1 ) nums[len - 1 ] = -nums[len - 1 ];return Arrays.stream(nums).sum();
9.9 加油站 方法一:利用每个站点的剩余油量 首先如果总油量减去总消耗大于等于零那么一定可以跑完一圈,说明 各个站点的加油站 剩油量rest[i]相加一定是大于等于零的。
每个加油站的剩余量rest[i]为gas[i] - cost[i]。
i从0开始累加rest[i],和记为curSum,一旦curSum小于零,说明[0, i]区间都不能作为起始位置,因为这个区间选择任何一个位置作为起点,到i这里都会断油,那么起始位置从i+1算起,再从0计算curSum。
反证:
那有没有可能 [0,i] 区间 选某一个作为起点,累加到 i这里 curSum是不会小于零呢? 如图:
如果 curSum<0 说明 区间和1 + 区间和2 < 0, 那么 假设从上图中的位置开始计数curSum不会小于0的话,就是 区间和2>0。
区间和1 + 区间和2 < 0 同时 区间和2>0,只能说明区间和1 < 0, 那么就会从假设的箭头初就开始从新选择起始位置了。
那么局部最优:当前累加rest[i]的和curSum一旦小于0,起始位置至少要是i+1,因为从i之前开始一定不行。全局最优:找到可以跑一圈的起始位置 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution {public int canCompleteCircuit (int [] gas, int [] cost) {int [] used = new int [gas.length];for (int i = 0 ; i < gas.length; i++) {int start = 0 ;int curNum = 0 ;int totalNum = 0 ;for (int i = 0 ; i < used.length; i++) {if (curNum < 0 ) {1 ;0 ;if (totalNum < 0 ) return -1 ;return start;
方法二:规则怪谈 直接从全局进行贪心选择,情况如下:
情况一:如果gas的总和小于cost总和,那么无论从哪里出发,一定是跑不了一圈的
情况二:rest[i] = gas[i]-cost[i]为一天剩下的油,i从0开始计算累加到最后一站,如果累加没有出现负数,说明从0出发,油就没有断过,那么0就是起点。
情况三:如果累加的最小值是负数,汽车就要从非0节点出发,从后向前,看哪个节点能把这个负数填平,能把这个负数填平的节点就是出发节点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 class Solution {public int canCompleteCircuit (int [] gas, int [] cost) {int sum = 0 ;int min = 0 ;for (int i = 0 ; i < gas.length; i++) {if (sum < 0 ) return -1 ;if (min >= 0 ) return 0 ;for (int i = gas.length - 1 ; i > 0 ; i--) {if (min >= 0 ) return i;return -1 ;class Solution {public :int canCompleteCircuit (vector<int >& gas, vector<int >& cost) {int curSum = 0 ;int min = INT_MAX; for (int i = 0 ; i < gas.size(); i++) {int rest = gas[i] - cost[i];if (curSum < min) {if (curSum < 0 ) return -1 ; if (min >= 0 ) return 0 ; for (int i = gas.size() - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) {int rest = gas[i] - cost[i];if (min >= 0 ) {return i;return -1 ;
9.10 分发糖果 这道题目一定是要确定一边之后,再确定另一边,例如比较每一个孩子的左边,然后再比较右边,如果两边一起考虑一定会顾此失彼 。
如果 ratings[i] > ratings[i + 1],此时candyVec[i](第i个小孩的糖果数量)就有两个选择了,一个是candyVec[i + 1] + 1(从右边这个加1得到的糖果数量),一个是candyVec[i](之前比较右孩子大于左孩子得到的糖果数量)。
那么又要贪心了,局部最优:取candyVec[i + 1] + 1 和 candyVec[i] 最大的糖果数量,保证第i个小孩的糖果数量既大于左边的也大于右边的。全局最优:相邻的孩子中,评分高的孩子获得更多的糖果。
局部最优可以推出全局最优。
所以就取candyVec[i + 1] + 1 和 candyVec[i] 最大的糖果数量,candyVec[i]只有取最大的才能既保持对左边candyVec[i - 1]的糖果多,也比右边candyVec[i + 1]的糖果多 。
那么本题我采用了两次贪心的策略 :
一次是从左到右遍历,只比较右边孩子评分比左边大的情况。
一次是从右到左遍历,只比较左边孩子评分比右边大的情况。
这样从局部最优推出了全局最优,即:相邻的孩子中,评分高的孩子获得更多的糖果。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution {public int candy (int [] ratings) {int [] candy = new int [ratings.length];int sum = 0 ;if (ratings.length == 1 ) return 1 ;for (int i = 0 ; i < candy.length; i++) candy[i] = 1 ;for (int i = 1 ; i < candy.length; i++) {if (ratings[i] > ratings[i - 1 ]) {1 ] + 1 ;for (int i = candy.length - 2 ; i >= 0 ; i--) {if (ratings[i] > ratings[i + 1 ]) {1 ] + 1 , candy[i]);for (int c: candy) {return sum;
9.11 根据身高重建队列 那么按照身高h来排序呢,身高一定是从大到小排(身高相同的话则k小的站前面),让高个子在前面。
此时我们可以确定一个维度了,就是身高,前面的节点一定都比本节点高!
那么只需要按照k为下标重新插入队列就可以了,为什么呢?
以图中{5,2} 为例:
按照身高排序之后,优先按身高高的people的k来插入,后序插入节点也不会影响前面已经插入的节点,最终按照k的规则完成了队列。
所以在按照身高从大到小排序后:
局部最优:优先按身高高的people的k来插入。插入操作过后的people满足队列属性
全局最优:最后都做完插入操作,整个队列满足题目队列属性
排序完的people: [[7,0], [7,1], [6,1], [5,0], [5,2], [4,4]]
插入的过程:
插入[7,0]:[[7,0]]
插入[7,1]:[[7,0],[7,1]]
插入[6,1]:[[7,0],[6,1],[7,1]]
插入[5,0]:[[5,0],[7,0],[6,1],[7,1]]
插入[5,2]:[[5,0],[7,0],[5,2],[6,1],[7,1]]
插入[4,4]:[[5,0],[7,0],[5,2],[6,1],[4,4],[7,1]]
使用链表类型List(LinkedList)比ArrayList效率高,因为ArrayList插入需要扩容操作。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution {public int [][] reconstructQueue(int [][] people) {if (a[0 ] == b[0 ]) return a[1 ] - b[1 ]; return b[0 ] - a[0 ]; int []> que = new LinkedList <>();for (int [] p : people) {1 ],p); return que.toArray(new int [people.length][]);
9.12 区间选点,选择最少的点覆盖所有区间 方法一:排序右端点
参考ACwing905:区间选点
将每个区间按照右端点从小到大进行排序
从前往后枚举区间,end值初始化为无穷小
如果本次区间不能覆盖掉上次区间的右端点, ed < range[i].l
说明需要选择一个新的点, res ++ ; ed = range[i].r;
如果本次区间可以覆盖掉上次区间的右端点,则进行下一轮循环
时间复杂度 O(nlogn)
证明
证明ans<=cnt :cnt 是一种可行方案, ans是可行方案的最优解,也就是最小值。
证明ans>=cnt : cnt可行方案是一个区间集合,区间从小到大排序,两两之间不相交。
所以覆盖每一个区间至少需要cnt个点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution {public int findMinArrowShots (int [][] points) {1 ], b[1 ]));long end = Long.MIN_VALUE;int count = 0 ;for (int [] point: points) {if (end < point[0 ]) {1 ];return count;
方法二:排序左端点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution {public int findMinArrowShots (int [][] points) {0 ], b[0 ]));int count = 1 ; for (int i = 1 ; i < points.length; i++) {if (points[i][0 ] > points[i - 1 ][1 ]) { else { 1 ] = Math.min(points[i][1 ], points[i - 1 ][1 ]); return count;
9.13 最大不相交区间的数量 无重叠区间即最大不相交区间的数量,可以转化为区间选点问题,两者本质是一样的。
思路即是按照右端点从小到大排序,不断寻找右端点最小且与之前的区间无交集的那个区间,然后结果加1,得到最终答案。
详细思路见https://leetcode.cn/problems/non-overlapping-intervals/solutions/541543/wu-zhong-die-qu-jian-by-leetcode-solutio-cpsb。
我们可以不断地寻找右端点在首个区间右端点左侧的新区间,将首个区间替换成该区间。那么当我们无法替换时,首个区间就是所有可以选择的区间中右端点最小的那个区间。因此我们将所有区间按照右端点从小到大进行排序,那么排完序之后的首个区间,就是我们选择的首个区间。
如果有多个区间的右端点都同样最小怎么办?由于我们选择的是首个区间,因此在左侧不会有其它的区间,那么左端点在何处是不重要的,我们只要任意选择一个右端点最小的区间即可。
当确定了首个区间之后,所有与首个区间不重合的区间就组成了一个规模更小的子问题。由于我们已经在初始时将所有区间按照右端点排好序了,因此对于这个子问题,我们无需再次进行排序,只要找出其中与首个区间不重合并且右端点最小的区间即可。用相同的方法,我们可以依次确定后续的所有区间。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution {public int eraseOverlapIntervals (int [][] intervals) {1 ], b[1 ]));int end = Integer.MIN_VALUE;int count = 0 ;for (int [] interval: intervals) {if (interval[0 ] >= end) {1 ];return intervals.length - count;
本题也可左端点排序
9.14 划分字母区间 模拟题,感觉不算贪心,只需要找到每个字母对应的最远位置下标,在遍历的过程中不断更新更远的下标,直到当前遍历的元素下标==记录的最远的下标,此时一个区间完毕。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution {public List<Integer> partitionLabels (String s) {new ArrayList <>();int [] edge = new int [26 ];char [] chars = s.toCharArray();for (int i = 0 ; i < chars.length; i++) {'a' ] = i;int index = 0 ;int cover = 0 ;for (int i = 0 ; i < chars.length; i++) {'a' ], cover);if (i == cover) {1 );1 ;return ans;
9.15 合并区间 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution {public int [][] merge(int [][] intervals) {int []> res = new LinkedList <>();0 ], y[0 ]));int start = intervals[0 ][0 ];int rightmostRightBound = intervals[0 ][1 ];for (int i = 1 ; i < intervals.length; i++) {if (intervals[i][0 ] > rightmostRightBound) {new int []{start, rightmostRightBound});0 ];1 ];else {1 ]);new int []{start, rightmostRightBound});return res.toArray(new int [res.size()][]);
9.16 监控二叉树(hard) 下次再刷
10. 动态规划 1. DP理论基础 动态规划五步曲
确定dp数组(dp table)以及下标的含义
确定递推公式
dp数组如何初始化
确定遍历顺序
举例推导dp数组
关键点 :
确定状态 (dp数组的含义)与状态转移方程 (dp数组怎么由前面的dp推理得到)
记忆化搜索:
递归搜索+保存计算结果=记忆化搜索
时间复杂度计算:
状态个数*单个状态的计算时间
记忆化搜索和递推的区别
自顶向下算=记忆化搜索(递归树的记录做剪枝)
自底向上算=递推
把dfs函数 改为数组 ,把递归 改为循环
2. 背包问题
2.1 01背包 1. 题目介绍
有 N 件物品和一个容量为 V 的背包,每件物品有各自的价值且只能被选择一次,要求在有限的背包容量下,装入的物品总价值最大。
2.解题思路
2.1 二维dp数组
dp数组:$dp[i][j]$
状态转移函数:$dp[i][j]=max(dp[i-1][j], dp[i-1][j-v[i]]+w[i])$
dp数组含义解析:前$i$个物体,存储在体积为j的背包中的最大价值
dp数组初始化:$dp[0][0]=0$
遍历顺序:先遍历物体,再遍历背包体积
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 import java.util.*;public class Main {public static void main (String[] args) {Scanner scan = new Scanner (System.in);int n = scan.nextInt(), m = scan.nextInt();int [][] dp = new int [n + 1 ][m + 1 ];int [] w = new int [n + 1 ];int [] v = new int [n + 1 ];for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) {for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) {for (int j = 1 ; j <= m; j++) {1 ][j];if (j >= v[i]) dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i][j], dp[i - 1 ][j - v[i]] + w[i]);
2.2 **一维dp数组:优化空间(滚动数组) **
dp数组:$dp[j]$
状态转移函数:$dp[j]=max(dp[j], dp[j-v[i]]+w[i])$
dp数组含义解析:前$i$个物体(i在遍历过程中体现),存储在体积为j的背包中的最大价值
dp数组初始化:$dp[0]=0$
遍历顺序:先遍历物体,再遍历背包体积(倒序遍历)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 import java.util.*;public class Main {public static void main (String[] args) {Scanner scan = new Scanner (System.in);int n = scan.nextInt(), m = scan.nextInt();int [] dp = new int [m + 1 ];int [] w = new int [n + 1 ];int [] v = new int [n + 1 ];for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) {for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) {for (int j = m; j >= v[i]; j--) {
2.2 完全背包
当问题为组合问题时:先遍历物品,再遍历背包
当问题为排列问题时:先遍历背包,再遍历物品
2.解题思路
2.1 二维dp数组
dp数组:$dp[i][j]$
状态转移函数:$dp[i][j]=max(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-v[i]]+w[i])$
dp数组含义解析:前$i$个物体,存储在体积为j的背包中的最大价值
dp数组初始化:$dp[0][0]=0$
遍历顺序:先遍历物体,再遍历背包体积
2.2 **一维dp数组:优化空间(滚动数组) **
dp数组:$dp[j]$
状态转移函数:$dp[j]=max(dp[j], dp[j-v[i]]+w[i])$
dp数组含义解析:前$i$个物体(i在遍历过程中体现),存储在体积为j的背包中的最大价值
dp数组初始化:$dp[0]=0$
遍历顺序:先遍历物体,再遍历背包体积(正序遍历)
2.3 多重背包 可以拆解为01背包问题。
二维dp数组的情况下,使用三重循环,第三重负责枚举使用了0~k个物体.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;const int N = 110 ;int n, m;int v[N], w[N], s[N];int dp[N][N];int main () for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++)for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++)for (int j = 0 ; j <= m; j++ )for (int k = 0 ; k <= s[i] && k * v[i] <= j; k++)max (dp[i][j], dp[i - 1 ][j - k * v[i]] + k * w[i]);return 0 ;
Java版
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 import java.util.*;public class Main {public static void main (String[] argc) {Scanner scan = new Scanner (System.in);int n = scan.nextInt();int m = scan.nextInt();int [] v = new int [n + 1 ];int [] w = new int [n + 1 ];int [] s = new int [n + 1 ];for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) {int [][] dp = new int [n + 1 ][m + 1 ];for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) {for (int j = 1 ; j <= m; j++) {for (int k = 0 ; k <= s[i] && j - k * v[i] >= 0 ; k++) {1 ][j - k * v[i]] + k * w[i]);
可以在空间上优化为一维
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 import java.util.*;public class Main {public static void main (String [] args) {Scanner sc = new Scanner (System.in);int bagWeight, n;int [] weight = new int [n];int [] value = new int [n];int [] nums = new int [n];for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) weight[i] = sc.nextInt();for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) value[i] = sc.nextInt();for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) nums[i] = sc.nextInt();int [] dp = new int [bagWeight + 1 ];for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) {for (int j = bagWeight; j >= weight[i]; j--) {for (int k = 1 ; k <= nums[i] && (j - k * weight[i]) >= 0 ; k++) {
3.可以使用二进制优化
把每种物品的数量,打包成一个个独立的包。
把一个拥有s个的物体,可以拆分为$log_2(s)$份。
复杂度从$n$降为$log(n)$。
接下来,我介绍一个二进制优化的方法,假设有一组商品,一共有11个。我们知道,十进制数字 11 可以这样表示
正常背包的思路下,我们要求出含这组商品的最优解,我们要枚举12次(枚举装0,1,2….12个)。
现在,如果我们把这11个商品分别打包成含商品个数为1个,2个,4个,4个(分别对应0001,0010,0100,0100)的四个”新的商品 “, 将问题转化为01背包问题,对于每个商品,我们都只枚举一次,那么我们只需要枚举四次 ,就可以找出这含组商品的最优解。 这样就大大减少了枚举次数。
这种优化对于大数尤其明显,例如有1024个商品,在正常情况下要枚举1025次 , 二进制思想下转化成01背包只需要枚举10次。
一个物品有s件,则将其拆分为1、2、4、8、……
即($2^0, 2^1, 2^2,…$),拆分的包的个数为$⌈log_2s⌉$,由于包的总和不能超过s,如果s不是2的整次幂-1,则最后一个数不为2的某个整次幂,为$s-1-2-4-8-…$直到s为大于0的最小值为止,此时为最后一个包的大小。
比如10:拆分为1、2、4、3(10-1-2-4 = 3)
然后将拆分的包作为单独的一个物体,使用01背包求解即可。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std;const int N = 25000 ;int f[N], v[N], w[N];int n, m;int main () int cnt = 0 ;for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i ++){int a, b, s;int k = 1 ;while (k <= s){2 ;if (s > 0 ){for (int i = 1 ; i <= cnt; i ++){for (int j = m; j >= v[i]; j --){max (f[j], f[j - v[i]] + w[i]);return 0 ;
2.4 疑难问题
377.组合总和iv:看似为完全背包的排列类问题,实际上可以看成是爬楼梯,用一维dp数组的含义来思考,不要被完全背包的套路束缚
下面是一种二维dp的理解方法:
https://leetcode.cn/problems/combination-sum-iv/solutions/2663854/zu-he-zong-he-ivshu-xue-tui-dao-xian-gou-ap8y
3. 线性DP dp[i][j]的含义:
求连续子数组:以s[i]结尾和以t[j]结尾(最终结果可能不是dp[n][m])
求子序列:1~A[i]和1~B[j](最终结果是dp[n][m])
3.1 最长递增子序列 解法1:贪心+二分
lowerbound(x):大于等于x(≥x)的第一个数的下标位置
upperbound(x):大于x(>x)的第一个数的下标位置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution {public int lengthOfLIS (int [] nums) {new ArrayList <>();for (int num: nums) {int index = lowerbound(g, num);if (index == g.size()) {else {return g.size();public int lowerbound (List<Integer> nums, int target) {int left = 0 , right = nums.size();while (left < right) {int mid = left + (right - left)/2 ;if (nums.get(mid) < target) {1 ;else {return left;
解法2:动态规划 dp [i ] 表示以 nums [i ] 结尾的最长递增子序列(LIS)的长度。
dp[i]表示i之前包括i的以nums[i]结尾的最长递增子序列的长度
状态转移方程
位置i的最长升序子序列等于j从0到i-1各个位置的最长升序子序列 + 1 的最大值。
$if (nums[i] > nums[j]) dp[i] = max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1);$
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution {public int lengthOfLIS (int [] nums) {int n = nums.length;int [] dp = new int [n];int ans = 1 ;1 );for (int i = 1 ; i < n; i++) {for (int j = 0 ; j < i; j++) {if (nums[j] < nums[i]) {1 );if (dp[i] > ans) ans = dp[i];return ans;
3.2 最长公共子序列
**dp[i][j]**:长度为[0, i - 1]的字符串text1与长度为[0, j - 1]的字符串text2的最长公共子序列为dp[i][j]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution {public int longestCommonSubsequence (String text1, String text2) {int len1 = text1.length();int len2 = text2.length();int [][] dp = new int [len1 + 1 ][len2 + 2 ];char [] text1Arr = text1.toCharArray();char [] text2Arr = text2.toCharArray();for (int i = 1 ;i <= len1;i++){for (int j = 1 ;j <= len2;j++){if (text1Arr[i - 1 ] == text2Arr[j - 1 ])1 ][j - 1 ] + 1 ;else 1 ],dp[i - 1 ][j]);return dp[len1][len2];
3.3 编辑距离
条件转移方程:
$s[i] == s[j]$: $dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1]$
$s[i] ≠ s[j]$: $dp[i][j] = min(dp[i-1][j],dp[i][j-1],dp[i-1][j-1])+1$
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution {public int minDistance (String word1, String word2) {char [] ca1 = word1.toCharArray();char [] ca2 = word2.toCharArray();int [][] dp = new int [ca1.length+1 ][ca2.length+1 ];for (int i = 0 ;i <= ca1.length;i++){0 ] = i;for (int j = 0 ;j <= ca2.length;j++){0 ][j] = j;for (int i = 1 ;i <= ca1.length;i++){for (int j = 1 ;j <= ca2.length;j++){if (ca1[i-1 ] == ca2[j-1 ]){1 ][j-1 ];else {1 ][j],dp[i][j-1 ]),dp[i-1 ][j-1 ])+1 ;return dp[ca1.length][ca2.length];
3.4 数字金字塔 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 import java.util.*;public class Main {public static void main (String[] args) {Scanner scan = new Scanner (System.in);int N = 501 ;int [][] a = new int [N][N];int [][] dp = new int [N][N];int n = scan.nextInt();for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) {for (int j = 1 ; j <= i; j++) {for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) {for (int j = 0 ; j <= i + 1 ; j++) {1 ][1 ] = a[1 ][1 ];for (int i = 2 ; i <= n; i++) {for (int j = 1 ; j <= i; j++) {1 ][j - 1 ], dp[i - 1 ][j]) + a[i][j];int result = Integer.MIN_VALUE;for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) {
4. 区间DP 4.1 回文子串个数 状态:
dp[i][j]为下标为i-1~j-1的子串是否为回文串,是为1,否为0.
状态转移方程:
$s[i]==s[j] \ &\ dp[i+1][j-1] == 1$, 则有$dp[i][j] = 1$
否则$dp[i][j] = 0$
遍历顺序1:
由于是从两边向中间缩放,计算外侧的dp需要内侧dp值已知,则遍历顺序按照长度可以如下:
首先初始化长度 为1和2的子串:dp[i][i]=1, if(s[i]==s[i+1]) dp[i][i+1]=1
再依次遍历长度为3、4……的子串
最后,在统计的过程中计数回文串个数即可。
代码实现1:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution {public int countSubstrings (String s) {int n = s.length();char [] ss = s.toCharArray();int [][] dp = new int [n][n];int result = 0 ;for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) {1 ;for (int i = 0 ; i < n - 1 ; i ++) {if (ss[i] == ss[i + 1 ]) {1 ] = 1 ;for (int len = 3 ; len <= n; len++) {for (int i = 0 ; i + len - 1 < n; i++) {int j = i + len - 1 ;1 ][j - 1 ] == 1 ) ? 1 : 0 ;if (dp[i][j] == 1 ) result++;return result;
遍历顺序2: 从下到上,从左到右
在确定递推公式时,就要分析如下几种情况。
整体上是两种,就是s[i]与s[j]相等,s[i]与s[j]不相等这两种。
当s[i]与s[j]不相等,那没啥好说的了,dp[i][j]一定是false。
当s[i]与s[j]相等时,这就复杂一些了,有如下三种情况
情况一:下标i 与 j相同,同一个字符例如a,当然是回文子串
情况二:下标i 与 j相差为1,例如aa,也是回文子串
情况三:下标:i 与 j相差大于1的时候,例如cabac,此时s[i]与s[j]已经相同了,我们看i到j区间是不是回文子串就看aba是不是回文就可以了,那么aba的区间就是 i+1 与 j-1区间,这个区间是不是回文就看dp[i + 1][j - 1]是否为true。
首先从递推公式中可以看出,情况三是根据dp[i + 1][j - 1]是否为true,在对dp[i][j]进行赋值true的。
dp[i + 1][j - 1] 在 dp[i][j]的左下角,如图:
如果这矩阵是从上到下,从左到右遍历,那么会用到没有计算过的dp[i + 1][j - 1],也就是根据不确定是不是回文的区间[i+1,j-1],来判断了[i,j]是不是回文,那结果一定是不对的。
所以一定要从下到上,从左到右遍历,这样保证dp[i + 1][j - 1[j - 1]都是经过计算的 。
有的代码实现是优先遍历列,然后遍历行,其实也是一个道理,都是为了保证dp[i + 1][j - 1[j - 1]都是经过计算的。
代码实现2:
举例,输入:”aaa”,dp[i][j]状态如下:
图中有6个true,所以就是有6个回文子串。
注意因为dp[i][j]的定义,所以j一定是大于等于i的,那么在填充dp[i][j]的时候一定是只填充右上半部分 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 class Solution {public int countSubstrings (String s) {char [] chars = s.toCharArray();int len = chars.length;boolean [][] dp = new boolean [len][len];int result = 0 ;for (int i = len - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) {for (int j = i; j < len; j++) {if (chars[i] == chars[j]) {if (j - i <= 1 ) { true ;else if (dp[i + 1 ][j - 1 ]) { true ;return result;class Solution {public int countSubstrings (String s) {boolean [][] dp = new boolean [s.length()][s.length()];int res = 0 ;for (int i = s.length() - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) {for (int j = i; j < s.length(); j++) {if (s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j) && (j - i <= 1 || dp[i + 1 ][j - 1 ])) {true ;return res;
中心扩散法
动态规划的空间复杂度是偏高的,我们再看一下双指针法。
首先确定回文串,就是找中心然后向两边扩散看是不是对称的就可以了。
在遍历中心点的时候,要注意中心点有两种情况 。
一个元素可以作为中心点,两个元素也可以作为中心点。
那么有人同学问了,三个元素还可以做中心点呢。其实三个元素就可以由一个元素左右添加元素得到,四个元素则可以由两个元素左右添加元素得到。
所以我们在计算的时候,要注意一个元素为中心点和两个元素为中心点的情况。
这两种情况可以放在一起计算,但分别计算思路更清晰,我倾向于分别计算 ,代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution {public int countSubstrings (String s) {int len, ans = 0 ;if (s == null || (len = s.length()) < 1 ) return 0 ;for (int i = 0 ; i < 2 * len - 1 ; i++) {int left = i / 2 , right = left + i % 2 ;while (left >= 0 && right < len && s.charAt(left) == s.charAt(right)) {return ans;
4.2 最长回文子序列
确定dp数组(dp table)以及下标的含义
**dp[i][j]:字符串s在[i, j]范围内最长的回文子序列的长度为dp[i][j]**。
确定递推公式
在判断回文子串的题目中,关键逻辑就是看s[i]与s[j]是否相同。
如果s[i]与s[j]相同,那么dp[i][j] = dp[i + 1][j - 1] + 2;
如图:
如果s[i]与s[j]不相同,说明s[i]和s[j]的同时加入 并不能增加[i,j]区间回文子序列的长度,那么分别加入s[i]、s[j]看看哪一个可以组成最长的回文子序列。
加入s[j]的回文子序列长度为dp[i + 1][j]。
加入s[i]的回文子序列长度为dp[i][j - 1]。
那么dp[i][j]一定是取最大的,即:dp[i][j] = max(dp[i + 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);
dp数组如何初始化
首先要考虑当i 和j 相同的情况,从递推公式:dp[i][j] = dp[i + 1][j - 1] + 2; 可以看出 递推公式是计算不到 i 和j相同时候的情况。
所以需要手动初始化一下,当i与j相同,那么dp[i][j]一定是等于1的,即:一个字符的回文子序列长度就是1。
其他情况dp[i][j]初始为0就行,这样递推公式:dp[i][j] = max(dp[i + 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]); 中dp[i][j]才不会被初始值覆盖。
确定遍历顺序
从递归公式中,可以看出,dp[i][j]依赖于 dp[i + 1][j - 1] ,dp[i + 1][j] 和 dp[i][j - 1],如图:
所以遍历i的时候一定要从下到上遍历,这样才能保证下一行的数据是经过计算的 。
j的话,可以正常从左向右遍历。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution {public int longestPalindromeSubseq (String s) {int n = s.length();char [] ss = s.toCharArray();int len = 0 ;int [][] dp = new int [n + 1 ][n + 1 ];for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) dp[i][i] = 1 ;for (int i = n - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) {for (int j = i + 1 ; j < n; j++) {if (ss[i] == ss[j]) {1 ][j - 1 ] + 2 ;else {1 ][j], dp[i][j - 1 ]);return dp[0 ][n - 1 ];
5. 状态机DP 一般定义$f[i][j]$表示前缀$a[:i]$在状态$j$下的最优值。一般$j$都很小。代表题目是「买卖股票」系列。
注:某些题目做法不止一种,除了状态机 DP 以外,也有前后缀分解的做法。
5.1 买卖股票Ⅱ(交易次数不限)
代码实现:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution {public int maxProfit (int [] prices) {int n = prices.length;int [][] dp = new int [n + 1 ][2 ];0 ][0 ] = 0 ;0 ][1 ] = -prices[0 ];for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) {0 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][0 ], dp[i - 1 ][1 ] + prices[i - 1 ]);1 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][1 ], dp[i - 1 ][0 ] - prices[i - 1 ]);return dp[n][0 ];
空间优化:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution {public int maxProfit (int [] prices) {int n = prices.length;int f0 = 0 ;int f1 = -prices[0 ];for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) {int new_f0 = Math.max(f0, f1 + prices[i]);return f0;
5.2 买卖股票Ⅲ(交易两次) 可以用三维dp数组实现,也可用二维dp(状态机)
代码实现:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution {public int maxProfit (int [] prices) {int n = prices.length;int [][] dp = new int [n + 1 ][5 ];0 ], Integer.MIN_VALUE/2 );for (int j = 0 ; j < 5 ; j += 2 ) {0 ][j] = 0 ;for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) {0 ] = dp[i - 1 ][0 ];1 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][1 ], dp[i - 1 ][0 ] - prices[i - 1 ]);2 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][2 ], dp[i - 1 ][1 ] + prices[i - 1 ]);3 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][3 ], dp[i - 1 ][2 ] - prices[i - 1 ]);4 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][4 ], dp[i - 1 ][3 ] + prices[i - 1 ]); return dp[n][4 ];
空间优化:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution {public int maxProfit (int [] prices) {int buys1 = Integer.MIN_VALUE, sell1 = 0 ;int buys2 = Integer.MIN_VALUE, sell2 = 0 ;for (int price: prices) {return sell2;
5.3 买卖股票Ⅳ(交易k次) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution {public int maxProfit (int k, int [] prices) {int n = prices.length;int [][] dp = new int [n + 1 ][2 * k + 1 ];0 ], Integer.MIN_VALUE/2 );for (int j = 0 ; j < 2 * k + 1 ; j += 2 ) {0 ][j] = 0 ;for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) {for (int j = 1 ; j < 2 * k + 1 ; j++) {if (j % 2 == 0 ) {1 ][j], dp[i- 1 ][j - 1 ] + prices[i - 1 ]);else {1 ][j], dp[i - 1 ][j - 1 ] - prices[i - 1 ]);return dp[n][2 * k];
5.4 买卖股票含冷冻期 将买入时的操作由i-1变为i-2。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution {public int maxProfit (int [] prices) {int n = prices.length;int [][] dp = new int [n + 2 ][2 ];0 ][0 ] = 0 ;0 ][1 ] = -prices[0 ];1 ][1 ] = -prices[0 ];for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) {2 ][0 ] = Math.max(dp[i + 1 ][0 ], dp[i + 1 ][1 ] + prices[i]);2 ][1 ] = Math.max(dp[i + 1 ][1 ], dp[i][0 ] - prices[i]);return dp[n + 1 ][0 ];class Solution {public int maxProfit (int [] prices) {int n = prices.length;int [][] f = new int [n][2 ];0 ][1 ] = -prices[0 ];for (int i = 1 ; i < n; i++) {0 ] = Math.max(f[i - 1 ][0 ], f[i - 1 ][1 ] + prices[i]);1 ] = Math.max(f[i - 1 ][1 ], (i > 1 ? f[i - 2 ][0 ] : 0 ) - prices[i]);return f[n - 1 ][0 ];
5.5 买卖股票含手续费 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution {public int maxProfit (int [] prices, int fee) {int n = prices.length;int [][] dp = new int [n][2 ];0 ][0 ] = 0 ;0 ][1 ] = -prices[0 ];for (int i = 1 ; i < n; i++) {0 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][0 ], dp[i - 1 ][1 ] + prices[i] - fee);1 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][1 ], dp[i - 1 ][0 ] - prices[i]);return dp[n - 1 ][0 ];
6. 树形DP 打家劫舍Ⅲ 通过树的遍历过程代替物品的遍历过程,dp数组对应于普通dp的一维dp数组模式。
后序遍历自底向上计算,逐步覆盖dp数组(重复利用上一层的dp状态)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 class Solution {public int rob (TreeNode root) {int [] nums = dfs(root);return Math.max(nums[0 ], nums[1 ]);public int [] dfs(TreeNode node) {if (node == null ) {return new int []{0 , 0 };int [] left = dfs(node.left);int [] right = dfs(node.right);int [] nums = new int [2 ];0 ] = Math.max(left[0 ], left[1 ]) + Math.max(right[0 ], right[1 ]);1 ] = node.val + left[0 ] + right[0 ];return nums;
7.记忆化搜索 11. 单调栈 什么时候用单调栈 :
通常是一维数组,要寻找任一个元素的右边或者左边第一个比自己大或者小的元素的位置,此时我们就要想到可以用单调栈了 。时间复杂度为O(n)。单调栈的本质是空间换时间 ,因为在遍历的过程中需要用一个栈来记录右边第一个比当前元素高的元素,优点是整个数组只需要遍历一次。
单调栈里存放的元素是什么?
单调栈里只需要存放元素的下标 i就可以了,如果需要使用对应的元素,直接T[i]就可以获取。
单调栈里元素是递增呢? 还是递减呢?
注意以下讲解中,顺序的描述为 从栈顶到栈底 的顺序 ,因为单纯的说从左到右或者从前到后,不说栈头朝哪个方向的话,大家一定比较懵。
这里我们要使用递增循序(再强调一下是指从栈头到栈底的顺序),因为只有递增的时候,栈里要加入一个元素i的时候,才知道栈顶元素在数组中右面第一个比栈顶元素大的元素是i。
即:如果求一个元素右边第一个更大元素,单调栈就是递增的,如果求一个元素右边第一个更小元素,单调栈就是递减的。
文字描述理解起来有点费劲,接下来我画了一系列的图,来讲解单调栈的工作过程,大家再去思考,本题为什么是递增栈。
使用单调栈主要有三个判断条件。
当前遍历的元素T[i]小于栈顶元素T[st.top()]的情况
当前遍历的元素T[i]等于栈顶元素T[st.top()]的情况
当前遍历的元素T[i]大于栈顶元素T[st.top()]的情况
把这三种情况分析清楚了,也就理解透彻了 。
自己的理解:
寻找右边第一个比自己大的元素:
按照从栈底到栈顶的顺序,需要递减,即放入的元素必须比栈顶元素小,大于栈顶元素则把栈顶元素推出再填入
只有单调栈递增(从栈口到栈底顺序),就是求右边第一个比自己大的,单调栈递减的话,就是求右边第一个比自己小的。
11.1 每日温度 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution {public int [] dailyTemperatures(int [] temperatures) {new ArrayDeque <>();int n = temperatures.length;int [] answer = new int [n];for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) {while (!st.isEmpty() && temperatures[i] > temperatures[st.peek()]) {return answer;
11.2 下一个更大元素 I 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution {public int [] nextGreaterElement(int [] nums1, int [] nums2) {int n = nums1.length, m = nums2.length;new HashMap <>();for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) {int [] ans = new int [n];1 );new ArrayDeque <>();for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i++) {while (!st.isEmpty() && nums2[st.peek()] < nums2[i]) {int pre = nums2[st.pop()];if (map.containsKey(pre)) {return ans;
11.3 下一个更大元素 Ⅱ 在遍历的过程中模拟走了两边nums
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution {public int [] nextGreaterElements(int [] nums) {int n = nums.length;int [] ans = new int [n];new ArrayDeque <>();1 );for (int i = 0 ; i < n * 2 ; i++) {while (!st.isEmpty() && nums[st.peek()] < nums[i % n]) {return ans;
11.4 接雨水 解法1:单调栈 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 class Solution {public int trap (int [] height) {int n = height.length;int sum = 0 ;new ArrayDeque <>();0 );for (int i = 1 ; i < n; i++) {while (!st.isEmpty() && height[st.peek()] <= height[i]) {int mid = st.pop();if (!st.isEmpty()) {int h = Math.min(height[st.peek()], height[i]) - height[mid];int w = i - st.peek() - 1 ;return sum;class Solution {public int trap (int [] height) {int size = height.length;if (size <= 2 ) return 0 ;new Stack <Integer>();0 );int sum = 0 ;for (int index = 1 ; index < size; index++){int stackTop = stack.peek();if (height[index] < height[stackTop]){else if (height[index] == height[stackTop]){else {int heightAtIdx = height[index];while (!stack.isEmpty() && (heightAtIdx > height[stackTop])){int mid = stack.pop();if (!stack.isEmpty()){int left = stack.peek();int h = Math.min(height[left], height[index]) - height[mid];int w = index - left - 1 ;int hold = h * w;if (hold > 0 ) sum += hold;return sum;
解法2:双指针优化 双指针优化:
相当于动态规划方法的空间优化
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 class Solution {public int trap (int [] height) {if (height.length <= 2 ) {return 0 ;int maxLeft = height[0 ], maxRight = height[height.length - 1 ];int l = 1 , r = height.length - 2 ;int res = 0 ;while (l <= r) {if (maxLeft < maxRight) {else {return res;class Solution {public int trap (int [] height) {int ans = 0 ;int left = 0 ;int right = height.length - 1 ;int preMax = 0 ; int sufMax = 0 ; while (left < right) {return ans;
解释:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 def trap (self, height: List [int ] ) -> int :len (height)1 2 0 0 0 while (left <= right):max (lmax, height[left - 1 ])max (rmax, height[right + 1 ])if lmax >= rmax:if rmax > height[right]:1 elif lmax < rmax:if lmax > height[left]:1 return result
解法3:动态规划 记录左边柱子的最高高度 和 右边柱子的最高高度,就可以计算当前位置的雨水面积,这就是通过列来计算。
当前列雨水面积:min(左边柱子的最高高度,记录右边柱子的最高高度) - 当前柱子高度。
为了得到两边的最高高度,使用了双指针来遍历,每到一个柱子都向两边遍历一遍,这其实是有重复计算的。我们把每一个位置的左边最高高度记录在一个数组上(maxLeft),右边最高高度记录在一个数组上(maxRight),这样就避免了重复计算。
当前位置,左边的最高高度是前一个位置的左边最高高度和本高度的最大值。
即从左向右遍历:maxLeft[i] = max(height[i], maxLeft[i - 1]);
从右向左遍历:maxRight[i] = max(height[i], maxRight[i + 1]);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution {public int trap (int [] height) {int length = height.length;if (length <= 2 ) return 0 ;int [] maxLeft = new int [length];int [] maxRight = new int [length];0 ] = height[0 ];for (int i = 1 ; i< length; i++) maxLeft[i] = Math.max(height[i], maxLeft[i-1 ]);1 ] = height[length - 1 ];for (int i = length - 2 ; i >= 0 ; i--) maxRight[i] = Math.max(height[i], maxRight[i+1 ]);int sum = 0 ;for (int i = 0 ; i < length; i++) {int count = Math.min(maxLeft[i], maxRight[i]) - height[i];if (count > 0 ) sum += count;return sum;
11.5 柱状图中最大的矩形 12. 图论 HOT100